![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Whatare Freud’s Five Psychosexual Stages? |
Oral Anal Phallic/Oedipal Latency Genital |
|
|
What are the age ranges for Freud’s Five PsychosexualStages? (Oral, Anal, Phallic/Oedipal, Latency, Genital) |
Oral: 0 – 1 Anal: 2 – 3 Phallic /Oedipal: 3 – 6 Latency: 6 –11 Genital: 12 –18 (Adolescence) |
|
|
Whatare Piaget’s 4 Stages of Cognitive Development? |
Sensorimotor Thought Preoperational Thought Concrete Operations Formal Operations |
|
|
Whatare the age ranges for Piaget’s 4 Stages of Cognitive Development? (Sensorimotor Thought, Preoperational Thought, Concrete Operations, Formal Operations)
|
Sensorimotor Thought:0 – 2 Preoperational Thought: 2 ½ – 6 or 7 Concrete Operations: 7 – 11 Formal Operations: 11 – 18 |
|
|
What are Erikson’s 8 Psychosocial Stages? |
Trust vs Mistrust Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt Initiative vs Guilt Industry vs Inferiority Identity vs Identity Diffusion Intimacy vs Isolation Generativity vs Despair Integrity vs Despair |
|
|
What are the age ranges for Erikson’s 8 Psychosocial Stages? (Trust vs Mistrust, Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt, Initiative vs Guilt, Industry vs Inferiority, Identity vs Identity Diffusion, Intimacy vs Isolation, Generativity vs Despair, Integrity vs Despair)
|
Trust vs Mistrust: Infancy (0 – 1) Autonomy vs Shame And Doubt: Early Childhood (2 – 3) Initiative vs Guilt: Play Age (3 – 5) Industry vs Inferiority: School-Age (6 – 11) Identity vs Identity Diffusion/Role Confusion: Adolescence (12 – 18) Intimacy vs Isolation: Young Adulthood (19 – mid 30’s) Generativity vs Despair/Self-Absorption/Stagnation: Adulthood (mid 30’s – 50’s) Integrity vs Despair/Disgust: Senescence/Maturity (60’s and beyond) |
|
|
Matching: Piaget’s Cognitive Theory: A) Concrete Operations B) Sensorimotor Thought C) Formal Operations D) Preoperational Thought 1) Development of abstract thought. 2) Retains image of objects, develops primitive logic and manipulating objects, begins intentional actions, play is imitative, signals meaning – invest meaning in event, symbol meaning (language) – begins the last part of this phase. 3) Beginnings of abstract thought, plays games with rules, cause-effect relationship understood, logical implications understood, thinking is independent of experience, thinking is reversible, rules of logic are developed. 4) Language development enables symbolic functioning to occur, progress from concretism to abstract thinking, can comprehend past present future, night terrors, acquires words, math symbols, music symbols, and other codes, magical thinking, thinking is not generalized, thinking is concrete, irreversible, egocentric, centered on one detail or event. |
A) Concrete Operations = (3) Beginnings of abstract thought, plays games with rules, cause-effect relationship understood, logical implications understood, thinking is independent of experience, thinking is reversible, rules of logic are developed. B) Sensorimotor Thought = (2) Retains image of objects, develops primitive logic and manipulating objects, begins intentional actions, play is imitative, signals meaning – invest meaning in event, symbol meaning (language) – begins the last part of this phase. C) Formal Operations = (1) Development of abstract thought. D) Preoperational Thought = (4) Language development enables symbolic functioning to occur, progress from concretism to abstract thinking, can comprehend past present future, night terrors, acquires words, math symbols, music symbols, and other codes, magical thinking, thinking is not generalized, thinking is concrete, irreversible, egocentric, centered on one detail or event. |
|
|
Please define the the positive and negative outcomes of Erikson's 8 Psychosocial Stages: 1) Trust vs Mistrust 2) Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt 3) Initiative vs Guilt 4) Industry vs Inferiority 5) Identity vs Identity Diffusion/Role Confusion 6) Intimacy vs Isolation 7) Generativity vs Despair/Self-Absorption/ Stagnation 8) Integrity vs Despair |
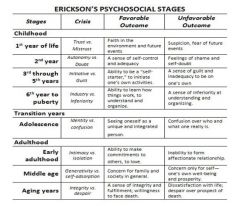
|
|
|
What are the stages of Margaret Mahler's Object Relations/Separation-Individuation Process? |

|

