![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
172 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following is not true about peptide hormones?
a. They utilize second messenger systems. b. They cannot enter target cells. c. They act on intercellular receptors that directly target genes. d. They act on plasma membrane receptors. |
c. They act on intercellular receptors that directly target genes.
|
|
|
Which of these is not a mechanism of hormone action?
a. Stimulating protein synthesis. b. Altering plasma membrane permeability. c. Preventing mitosis. d. Inducing secretory activity. e. All of these are mechanisms of hormone action. |
c. Preventing mitosis.
|
|
|
Steroid hormones function by
a. entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene. b. finding an appropriate cell receptor and initiating cAMP activity. c. stimulating the synthesis of a glycogen. d. increasing blood pressure. |
a. entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene.
|
|
|
Long-distance chemical signals that travel in the blood are
a. autocrines b. hormones c. paracrines d. exocrines e. endocrines |
b. hormones
|
|
|
In our example of a plasma membrane/second messenger system, which of the following is the second messenger?
a. The hormone b. the G protein c. cAMP d. Adenylate cyclase |
c. cAMP
|
|
|
The most complex endocrine responses involve the
a. thyroid gland. b. pancreas. c. adrenal glands. d. hypothalamus. e. thymus gland. |
d. hypothalamus
|
|
|
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on
a. the location of the tissue or organ with respect to the path of blood flow. b. the membrane potential of the target organ’s cells. c. the presence of the appropriate surface receptors on the target cells. d. nothing – all hormones are capable of stimulating any cells of the body. |
c. the presence of the appropriate surface receptors on the target cells.
|
|
|
Hormones are synthesized and released in response to
a. neural stimuli b. hormonal stimuli c. humoral stimuli d. all of the above |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the posterior pituitary gland?
a. It is a downgrowth of hypothalamic neural tissue b. It has a neural connection to the hypothalamus - the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract c. It consists of pituicytes and nerve fibers d. The hypothalamus synthesizes ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin which is transported to the posterior pituitary. e. The hypothalamus directs the posterior pituitary to synthesize ADH and oxytocin when needed. |
e. The hypothalamus directs the posterior pituitary to synthesize ADH and oxytocin when needed.
|
|
|
When more than one hormone produces the same effect on a target cell it is called
a. antagonism b. permissiveness c. synergism d. integration e. receptor-identity crisis |
c. synergism
|
|
|
Thyroid hormone contains the element
a. iodine. b. fluorine. c. iron. d. chlorine. e. zinc. |
a. iodine.
|
|
|
Catecholamines
a. are secreted by the adrenal cortex. b. are secreted by the adrenal medulla. c. are typically released due to neural stimulus. d. are epinephrine e. a, c and d are correct ab. b, c and d are correct |
ab. b, c and d are correct
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The adrenal gland is found in the brain. b. The adrenal gland is found on top of the kidney. c. The adrenal gland consists of the inner cortex layer and the outer medulla layer. d. The adrenal gland consists of the inner medulla layer and the outer cortex layer. e. Both a and c are true ab. Both a and d are true ac. Both b and c are true ad. Both b and d are true |
ad. Both b and d are true
|
|
|
Cortisol
a. is released in response to ACTH, patterns of eating and activity, and stress b. has a prime metabolic effect of gluconeogenesis formation of glucose from fats and proteins c. promotes a rise in blood glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids d. is produced in the zona fasciculata. e. All of the above are true. |
e. All of the above are true.
|
|
|
The C cells (parafollicular cells) of the thyroid gland produce
a. thyroxine. b. TSH. c. calcitonin. d. PTH. e. triiodothyronine. |
c. calcitonin.
|
|
|
Mineralocorticoids
a. are produced in the zona glomerulosa b. regulate electrolytes c. include aldosterone d. a and b are correct e. a, b and c are correct |
e. a, b and c are correct
|
|
|
Epinephrine
a. stimulates bronchial dilation b. influences peripheral vasoconstriction c. is produced in the adrenal medulla d. both a and c e. both b and c |
d. both a and c
|
|
|
In the pancreas
a. the pancreatic islets contains endocrine cells. b. acinar cells produce digestive enzymes. c. cells produce glucagon. d. cells produce insulin. e. all of the above are true. |
e. all of the above are true.
|
|
|
19. Which of the following is not true concerning insulin?
a. It inhibits glycogenolysis. b. It lowers blood glucose levels. c. It causes cells to polymerize glucose to form glycogen. d. It activates gluconeogenesis. |
d. It activates gluconeogenesis.
|
|
|
Growth hormone
a. reduces blood glucose by decreasing glucose uptake and encouraging glycogen breakdown. b. elevates blood glucose by decreasing glucose uptake and encouraging glycogen breakdown. c. Targets chondrocytes and skeletal muscle. d. Both a and c are correct e. Both b and c are correct |
e. Both b and c are correct
|
|
|
The liver is the major target for
a. ADH. b. cortisol. c. aldosterone. d. glucagon. e. thyroxine. |
b. cortisol
|
|
|
Which of the following is not correct?
a. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is produced in the hypothalamus. b. ACTH is secreted from the anterior pituitary. c. ACTH stimulates the zona fasciculata to release cortisol. d. ACTH is regulated by CRH in a daily rhythm. e. all of the above are correct |
a. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is produced in the hypothalamus.
|
|
|
The function of TSH is to
a. make follicle cells permeable to T3 and T4 b. open iodide channels c. increase thyroglobulin output d. inhibit TRH e. inhibit TH |
b. open iodide channels
|
|
|
Protein kinases exert their action through
a. deamination b. decarboxylation c. methylation d. phosphorylation e. hydroxylation |
d. phosphorylation
|
|
|
Before the discovery of these glands, thyroid surgery often led to a rapid drop in blood calcium levels, which triggered muscle contractions and cardiac arrhythmias. What glands are these and which hormone is lacking?
a. thyroid glands; calcitonin b. parathyroid glands; calcitonin c. parathyroid glands; parathyroid hormone d. thyroid glands; levothyroxine e. parathyroid glands; levothyroxine |
c. parathyroid glands; parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
Lipid derivative hormones
a. are called steroid hormones. b. are derived from cholesterol. c. use second messenger systems for their activity. d. a and b are correct e. a, b and c are all correct |
d. a and b are correct
|
|
|
Parathyroid hormone
a. stimulates osteoclast activity. b. increases the rate of calcium absorption. c. decreases the rate of calcium excretion. d. raises the level of calcium ions in the blood. e. all of the answers are correct. |
e. all of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
Elevated levels of calcium ions in the blood stimulate the secretion of
a. calcitonin. b. thyroid hormone. c. parathyroid hormone. d. aldosterone e. cortisol |
a. calcitonin.
|
|
|
Which of the events below does not occur when the semilunar valves are open?
a. Blood enters pulmonary arteries and the aorta. b. AV valves are closed. c. Ventricles are in systole. d. Ventricles are in diastole. |
d. Ventricles are in diastole.
|
|
|
Which of these is not true concerning cardiac muscle?
a. Intercalated discs serve as junctions between cells. b. Desmosomes act as “rivets” to prevent separation during contraction. c. Desmosomes allow ions to pass from cell to cell. d. Gap junctions electrically couple all cardiac cells. e. Heart muscle behaves as a functional syncytium. |
c. Desmosomes allow ions to pass from cell to cell.
|
|
|
Isovolumetric contraction
a. occurs only in people with heart valve defects b. occurs while the AV valves are open c. refers to the short period during ventricular systole when the ventricles are completely closed chambers d. occurs immediately after the aortic and pulmonary valves close e. refers to the short period during ventricular diastole when the ventricles are completely closed chambers |
c. refers to the short period during ventricular systole when the ventricles are completely closed chambers
|
|
|
If the length of the time between depolarization and repolarization in cardiac muscle cells was the same as it is for skeletal muscle cells
a. tetanic contractions might occur, which would stop the heart's pumping action b. it would be less than 1-2 ms c. contractions would last as long as the refractory period d. it would be much longer before cardiac cells could respond to a second stimulation |
a. tetanic contractions might occur, which would stop the heart's pumping action
|
|
|
Blood flow is ________.
a. directly proportional to the blood pressure gradient b. inversely proportional to the blood pressure gradient. c. influenced most by the resistance encountered within the blood vessels. d. equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for the entire vascular system e. a, c and d are correct ab. b, c and d are correct |
e. a, c and d are correct
|
|
|
Which of the following processes provides a long-term response to changes in blood pressure?
a. renal regulation b. baroreceptor-initiated reflexes c. neural controls d. chemoreceptor-initiated reflexes e. chanting |
a. renal regulation
|
|
|
Peripheral resistance
a. increases as blood viscosity increases b. increases as blood vessel diameter increases c. decreases with increasing length of the blood vessel d. is not a major factor in blood pressure in healthy individuals e. decreases as blood vessel diameter decreases |
a. increases as blood viscosity increases
|
|
|
Select the correct statement about factors that influence blood pressure.
a. An increase in cardiac output corresponds to a decrease in blood pressure, due to the increased delivery. b. Excess red cell production would cause a blood pressure increase. c. Excess protein production would decrease blood pressure. d. Systemic vasodilation would increase blood pressure, due to diversion of blood to essential areas. |
b. Excess red cell production would cause a blood pressure increase.
|
|
|
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is
a. the pressure that propels the blood to the tissues b. is equal to the systolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure c. is equal to the diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure d. both a and b e. both a and c |
e. both a and c
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true regarding the intrinsic pathway?
a. It is triggered by negatively charged surfaces b. It is triggered by factor III c. It requires the presence of Ca2+ d. It is slower than the extrinsic pathway e. All of the above are true |
b. It is triggered by factor III
|
|
|
Which of the following does not have an effect on EDV?
a. Venous return b. contractility c. preload d. filling time |
b. contractility
|
|
|
Which statement below is correct?
a. More filtration occurs at the arteriole end of a capillary. b. More filtration occurs at the venous end of a capillary. c. More reabsorption occurs at the arteriole end of a capillary d. More reabsorption occurs at the venous end of a capillary. e. Both a and c are correct ab. Both a and d are correct ac. Both b and c are correct ad. Both b and d are correct. |
ab. Both a and d are correct
|
|
|
Positive inotropic action
a. influences EDV. b. influences ESV. c. leads to increased contraction of cardiac muscle. d. leads to decreased contraction of cardiac muscle. e. both a and c are correct ab. Both a and d are correct ac. Both b and c are correct ad. Both b and d are correct. |
ac. Both b and c are correct
|
|
|
The enzyme that can digest fibrin and dissolve a clot is
a. thrombin. b. plasmin. c. heparin. d. fibrinase. e. phosphokinase. |
b. plasmin.
|
|
|
The atrioventricular (AV) valves permit blood flow
a. in one direction only. b. in both directions. c. in many directions. d. in opposite directions on the right and left. e. from a ventricle to an atrium. |
a. in one direction only.
|
|
|
The visceral pericardium is the same as the
a. mediastinum. b. parietal pericardium. c. epicardium. d. myocardium. e. endocardium. |
c. epicardium
|
|
|
The long plateau phase of the cardiac muscle action potential is due to
a. movement of fewer sodium ions across the cell membrane. b. calcium channels remaining open. c. increased membrane permeability to potassium ion. d. decrease in the amount of calcium diffusing across the membrane. e. increased membrane permeability to sodium ions. |
b. calcium channels remaining open
|
|
|
During ventricular systole,
a. atria are contracting. b. blood is entering the ventricles. c. AV valves are closed. d. pressure in the ventricles remains constant. e. pressure in the aorta remains constant. |
c. AV valves are closed.
|
|
|
Stroke volume depends on
a. end diastolic volume. b. the contractility of the ventricle. c. the pressure required to pump blood into the aorta. d. venous return of blood to the heart. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
Which of these would cause stroke volume to increase?
a. when venous return is decreased b. when ventricular contraction is reduced c. when diastolic blood pressure is decreased d. decrease in heart rate e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
Which of these is considered the pacemaker of the heart?
a. AV node b. AV bundle c. SA node d. Baroreceptor of the right atrial wall e. Cupid |
c. SA node
|
|
|
Blood returning to the heart from the systemic circuit first enters the
a. right atrium. b. right ventricle. c. left atrium. d. left ventricle. e. conus arteriosus. |
a. right atrium.
|
|
|
Blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary circuit first enters the
a. right atrium. b. right ventricle. c. left atrium. d. left ventricle. e. conus arteriosus. |
c. left atrium.
|
|
|
The right atrium receives blood from the
a. coronary sinus. b. superior vena cava. c. inferior vena cava. d. systemic circuit. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
In cardiac muscle, the fast depolarization phase of the action potential is the result of
a. increased membrane permeability to sodium ions. b. increased membrane permeability to potassium ions. c. decreased membrane permeability to calcium ions. d. decreased membrane permeability to sodium ions. e. increased membrane permeability to chloride ions. |
a. increased membrane permeability to sodium ions.
|
|
|
The pulmonary arteries carry blood to the
a. heart. b. lungs c. brain. d. intestines e. liver |
b. lungs
|
|
|
The following is a list of vessels and structures that are associated with the heart.
1. right atrium 2. left atrium 3. right ventricle 4. left ventricle 5. venae cavae a. 1, 2, 7, 8, 3, 4, 6, 5 b. 1, 7, 3, 8, 2, 4, 6, 5 c. 5, 1, 3, 7, 8, 2, 4, 6 d. 5, 3, 1, 7, 8, 4, 2, 6 e. 5, 1, 3, 8, 7, 2, 4, 6 6. aorta 7. pulmonary trunk 8. pulmonary veins What is the correct order for the flow of blood entering from the systemic circulation? |
c. 5, 1, 3, 7, 8, 2, 4, 6
|
|
|
The glottis is
a. the soft tissue that hangs off the end of the soft palate. b. a flap of elastic cartilage. c. the opening to the larynx. d. the opening to the pharynx. e. part of the hard palate. |
c. the opening to the larynx.
|
|
|
The nose serves all the following functions except
a. as the initiator of the cough reflex b. cleansing the air c. warming and humidifying the air d. as a passageway for air movement |
a. as the initiator of the cough reflex
|
|
|
Which of the choices below is not a function of the respiratory system?
a. pulmonary respiration b. pulmonary ventilation c. transport of respiratory gases d. external respiration |
c. transport of respiratory gases
|
|
|
The area in which gas exchange occurs is called the
a. conducting zone b. respiratory zone c. respiratory muscles d. nose e. local Shell station |
b. respiratory zone
|
|
|
The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, pneumocyte type I and pneumocyte type II. The function of type II is to
a. replace mucus in the alveoli b. protect the lungs from bacterial invasion c. trap dust and other debris d. secrete surfactant |
d. secrete surfactant
|
|
|
Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is
a. greater than the intra-alveolar pressure. b. greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. c. equal to the pressure in the atmosphere. d. less than the pressure in the atmosphere. |
b. greater than the pressure in the atmosphere
|
|
|
Intrapulmonary pressure is the
a. pressure within the pleural cavity b. pressure within the alveoli of the lungs c. difference between atmospheric pressure and respiratory pressure d. negative pressure in the intrapleural space |
b. pressure within the alveoli of the lungs
|
|
|
The relationship between the pressure and volume of gases is given by
a. Dalton's law b. Henry's law c. Boyle's law d. Charles' law |
c. Boyle's law
|
|
|
Which of the choices below determines the direction of respiratory gas movement?
a. the temperature b. the molecular weight and size of the gas molecule c. the partial pressure gradient of each gas d. solubility of the gas in water |
c. the partial pressure gradient of each gas
|
|
|
The C shape of the tracheal cartilages is important because
a. large masses of food can pass through the esophagus during swallowing. b. large masses of air can pass through the trachea. c. it facilitates turning of the head. d. the bronchi are also C-shaped. e. it permits the trachea to pinch shut prior to sneezing. |
a. large masses of food can pass through the esophagus during swallowing.
|
|
|
Pulmonary ventilation refers to the
a. movement of air into and out of the lungs. b. movement of dissolved gases from the alveoli to the blood. c. movement of dissolved gases from the blood to the interstitial space. d. movement of dissolved gases from the interstitial space to the cells. e. utilization of oxygen. |
a. movement of air into and out of the lungs
|
|
|
Henry's law states that
a. gas volume and temperature are directly proportional. b. gas volume and pressure are inversely proportional. c. the volume of gas that will dissolve in a liquid is proportional to both the solubility of the gas and its pressure. d. in a mixture of gases such as air, the total pressure is the sum of the individual partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. e. gas pressure is inversely proportional to gas volume. |
c. the volume of gas that will dissolve in a liquid is proportional to both the solubility of the gas and its pressure.
|
|
|
68. Which of the following is not true concerning gases in respiration?
a. The partial pressure of each gas is directly proportional to its percentage in the mixture. b. CO2 is much more soluble in plasma than O2. c. The partial pressure gradient for CO2 is very steep. d. The alveoli contain more CO2 and water vapor than atmospheric air. e. All of the above are true. |
c. The partial pressure gradient for CO2 is very steep.
|
|
|
Which statement about CO2 is incorrect?
a. Its concentration in the blood is decreased by hyperventilation. b. CO2 concentrations are greater in venous blood than arterial blood. c. Its accumulation in the blood is associated with a decrease in pH. d. More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs. |
d. More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs.
|
|
|
How is the bulk of carbon dioxide carried in blood?
a. as the bicarbonate ion in the plasma after first entering the red blood cells b. as carbaminohemoglobin in the red blood cells c. chemically combined with the heme portion of hemoglobin d. as carbonic acid in the plasma e. as carbonic acid in the red blood cell |
a. as the bicarbonate ion in the plasma after first entering the red blood cells
|
|
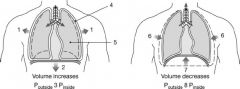
What is the relationship between the pressures at label "3"?
a. P outside = P inside b. P outside > P inside c. P outside < P inside d. P outside + P inside e. P outside - P inside |
b. P outside > P inside
|
|
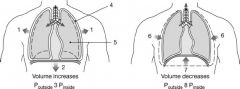
What pressure will be present in the space labeled "4"?
a. alveolar pressure b. interpleural pressure c. intrapleural pressure d. subatmospheric pressure e. atmospheric pressure |
c. intrapleural pressure
|
|
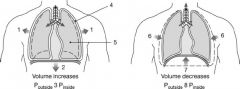
What is the relationship between the pressures at label "8"?
a. P outside = P inside b. P outside > P inside c. P outside < P inside d. P outside + P inside e. P outside - P inside |
c. P outside < P inside
|
|
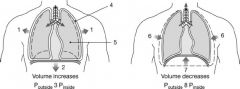
How does the pressure "P4" at label "4" compare to the pressure "P5" at label "5"?
a. P4 is higher than P5 during inhalation and then lower during exhalation. b. P4 is always be higher than P5. c. P4 is always lower than P5. d. P4 always equals P5. e. P4 is lower than P5 during inhalation and then higher during exhalation |
c. P4 is always lower than P5.
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide and water combine to form
a. hydrochloric acid. b. carbonic acid. c. oxygen. d. carbaminohemoglobin. e. nitric acid. |
e. nitric acid.
|
|
|
When does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration?
a. during external respiration b. immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c. when the chloride shift occurs d. during pulmonary ventilation e. during internal respiration |
b. immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a reason for the partial pressure of gases in the alveoli to differ from pressures in the atmosphere?
a. humidification of the air b. nitrogen retention in the alveoli c. the exchange of gases between the alveoli and the capillaries d. the mixing of new and old air |
a. humidification of the air
|
|
|
The term hypercapnia refers to
a. the cessation of breathing. b. elevated PCO2. c. elevated PO2. d. an increase in pH. e. labored breathing. |
b. elevated PCO2.
|
|
|
In quiet breathing,
a. inspiration and expiration involve muscular contractions. b. inspiration is passive and expiration involves muscular contractions. c. inspiration involves muscular contractions and expiration is passive. d. inspiration and expiration are both passive. e. inspiration is deep and forceful. |
b. inspiration is passive and expiration involves muscular contractions.
|
|
|
Which of these is responsible for the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid and vice versa?
a. plasma b. bicarbonate ions c. chloride ions d. carbonic anhydrase e. concentration of hydrogen ions |
c. chloride ions
|
|
|
Which of these is responsible for the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid and vice versa?
a. plasma b. bicarbonate ions c. chloride ions d. carbonic anhydrase e. concentration of hydrogen ions |
d. carbonic anhydrase
|
|
|
Which direction does carbon dioxide move during internal respiration?
a. from the blood into the tissue cells b. from the blood into the lungs c. from the lungs into the atmosphere d. from the tissue cells into the blood e. from the lungs into the blood |
d. from the tissue cells into the blood
|
|
|
The chloride shift occurs in order to
a. force oxygen out of the blood and into tissues. b. transport bicarbonate ions into the blood plasma. c. produce salt for the cytosol of blood cells. d. produce carbonic acid. e. pump hydrochloric acid out of gastric cells. |
b. transport bicarbonate ions into the blood plasma.
|
|
|
Low pH alters hemoglobin structure so that oxygen binds less strongly to hemoglobin at low PO2. This increases the effectiveness of
a. external respiration. b. internal respiration. c. carbon dioxide transport. d. hemoglobin synthesis. e. acid-base balance. |
b. internal respiration.
|
|
|
Hyperventilation
a. leads to hypercapnia. b. leads to hypocapnia. c. will cause the pH to fall. d. will cause the pH to rise. e. both a and c are correct ab. Both a and d are correct ac. Both b and c are correct. ad. Both b and d are correct. |
ad. Both b and d are correct.
|
|
|
The most important chemical regulator of respiration is
a. oxygen. b. carbon dioxide. c. bicarbonate ion. d. sodium ion. e. hemoglobin. |
b. carbon dioxide
|
|
|
A chemical that minimizes changes in the pH of a body fluid by releasing or binding hydrogen ion is called a(n).
a. electrolyte. b. acid. c. alkali. d. compensation. e. buffer. |
e. buffer.
|
|
|
The primary role of the carbonic-acid-bicarbonate buffer system is to
a. buffer stomach acid. b. buffer carbonic acid formed by carbon dioxide. c. limit pH changes caused by organic and fixed acids. d. buffer the urine. e. increase ventilation. |
c. limit pH changes caused by organic and fixed acids
|
|
|
The carbonic acid – bicarbonate buffer system
a. cannot protect ECF from changes in pH that result from elevated or depressed levels of CO2 b. functions only when respiratory system and respiratory control centers are working normally. c. ability to buffer acids is limited by availability of bicarbonate ions. d. All of these are true |
d. All of these are true
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of Type I hypersensitivities (a hypersensitivity is an abnormal immune system response)?
a. They involve IgE antibodies and the release of histamine from mast cells and basophils. b. They are adaptive immune responses to disease organisms. c. They include allergic contact dermatitis, such as reactions to jewelry, latex or make-up. d. They are always systemic. e. They involve T cells which cause the release of histamine from mast cells and basophils. |
a. They involve IgE antibodies and the release of histamine from mast cells and basophils.
|
|
|
91. Which of the following is not a function of the inflammatory response?
a. disposes of cellular debris and pathogens b. replaces injured tissues with connective tissue c. prevents the spread of the injurious agent to nearby tissue d. sets the stage for repair processes |
b. replaces injured tissues with connective tissue
|
|
|
Immunocompetence
a. is the ability of individual cells to recognize a specific antigen by binding to it b. requires exposure to an antigen c. prevents intercellular communication so that only specific cell types respond to the invader d. occurs in one specific organ of the adaptive immune system |
a. is the ability of individual cells to recognize a specific antigen by binding to it
|
|
|
B lymphocytes develop immunocompetence in the
a. spleen b. red bone marrow c. thymus d. lymph nodes |
b. red bone marrow
|
|
|
The only T cells that can directly attack and kill other cells are the
a. plasma cells b. regulatory cells c. cytotoxic cells d. helper cells |
c. cytotoxic cells
|
|
|
What is the role of interferon in defense against disease?
a. protects cells that have not yet been infected by bacteria b. protects cells that have not yet been infected by viruses c. activates the complement mechanism d. activates the inflammatory process |
b. protects cells that have not yet been infected by viruses
|
|
|
The body's innate defenses include all of the following, except
a. the skin. b. complement. c. interferon. d. inflammation. e. antibodies. |
e. antibodies.
|
|
|
Using the list below, which of the following is the correct sequence of events in phagocytosis?
1. Digestion 2. Formation of phagolysosome 3. Adherence 4. Exocytosis (Expulsion) 5. Formation of phagosome a. 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 b. 5, 3, 1, 2, 4 c. 3, 5, 2, 1, 4 d. 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 e. 4, 5, 1, 2, 3 ab. 3, 5, 1, 2, 4 |
c. 3, 5, 2, 1, 4
|
|
|
During inflammation, white blood cells will cling to the walls of the capillaries and then squeeze out into the tissues. In order, this is called
a. chemotaxis and margination b. diapedesis and margination c. margination and diapedesis d. chemotaxis and diapedesis e. margination and chemotaxis |
c. margination and diapedesis
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a method by which antibody-antigen binding enhances the immune system response?
a. neutralization b. agglutination c. activation of cytokines d. enhancing phagocytosis through opsonization e. activating complement for cytolysis |
c. activation of cytokines
|
|
|
The adaptive immune system
a. is systemic b. has memory c. exhibits specificity d. consists of T cells and B cells e. all of the above |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following is true about the number of binding sites per functional antibody unit?
a. IgG contains 6 binding sites. b. IgM contains 10 binding sites. c. IgD contains 4 binding sites. d. IgA contains 2 binding sites. e. IgE contains 4 binding sites. |
b. IgM contains 10 binding sites.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is incorrect or false?
a. Class II MHC molecules appear only on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, thymic cells, and T cells that have been activated by exposure to antigens. b. Haptens are not immunogenic by themselves. c. MHC proteins are the cell’s identity markers. d. Class I MHC molecules are built into the plasma membranes of almost all body cells. e. Dendritic cells have both class I and class II MHC’s. |
a. Class II MHC molecules appear only on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, thymic cells, and T cells that have been activated by exposure to antigens.
|
|
|
Inflammation produces localized
a. swelling. b. redness. c. heat. d. pain. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
A sample of John's blood shows a high level of pyrogens. This would indicate that John
a. is feeling achy. b. is producing T lymphocytes. c. has a sore throat. d. is running a fever. e. has swollen lymph nodes. |
d. is running a fever.
|
|
|
Small molecules that bind with self-proteins (carriers) to produce antigenic substances are called
a. ions b. haptens c. reagins d. antibodies e. integrins |
b. haptens
|
|
|
Activation of B cells
a. cannot occur in the presence of antigens b. only occurs in the secondary immune response c. occurs during fetal development d. results in the formation of plasma cells and memory B cells e. results in the activation of helper T cells |
d. results in the formation of plasma cells and memory B cells
|
|
|
Cytotoxic T cells
a. are activated CD8 cells. b. self-destruct once the antigen has been neutralized. c. function mainly to stimulate the proliferation of other T cell populations. d. require the double recognition signal of I MHC plus II MHC on the target cell in order to function. e. are activated CD4 cells. |
a. are activated CD8 cells
|
|
|
The only antibodies that normally cross the placenta are
a. IgA. b. IgD. c. IgE. d. IgG. e. IgM. |
d. IgG.
|
|
|
The inflammatory response is triggered when
a. blood flow to an area increases. b. red blood cells release pyrogens. c. T cells produce interferon. d. bacteria are phagocytized. e. mast cells release histamine. |
e. mast cells release histamine.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true?
a. All antibodies are proteins. b. Antibodies bind to epitopes. c. Antibodies are collectively called immunoglobulins. d. Antibodies are found on the surface of all body cells. e. Antibodies have at least two identical antigen-binding sites. |
d. Antibodies are found on the surface of all body cells.
|
|
|
Compliment and antibodies
a. enhance the inflammatory response b. are both capable of opsonization c. are part of the innate immune system d. both a and b are correct e. a, b and c are all correct |
d. both a and b are correct
|
|
|
Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of adaptive immunity by
a. natural killer cells b. pinocytosis c. T lymphocytes d. B lymphocytes |
a. natural killer cells
|
|
|
Complement proteins and antibodies coat a microorganism and provide binding sites, enabling macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytize the organism. This is called
a. opsonization b. agglutination c. chemotaxis d. diapedesis e. neutralization |
a. opsonization
|
|
|
Which of these is unique to an individual and distinguishes self from non-self?
a. APCs b. NK cells c. MHC d. ADCC e. MAC. |
c. MHC
|
|
|
Select the correct statement about complement.
a. Complement can be activated through three pathways: classical, secondary, and alternate. b. Complement proteins C1 through C9 act exclusively in the classical pathway. c. An adaptive immune mechanism is often involved in directing complement to its target. d. The membrane attack complex consists of complement proteins C3a through C5. |
c. An adaptive immune mechanism is often involved in directing complement to its target.
|
|
|
Select the correct statement about both active and passive immunity.
a. The antibodies utilized in active immunity are acquired from another organism. b. Immunological memory is established by passive immunization. c. A vaccination is an example of the introduction of passive immunity into the body. d. Active and passive humoral immunity are both mechanisms of adaptive immunity that use antibodies. |
d. Active and passive humoral immunity are both mechanisms of adaptive immunity that use antibodies.
|
|
|
Which of the following cells is the most critical cell in immunity?
a. cytotoxic T cell b. B cell c. helper T cell d. APC e. NK cell |
c. helper T cell
|
|
|
Which complement factor is always present in the blood?
a. C1 b. C2 c. C3 d. C4 e. C5 |
c. C3
|
|
|
B cells are primarily activated by the activities of
a. antigens. b. antibodies. c. helper T cells. d. macrophages. e. plasma cells. |
c. helper T cells.
|
|
|
T cells undergo a two-step process for maturation. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding this process?
a. positive selection occurs before negative selection b. cells which are incapable of recognizing self will undergo apoptosis. c. negative selection occurs before positive selection d. They must recognize self-MHC. e. This process occurs in the thymus. |
a. positive selection occurs before negative selection
|
|
|
Which of the following is associated with passive immunity?
a. passage of IgG antibodies from a pregnant mother to her fetus b. booster shot of vaccine c. infusion of weakened viruses d. exposure to an antigen |
a. passage of IgG antibodies from a pregnant mother to her fetus
|
|
|
Characteristics of adaptive defenses include
a. versatility. b. tolerance. c. memory. d. specificity. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
In an experimental situation, a rabbit is exposed to a viral antigen to which it makes antibodies. These antibodies are then purified and injected into a human with the same viral disease. This is an example of
a. innate immunity. b. active immunization. c. passive immunization. d. natural immunity. e. alloimmunity. |
c. passive immunization.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about MHC proteins is not true?
a. bind complement b. allow the body to differentiate its own cells from foreign cells c. function in antigen presentation d. fall into two major classes e. are found on all nucleated cells |
a. bind complement
|
|
|
The primary function of the lymphatic system is
a. circulation of nutrients. b. the transport of hormones. c. defending the body against both environmental hazards and internal threats. d. the production and distribution of plasma proteins. |
c. defending the body against both environmental hazards and internal threats.
|
|
|
B lymphocytes develop immunocompetence in the
a. spleen b. red bone marrow c. thymus d. lymph nodes |
b. red bone marrow
|
|
|
If the thymus stops producing thymosins there would be an immediate decrease in the number of
a. B cells b. NK cells c. T cells d. neutrophils e. macrophages |
c. T cells
|
|
|
Areas of the spleen that contain large numbers of lymphocytes are known as
a. red pulp b. white pulp c. Peyer's patches d. tonsils e. nodules |
b. white pulp
|
|
|
T (cell) is to _____________ as B (cell) is to _______________.
a. top; bottom b. thyroid; bone-marrow c. thymus; bursa d. thymus; bone-marrow |
d. thymus; bone-marrow
|
|
|
Which of these statements is incorrect?
a. Lymph can only flow one way and will eventually be returned to the blood stream. b. Lymph nodes are capable of clearing 99% of all pathogens from lymphatic fluid. c. Lymph enters a lymph node through afferent vessels. d. Lymph enters a lymph node through efferent vessels. e. Lymph enters a lymph node through multiple vessels but can only exit through one. |
d. Lymph enters a lymph node through efferent vessels.
|
|
|
The cell that dominates the deep cortex of a lymph node is the ________ cell.
a. B b. T c. plasma d. nodule e. NK |
b. T
|
|
|
132. Which of the following does not contain mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT)?
a. digestive system b. circulatory system c. respiratory system d. reproductive system e. urinary system |
b. circulatory system
|
|
|
Which of the following is correct for flow of lymph through the lymph node?
a. afferent lymphatics, outer cortex, deep cortex, medullary sinus, efferent lymphatics b. afferent lymphatics, medullary sinus, outer cortex, deep cortex, efferent lymphatics c. efferent lymphatics, outer cortex, deep cortex, medullary sinus, afferent lymphatics d. efferent lymphatics, medullary sinus, outer cortex, deep cortex, afferent lymphatics |
a. afferent lymphatics, outer cortex, deep cortex, medullary sinus, efferent lymphatics
|
|
|
When lymphatic structures are blocked, the result is
a. abnormally high lymph drainage from the distal region b. shrinkage of tissues distal to the blockage due to inadequate delivery of lymph c. increased pressure in the lymphatics proximal to the blockage d. severe localized edema distal to the blockage |
d. severe localized edema distal to the blockage
|
|
|
The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is the
a. nephron loop b. nephron c. glomerulus d. glomerular capsule e. medullary papilla |
b. nephron
|
|
|
An increase in the permeability of the cells of the collecting tubule to water is due to a(n)
a. decrease in the production of ADH b. increase in the production of aldosterone c. increase in the production of ADH d. decrease in the concentration of the blood plasma |
c. increase in the production of ADH
|
|
|
The urinary system does all of the following,
except a. excrete excess albumin molecules. b. regulate blood volume. c. contribute to stabilizing blood pH. d. eliminate organic waste products. e. regulate plasma concentrations of electrolytes. |
a. excrete excess albumin molecules.
|
|
|
A glomerulus is
a. the expanded end of a nephron. b. a knot of capillaries within the renal corpuscle. c. the source of erythropoietin. d. attached to the collecting duct. e. the horseshoe-shaped segment of the nephron. |
b. a knot of capillaries within the renal corpuscle.
|
|
|
Alcohol acts as a diuretic because it
a. increases the rate of glomerular filtration b. inhibits the release of ADH c. inhibits the release of aldosterone d. is not reabsorbed by the tubule cells e. increases secretion of ADH |
b. inhibits the release of ADH
|
|
|
The function of angiotensin II is to
a. Stimulate the reabsorption via of Na+ b. constrict arteriolar smooth muscle, causing MAP to rise (Mean Arterial Pressure) c. increasing fluid reabsorption d. Stimulate the hypothalamus to release ADH and activates the thirst center e. All of these are functions of angiotensin II |
e. All of these are functions of angiotensin II
|
|
|
What would happen if the capsular hydrostatic pressure were increased above normal?
a. Net filtration would increase above normal. b. Capsular osmotic pressure would compensate so that filtration would not change. c. Net filtration would decrease. d. Filtration would increase in proportion to the increase in capsular pressure. e. The colloid osmotic pressure would decrease. |
c. Net filtration would decrease.
|
|
|
In the ascending limb of the nephron loop the
a. thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption b. thin segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption c. thick segment is permeable to water d. thin segment is freely permeable to water e. all fluid and ion movement is controlled hormonally |
a. thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption
|
|
|
Which of the choices below is the salt level-monitoring part of the nephron?
a. vasa recta b. principal cell c. nephron loop d. macula densa e. granular cell |
d. macula densa
|
|
|
Which of the choices below are the most important hormone regulators of electrolyte reabsorption and secretion?
a. angiotensin I and epinephrine b. angiotensin II and ADH c. angiotensin II and aldosterone d. angiotensin I and atrial natriuretic peptide e. angiotensin II and norepinephrine |
c. angiotensin II and aldosterone
|
|
|
The driving force for filtration within the glomerular capsule is the
a. capsular hydrostatic pressure b. glomerular hydrostatic pressure c. blood colloid osmotic pressure d. myogenic mechanism e. presence of too much Na+ in the bloodstream. |
b. glomerular hydrostatic pressure
|
|
|
One mechanism the kidney uses to raise systemic blood pressure is to
a. increase secretion of renin by the juxtaglomerular complex. b. decrease secretion of aldosterone. c. increase release of angiotensin II by the suprarenal glands. d. increase filtration into glomerular (Bowman's) capsule. e. decrease urinary albumin concentration. |
a. increase secretion of renin by the juxtaglomerular complex.
|
|
|
Which of the following formulas will allow you to calculate correctly the net filtration pressure (NFP)?
a. NFP = BP + CsHP - BCOP b. NFP = BP - (CsHP + BCOP) c. NFP = CsHP + BP - BCOP d. NFP = BCOP - BP + CsHP e. NFP = BCOP + (BP - CsHP) |
b. NFP = BP - (CsHP + BCOP)
|
|
|
What is the function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus/complex?
a. help regulate water and electrolyte excretion by the kidneys. b. help regulate urea absorption by the kidneys. c. help regulate blood pressure and the rate of excretion by the kidneys. d. help regulate blood pressure and the rate of blood filtration by the kidneys. |
c. help regulate blood pressure and the rate of excretion by the kidneys.
|
|
|
The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin
a. by an increase in the blood pressure b. when the peritubular capillaries are dilated c. when the specific gravity of urine rises above 1.10 d. by a decrease in the blood pressure e. only in infants |
d. by a decrease in the blood pressure
|
|
|
The macula densa cells respond to
a. antidiuretic hormone b. aldosterone c. changes in pressure in the tubule d. changes in solute content of the filtrate e. ANP |
d. changes in solute content of the filtrate
|
|
|
Which of the following is not correct regarding regulation of urine concentration and volume?
a. A countercurrent mechanism exists to establish and maintain an osmotic gradient. b. The descending limb of the nephron loop is freely permeable to water c. The ascending limb of the nephron loop is selectively permeable to solutes d. The vasa recta protects the cortical osmotic gradient. |
d. The vasa recta protects the cortical osmotic gradient.
|
|
|
The descending limb of the nephron loop
a. pulls water by osmosis into the lumen of the tubule b. contains fluid that becomes less concentrated as it moves down into the medulla c. is not permeable to water d. is freely permeable to sodium and urea e. is freely permeable to water |
e. is freely permeable to water
|
|
|
The mechanism that establishes the medullary osmotic gradient depends most on the permeability properties of the
a. glomerular filtration membrane b. collecting duct c. proximal convoluted tubule d. distal convoluted tubule e. nephron loop |
e. nephron loop
|
|
|
The chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood across the filtration membrane is
a. the design and size of the podocytes b. the size of the pores in the basement membrane of the capillaries c. glomerular blood pressure d. the thickness of the capillary endothelium e. solute composition |
c. glomerular blood pressure
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true concerning the filtration membrane?
a. Filtration slits prevent filtration of blood cells. b. The basement membrane is negatively charged. c. It allows passage of water and all solutes that are smaller than plasma proteins. d. Podocytes help make up the filtration membrane. e. both a and b are not true. |
b. The basement membrane is negatively charged
|
|
|
The mechanism for producing a concentrated urine involves
a. the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the posterior pituitary. b. aquaporins being inserted into the membranes of the collecting duct cells. c. a high concentration of NaCl in the interstitial fluid that surrounds the collecting ducts. d. an increase in facultative water reabsorption. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP) in the glomerulus is generated by
a. blood pressure. b. presence of large, non-diffusible proteins in blood plasma. c. constriction of the efferent arteriole. d. protein in the filtrate. e. filtrate in the capsular space. |
b. presence of large, non-diffusible proteins in blood plasma
|
|
|
A drug that inhibits angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) may lead to
a. less secretion of aldosterone. b. increased urinary loss of sodium. c. reduction of blood pressure. d. decreased sodium reabsorption. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
In response to increased levels of aldosterone, the kidneys produce
a. a larger volume of urine. b. urine with a higher concentration of sodium ions. c. urine with a lower concentration of potassium ions. d. urine with a lower concentration of sodium ions. e. urine with less glucose. |
d. urine with a lower concentration of sodium ions.
|
|
|
Under normal conditions, glomerular filtration depends on three main pressures. From the list below, what are these three main pressures?
1. Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (blood pressure) 2. capsular hydrostatic pressure 3. capsular colloid osmotic pressure 4. blood colloid osmotic pressure 5. urinary bladder hydrostatic pressure a. 1, 2, and 3 are correct. b. 2, 3, and 4 are correct. c. 3, 4, and 5 are correct. d. 1, 2, and 4 are correct. e. 2, 4, and 5 are correct. |
d. 1, 2, and 4 are correct.
|
|
|
About two-thirds of the body fluid is within cells and is termed ________ fluid.
a. intracellular b. intercellular c. extracellular d. interstitial e. vital |
a. intracellular
|
|
|
Intracellular fluid (ICF) is found only within
a. blood vessels. b. lymph. c. the cells of the body. d. the interstitial space. e. the cerebrospinal fluid. |
c. the cells of the body.
|
|
|
Which hormone stimulates the thirst mechanism?
a. ADH b. aldosterone c. BNP d. ANP e. epinephrine |
a. ADH
|
|
|
The principal cation in intracellular fluid is
a. sodium. b. potassium. c. calcium. d. magnesium. e. chloride. |
b. potassium.
|
|
|
The ions in highest concentration in the intracellular fluid are
a. potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate. b. sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate. c. sodium, potassium, and calcium. d. potassium, hydrogen, and chloride. e. proteins, potassium, and phosphate. |
e. proteins, potassium, and phosphate.
|
|
|
The ions in highest concentration in the extracellular fluid are
a. sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate. b. sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate. c. sodium, potassium, and calcium. d. sodium, hydrogen, and chloride. e. sodium, potassium, and phosphate. |
a. sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate.
|
|
|
Which hormone plays a central role in determining the rate of sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion?
a. ADH b. aldosterone c. BNP d. ANP e. epinephrine |
b. aldosterone
|
|
|
Which hormone most affects the osmolarity of blood?
a. ADH b. angiotensin II c. PTH d. ANP e. epinephrine |
a. ADH
|
|
|
Antidiuretic hormone
a. is released from the posterior pituitary gland. b. stimulates water intake. c. stimulates water conservation by the kidneys. d. is produced by the hypothalamus. e. All of the answers are correct. |
e. All of the answers are correct.
|
|
|
Exchange between the two main subdivisions of ECF occurs primarily at the
a. veins. b. muscles. c. tissues. d. capillaries. e. arteries. |
d. capillaries.
|
|
|
The most common problems with electrolyte balance are caused by an imbalance between gains and losses of
a. calcium ions. b. chlorine ions. c. potassium ions. d. sodium ions. e. electrons. |
d. sodium ions.
|
|
|
The primary role of the carbonic-acid-bicarbonate buffer system is to
a. buffer stomach acid. b. buffer carbonic acid formed by carbon dioxide. c. limit pH changes caused by organic and fixed acids. d. buffer the urine. e. increase ventilation. |
c. limit pH changes caused by organic and fixed acids.
|

