![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stakeholders
|
those who have a claim on the success and failure of an organization
|
|
|
The “reach” of the organization
|
?
|
|
|
Principal and agent theory
|
The principal-agent problem arises within the firm when ownership and control are separated and the self-interest of managers may lead them to act other than in the interest of the shareholders. The problem is to design monitoring or incentive systems that will make managers act in the best interest of the shareholders.
|
|
|
Type of Ethics
|
a. Societal – how members of a society should interact
b. Occupational – standards of behavior for a profession or trade c. Organizational – guiding practices for a company’s managers to view their responsibility to stakeholders d. Individual – personal standards and values on how one should interact with others |
|
|
Rules or Frameworks to Solve an Ethical Dilemma
|
a. Utilitarian rule: greatest good for the greatest number of people
b. Moral rights rule: protects the fundamental rights and privileges c. Justice rule: a fair and equable distribution of benefits and harms d. Practical rule: a “business model” that says you should only make decisions that you are willing to disclose to the public |
|
|
Trust
|
willingness of a person or a group to have confidence in the goodwill of another person or organization even though this willingness puts them at risk
|
|
|
Reputation
|
how others see managers and organizations as a result of their ethical behavior
|
|
|
Mission
|
What we do – this is a focus on the strategic business units –SBU’s and is an internal view.
EX: This is the mission statement for IBM Global Financing: “The mission of Global Financing is to facilitate clients’ acquisition of IBM hardware, software and services.” |
|
|
Vision
|
How we see ourselves and how we want our stakeholders to see us – this has a focus on the marketplace and is generally organizational-wide in its scope
EX: “IBM's vision is to be the world's most successful and important information technology company. |
|
|
Creativity
|
1. generate new and original ideas – the “R” in research and development
2. that are actionable – the “D” in research and development |
|
|
Areas or the focus of creativity
|
a. Productivity – generally called “process R&D”
b. New products c. New structures |
|
|
Innovation
|
applying new ideas to the organization
1. Invent – the application of the new idea from the “creative process” for the organization 2. Develop – makes the new idea practical 3. Diffuse – puts the idea into the hands of the end user 4. Integrate – makes the new idea permanent in the organization 5. Monitor – tracking of the innovation to validate its continued use |
|
|
General Theories of Leadership
|
a. Characteristic or trait theory: action and task oriented
b. Behavioral or psychological theory: need for power and accomplishments and low need for affiliation or friends c. Situational and contingency theory: the times or conditions produce the leaders d. Functional leadership theory: whatever is necessary to group needs is taken care of; thus, a leader can be said to have done their job well when they have contributed to group effectiveness and cohesion |
|
|
Leadership
|
A process of inspiring others to work hard to accomplish a goal
|
|
|
The “Integrity Line
|
how are people inspired
Honest - Consistent - Humble - Selfless Where leaders should be ----------------------------------------- Where leaders don’t want to be Dishonest - Inconsistent - Conceited - Selfish |
|
|
Terms from “What Makes a Leader”
|
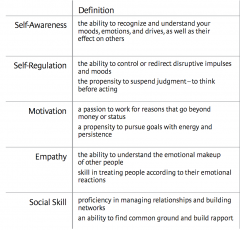
|
|
|
Styles of leadership: they are not exclusive but can overlap
|
a. Autocratic: command and control
b. Human relations: people over tasks c. Laissez-faire: do the best you can and don’t bother me d. Democratic style: people and tasks together |
|
|
Management Process
|
a. Organizing
b. Planning c. Controlling |
|
|
Types of Controls
|
a. Feed forward controls
b. Concurrent controls c. Feedback controls |
|
|
Contingency Thinking
|
Definition: Attempts to match managerial practices with situational demands
A. Bureaucracy – works well in a stable, predictable environment B. Flexible structure – works well in a changing and complex environment C. The contingency manager needs to work in both environments, not just the flexible environment |
|
|
Entrepreneurial Gap
|
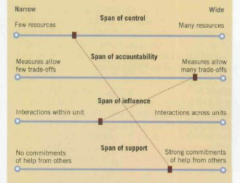
Company policies designed to provide support to ensure entrepreneurial initiatives. supply and demand of resources at their job are in balanced.
|

