![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Projection |
Attempts to banish or disown unwanted and disliked thoughts, behaviors, and even "parts of self" by projecting it attributing them to someone else. |
Seeing and experiencing a repressed disowned part of self in another person. Everyone else is selfish. |
|
|
Introjection |
The opposite of projection--subconsciously takes in to self an imprint of another person including their attitudes, messages, prejudices, expressions, even the sound of their voice |
Helpful if imprinted material is helpful advice or lessons learned for parents. Unhealthy if shaming, hatred or aggression is turned inwardly on self. |
|
|
Identification |
An ability available very early in life that children use to attache themselves to certain qualities, emotions, and attitudes of someone else... Especially during the modeling period between 8 and 13 |
Want to be just like Dad or copying elder siblings. I'm creative says one client. |
|
|
Isolation |
Separation of memory from emotion... Can remember and talk about the trauma but feels no emotions. |
Person talks about incident as if it's someone else's story. |
|
|
Sublimation |
Redirection of impulses into socially acceptable activities normal and healthy. |
An aggressive person joining sports. |
|
|
Displacement |
Reduces anxiety or stress by transferring feelings towards one person to another. |
Someone is mad at boss so kicks cat. |
|
|
Repression |
Emotions, memories, impulses, or drives that are SUBCONSCIOUSLY pushed down. This takes a lot of mental energy that could be better elsewhere. |
Not remembering details of abuse. |
|
|
Suppression |
Emotions, memories, impulses, or drives that are CONSCIOUSLY pushed down. |
Not wanting to talk about abuse. |
|
|
Conversion |
Mental conflict converted to physical symptom |
Dr. Watson's limp is psychological |
|
|
Regression |
Giving up current level of development and going back to a prior level. |
An older child under stress begins wetting the bed. |
|
|
Reaction Formulation |
Over compensation for fear of the opposite. |
The macho man bully who is really a homosexual. |
|
|
Simple Denial |
Unpleasant facts, emotions, or events are treated at if they ate not real or don't exist. |
Next to normal |
|
|
Fantasy |
Retreating into a dream world of times past. Unhealthy if action is required, healthy when used to finish unfinished business from the past or for nostalgia. Extremely common |
When a relationship turns abusive thinking about when things were good instead of fixing the problem. |
|
|
Cognitive Dissonance |
2 cognitions are in direct conflict. (Usually conscious and unconscious) creates a lot of anxiety |
Being a soldier but believing you should never kill anyone |
|
|
Defense Mechanism |
Ability of subconscious mind to protect the conscious mind |
|
|
|
Somatization |
The transformation of uncomfortable feelings towards others into uncomfortable feelings towards oneself: pain, illness, and anxiety. |
Hypochondriac client |
|
|
Dissociation |
Temporary drastic modification of one's personal identity or character to avoid emotional distress. |
Putting on a mask so to speak. |
|
|
Magical thinking |
Attribution of causal relationships between actions and events which cannot be justified by reason or observation. |
Grandson is angry at grandmother and thinks that's why she died, now feels guilty. |
|
|
Preoperational |
Representing things with words and images. Pretend play, egocentrism, language development. |
2-6 years Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development |
|
|
Sensorimotor |
Experiencing the world through senses and actions. Object permanence, stranger anxiety. |
Birth-2 Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development |
|
|
Concrete Operational |
Thinking logically about concrete events and grasping concrete analogies. Conservation, mathematical transformation. |
7-11 Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development |
|
|
Formal Operation |
Thinking about hypothetical scenarios and processing abstract thoughts. Abstract logic, potential fit mature moral, reasoning. |
12-adulthood Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development |
|
|
Trust vs. Mistrust |
Children develop a sense of trust when caregivers provide reliability, care, and affection. Feeding |
Infancy 0-18 months Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Autonomy vs. shame and doubt |
Children need to develop a sense of personal control over physical skills and a sense of independence. Toilet training |
Early Childhood 2-3 Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Initiative vs. Guilt |
Children need to begin asserting control and power over environment. Success in this stage leads to sense of purpose, children who try to exert too much power experience disapproval leading to a sense of guilt. Exploration. |
Preschool 3-5 Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Industry vs. Inferiority |
Children need to cope with new social and academic demands. School. |
Adolescence 12-18 Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Intimacy vs. Isolation |
Young adults need to form intimate, loving relationships with other people. Relationships |
Young adulthood 19-40 Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Generativity vs. Stagnation |
Adults need to create or nurture things that outlast them, often by having children or creating a positive change that benefits other people. Success leads to feeling of accomplishment, failure results in shallow involvement in world. Work and parenting. |
Middle adulthood 40-65 Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
|
Ego Integrity vs. Despair |
Older adults need to look back on life and feel a sense of fulfillment. Reflection on life. |
Maturity 65-death Erikson's psychosocial stages |
|
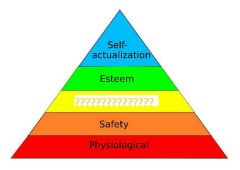
|
Love and belonging |
Friendship, family, sexual intimacy |
|
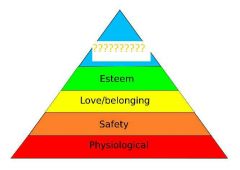
|
Self-actualization |
Morality, creativity, spontaneity, problem solving, lack of prejudice, acceptance of facts |
|
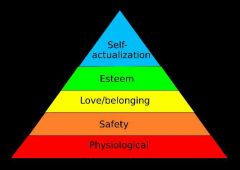
Maslow's hierarchy of needs |
A person's motivation to reach his or her full potential. A person's basic needs must be met before moving on to self actualization. |
|
|
|
Problem-solving |
Focuses on understanding the problem, brainstorming possible solutions, having client pick a solution, having a client try out a solution, and then evaluating how solution worked. |
Social work practice models |
|
|
Task-centered |
Focuses on breaking down problem into small tasks that the client can accomplish. Social worker may use rehearsal, deadlines, and contracts in order to help client feel successful and motivated towards solving the problem. |
Social work practice models |
|
|
Solution focused |
Starts with the solution and then helps the client establish the steps that will lead to the solution. This model uses the miracle question to help clients envision the future they want to obtain. |
Social work practice models |
|
|
Narrative |
Uses letters and other methods to help the client re-author their lives. |
Social work practice models |
|
|
Strengths perspective |
Social work assumes that the client had multiple strengths. Social worker tries to assess the strengths of clients and emphasizes these strengths in the helping relationship. |
Stems from work of Saleeby (1996) |
|
|
Feminist perspective |
Takes into account the role of gender and historical lack of power experienced by women in our society. Feminist social workers emphasize the collaborative relationship between the social worker and the client and place an emphasis on equality and empowerment of women in our society. |
|
|
|
Preconventional |
Stage 1: avoidance of punishment ex:"I would cheat if I knew I wouldn't get caught. " Stage 2: Exchange of favors ex: "I'll let you copy my homework, of I can copy yours. |
Kohlberg's stages of moral development Preschool--elementary; some Jr. High, few high school students |
|
|
Conventional |
Stage 3: good child "I'm not going to do that because I want her to like me" Stage 4: law and order "you can't do that because the teacher said no" doesn't show up until high school typically |
Kohlberg's stages of moral development Few older elementary students, some Jr. High, many high school students |
|
|
Postconventional |
Stage 5: social contract "In this case, the role may be wrong" Stage 6: Universal ethical principle "you shouldn't lie because it violates the golden rule" |
Kohlberg's stages of moral development Rarely seen before college (stage 6 extremely rare) |
|
|
Broker |
Making referrals to link a client to needed resources. They follow up to make sure needed resources are attained. |
|
|
|
Advocate |
Fights for the rights of others and works to obtain needed resources by convincing others of legitimate needs and rights of members in society. Specifically concerned about vulnerable populations. |
|
|
|
Case Manager |
Involved in locating services and assisting clients to access those services. |
|
|
|
Educator |
Involved in teaching people about resources and how to develop particular skills. |
|
|
|
Facilitator |
Involved in gathering groups of people together for a variety of purposes. Involved as group therapists and task group leaders. |
|
|
|
Organizer |
Involved in many levels of community organization and action including economic development, union organization, and research and policy specialists. |
|
|
|
Manager |
Because of expertise in wide variety of applications, social workers are well suited to work as managers and supervisors in almost any setting. As managers, they are better able to influence policy change, and advocate for others. |
|
|
|
Counselor |
Focuses on improving social functioning. Empower people by using strength perspective to desk with problems more effectively. |
|
|
|
Mediator |
Intervenes in disputes to help find compromise, reconcile differences, and reach mutual agreement. Stays neutral. |
|
|
|
Researcher |
Evaluates practice interventions. Seeks to critically analyze literature to use in practice. Disseminates knowledge and seeks to enhance the effectiveness of social work practice. |
|
|
|
Characteristics of a crisis event |
Event perceived add threatening Apparent inability to reduce impact of stressful events Increased fear, tension, and confusion High level of subjective discomfort |
|
|
|
Acute phase of crisis |
In response to a traumatic event. Reactions are usually physiological and psychological, mostly emotion ran reactions |
|
|
|
Outward adjustment phase of crisis |
On outside everything appears normal. Makes effort to resume daily schedule. May withdraw from support. An attempt to return to normal while still processing the trauma. |
|
|
|
Integration phase of crisis |
Victim attempts to make sense of what has happened. Important task is to resolve feelings of blame and guilt |
|

