![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Three main cavities:
|
Oral, nasal, pharyngeal
|
|
|
Change the resonance by:
|
changing size or shape
|
|
|
Resonance
|
process of filtering sounds produced through the oral, nasal, or pharyngeal cavities by changing configuration of each cavity
|
|
|
Articulation
|
process of shaping the articulators to distinct speech sounds
|
|
|
Articulators
|
used to alter the shape and size of the vocal tract to achieve different speech sounds
|
|
|
Mobile Articulators (7)
|
Mandible †
Jaw Muscles * Face (Lips & Cheeks) * Tongue * Velum (soft palate) * Pharynx (throat) * |
|
|
Immobile Articulators (3)
|
Alveolar ridge †
Hard palate † Teeth † |
|
|
Oral Cavity
|
[from the lips to the posterior faucial pillar]
lips in front cheeks on the sides tongue on the bottom teeth around edges roof of mouth on top palatine tonsils between 2 faucial pillars posterior faucial pillar at back |
|
|
Occlusions
|
Class I (Occlusion) no air allowed
Class II Malocclusion: overbite Class III Malocclusion: underbite |
|
|
Nasal Cavity
|
[from the nares to the nasal choanae (“funnel”)]
nares in front nasal philtrum between nose and lips nasal septum separates left & right sides of nasal cavity 3 nasal conchae (turbinades) create three meatuses (passageways) nasal choanae (“funnel”) at back |
|
|
Pharyngeal Cavity (“Pharynx”
|
[from the nasal choanae and posterior faucial pillar to the laryngeal vestibule]
closed posteriorly & laterally by pharyngeal wall muscles 3 segments: 1. nasopharynx (pharyngeal tonsil and Eustachian tube opening) 2. oropharynx 3. laryngopharynx (hypopharynx) |
|
|
suture joint
|
fusion of skull bones; immobile joint; occurs during development
|
|
|
fontanelle
|
unfused connection between skull bones in infants, before fusion
|
|
|
foramen
|
hole (be sure to specify which hole)
|
|
|
symphysis
|
a point of union in a single bone where two halves once joined
|
|
|
alveolus
|
a small hole/pocket/sack
|
|
|
mental
|
chin
|
|
|
Facial bones
|
Palatine
Zygomatic Mandible Maxilla Hyoid |
|
|
Landmarks of Mandible
|
corpus (body) of mandible
mental symphysis mental protuberance alveolar arch mylohyoid groove angle of mandible ramus of mandible coronoid process condylar process |
|
|
Landmarks of Maxilla
|
frontal process
zygomatic process alveolar process anterior nasal spine palatine process alveolar ridge intermaxillary suture premaxillary suture |
|
|
Landmarks of Hyoid
|
Corpus
Greater horn Lesser horn |
|
|
Cranial bones
|
Sphenoid
Temporal |
|
|
Landmarks of sphenoid bone
|
medial pterygoid plate
lateral pterygoid plate |
|
|
Landmarks of temporal bone
|
external auditory meatus
mastoid process styloid process zygomatic process of temporal bone + temporal process of zygomatic bone form zygomatic arch |
|
|
Functions of facial muscles
|
• Speech production [Filter]
• Facial expression • Chewing, eating from a utensil, prevent drooling, sucking from a straw |
|
|
Functions of Jaw Muscles
|
• Speech production [Filter]
• Chewing & biting (among strongest muscles in body) |
|
|
Functions of the Tongue
|
• Speech production [Filter] (tongue as mobile articulator)
• Chewing & swallowing • Taste sensation |
|
|
oris
|
mouth
|
|
|
labii
|
lips
|
|
|
anguli oris
|
corner of mouth
|
|
|
orbicularis
|
makes a complete circle
|
|
|
mental & “genio-“
|
chin
|
|
|
glossal
|
tongue
|
|
|
all muscles of the face
|
are innervated by CN VII (Facial Nerve).
occur as a pair, on the left & right sides. |
|
|
Origin: orbicularis oris
(superior & inferior) |
corner of lips
|
|
|
Insertion: orbicularis oris
(superior & inferior) |
opposite corner of lips
|
|
|
origin: risorius
|
posterior face & masseter muscle
|
|
|
insertion: risorius
|
corner of mouth
|
|
|
origin: zygomatic
|
zygomatic bone
|
|
|
Insertion: zygomatic
|
corner of mouth & upper lip
|
|
|
origin: levator labii superioris
|
infraorbital margin of maxilla
|
|
|
insertion: levator labii superioris
|
upper lip
|
|
|
origin: levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
|
frontal process of maxilla
|
|
|
insertion: levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
|
upper lip
|
|
|
Origin: levator anguli oris
|
maxilla (below infraorbital margin)
[deep to levator labii superioris] |
|
|
Insertion: levator anguli oris
|
corner of mouth
|
|
|
origin: depressor labii inferioris
|
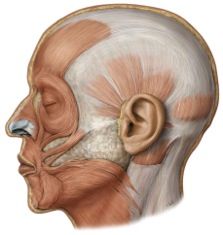
mandible
[deep to depressor anguli oris] |
|
|
insertion: depressor labii inferioris
|
lower lip
|
|
|
origin: depressor anguli oris
|
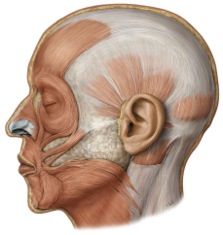
mandible
|
|
|
insertion: depressor anguli oris
|
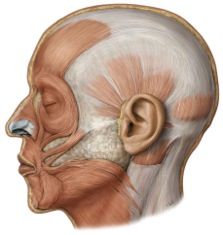
corner of mouth &
upper lip |
|
|
origin: mentalis
|
mandible
[deep to depressor labii inferioris] |
|
|
insertion: mentalis
|
skin of chin below
|
|
|
origin: buccinator
|
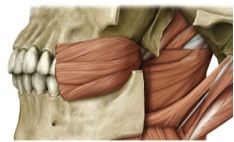
pterygomandibular ligament
alveolar processes of mandible & maxilla |
|
|
insertion: buccinator
|
corners of mouth
|
|
|
All jaw muscles but geniohyoid innervated by
|
CN V (Trigeminal)
|
|
|
geniohyoid innervation:
|
*CN XII (Hypoglossal)
|
|
|
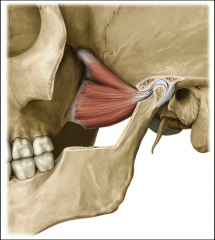
origin: temporalis
|
temporal bone
|
|
|
insertion: temporalis
|
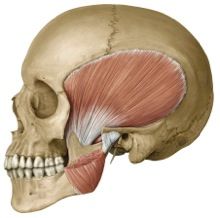
coronoid process of mandible
|
|
|
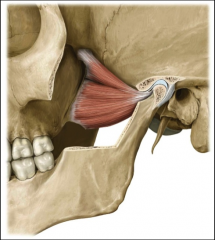
origin: masseter
|
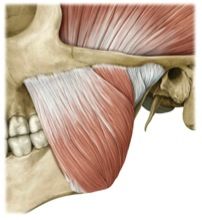
zygomatic arch
|
|
|
insertion: masseter
|
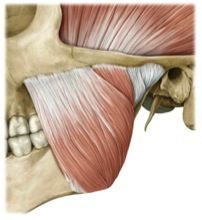
angle & ramus of mandible
|
|
|
origin: medial pterygoid
|
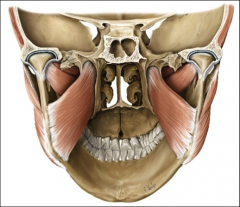
medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate (sphenoid bone)
|
|
|
insertion: medial pterygoid
|
medial surface of angle of mandible
|
|
|
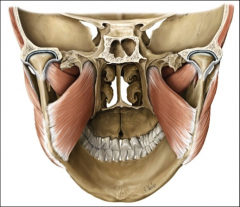
origin: lateral pterygoid
|
lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate (sphenoid bone)
|
|
|
insertion: lateral pterygoid
|
condylar process of mandible
|
|
|
origin: anterior belly of digastric
|
symphysis of mandible
|
|
|
insertion: anterior belly of digastric
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
origin: mylohyoid
|
mylohyiod groove of mandible
|
|
|
insertion: mylohyoid
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
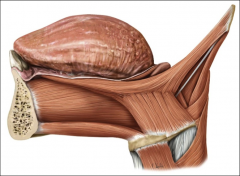
origin: geniohyoid
|
Symphysis of mandible
|
|
|
insertion: geniohyoid
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
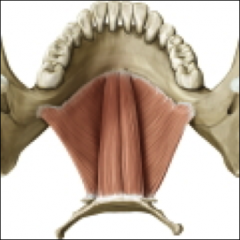
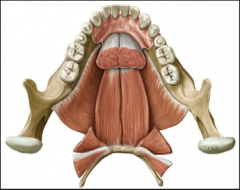
Intrinsic muscles of the tongue
|
superior longitudinal muscles
inferior longitudinal muscles transverse muscles vertical muscles The intrinsic muscles of the tongue help with fine, controlled movements for articulation. Each of these muscles occurs as a pair, on the left & right sides. |
|
|
EXTRINSIC MUSCLES OF THE TONGUE
|
genioglossus
hyoglossus styloglossus *The extrinsic muscles of the tongue help with gross movements of the tongue as a unit. *The bulk of the tongue is made up of the genioglossus muscle. *Each of these muscles occurs as a pair, on the left & right sides. |
|
|
course: superior longitudinal muscles
|
back to front of tongue
|
|
|
action: superior longitudinal muscles
|
elevate tongue tip
pull tongue to side *retract tongue |
|
|
course: inferior longitudinal muscles
|
back to front of tongue
|
|
|
action: inferior longitudinal muscles
|
depress tongue tip
pull tongue to side *retract tongue |
|
|
course: transverse muscles
|
midline to lateral edges of tongue
|
|
|
action: transverse muscles
|
narrow the tongue
|
|
|
course: vertical muscles
|
inferior to superior surface of tongue
|
|
|
action: vertical muscles
|
flatten the tongue
pull tongue downward |
|
|
origin: genioglossus
|
mental symphysis of mandible
|
|
|
insertion: genioglossus
|
all along tongue at midline (fan-like)
|
|
|
action: genioglossus
|
protrude tongue anteriorly
depress tongue inferiorly |
|
|
origin:hyoglossus
|
greater horns of hyoid bone
|
|
|
insertion: hyoglossus
|
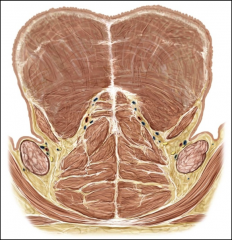
sides of tongue
|
|
|
action: hyoglossus
|
pulls sides of tongue down & back
|
|
|
origin: styloglossus
|
styloid process of temporal bone
|
|
|
insertion: styloglossus
|
sides of tongue
|
|
|
action: styloglossus
|
pulls tongue back (retract) & up (raise)
|
|
|
innervation of tongue muscles
|
CN XII hypoglossal nerve
|
|
|
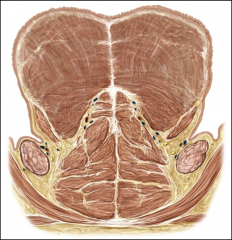
Landmarks of oral cavity
|
labial frenulum
alveolar ridge hard palate velum (soft palate) uvula buccal cavities anterior faucial pillar (-palatoglossal arch/muscle) palatine tonsil posterior faucial pillar (- palatopharyngeal arch/muscle) |
|
|
Describe actions of velum related to oral/nasal speech sound production.
|
raises to close the velopharyngeal port for oral sounds and swallowing.
lowers to open the velopharyngeal port for nasal sounds (m, n, ŋ) and breathing. |
|
|
The bulk of the velum is made up of the
|
levator veli palatini muscle.
|
|
|
origin: levator veli palatini
|
temporal bone, near styloid process
|
|
|
action: levator veli palatini
|
pull velum up & back
|
|
|
insertion: levator veli palatini
|
midline of velum
|
|
|
origin: musculus uvulae
|
posterior nasal spine
|
|
|
insertion: musculus uvulae
|
uvula
|
|
|
action: musculus uvulae
|
shorten velum & uvula
|
|
|
origin: palatoglossus
(anterior faucial pillar) |
midline of velum
toward front |
|
|
insertion: palatoglossus
(anterior faucial pillar) |
sides of tongue
|
|
|
action: palatoglossus
(anterior faucial pillar) |
depress velum
(raise tongue) |
|
|
origin: palatopharyngeus
(posterior faucial pillar) |
midline of velum
toward back |
|
|
insertion: palatopharyngeus
(posterior faucial pillar) |
thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
action: palatopharyngeus
(posterior faucial pillar) |
depress velum
(narrow pharynx) |
|
|
action: *tensor veli palatini
|
(opens Eustachian tube)
|
|
|
innervation of velum muscles (except tensor veli palatini)
|
X (Vagus)
pharyngeal branch |
|
|
innervation of tensor veli palatini
|
V (Trigeminal)
|
|
|
Pharynx
|
courses from the nasal choanae to the laryngeal vestibule
(or skull base to the esophagus) |
|
|
three parts of the pharynx:
|
nasopharynx – the space behind the nose and above the velum
oropharynx – the space behind the posterior faucial pillar, below the velum, and down to the hyoid bone hypopharynx (laryngopharynx) – the space below the hyoid bone and above the esophagus (not including the larynx) |
|
|
origin: superior pharyngeal constrictor
|
pterygomandibular ligament
(buccinator) |
|
|
insertion: superior pharyngeal constrictor
|
midline of posterior pharynx
|
|
|
action: superior pharyngeal constrictor
|
narrow nasopharynx
(close velopharyngeal port - Passavant’s pad) |
|
|
origin: middle pharyngeal constrictor
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
insertion: middle pharyngeal constrictor
|
midline of posterior pharynx
|
|
|
action: middle pharyngeal constrictor
|
narrow oropharynx
|
|
|
origin: inferior pharyngeal constrictor
|
sides of thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
insertion: inferior pharyngeal constrictor
|
midline of posterior pharynx
|
|
|
action: inferior pharyngeal constrictor
|
narrow hypopharynx
|
|
|
origin: cricopharyngeus
(“upper esophageal sphincter; UES”) |
sides of cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
insertion: cricopharyngeus
(“upper esophageal sphincter; UES”) |
midline of posterior pharynx (top of esophagus)
|
|
|
action: cricopharyngeus
(“upper esophageal sphincter; UES”) |
constrict upper esophageal opening
|
|
|
action: salpingopharyngeus
|
raise & dilate pharynx
|
|
|
action: stylopharyngeus
|
raise & dilate pharynx
|
|
|
innervation of pharyngeal muscles (except stylopharyngeus)
|
X (Vagus)
pharyngeal branch |
|
|
innervation of stylopharyngeus
|
IX (Glossopharyngeal)
|
|
|
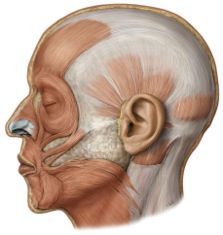
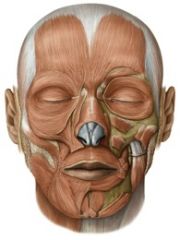
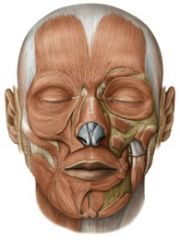
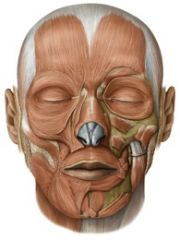
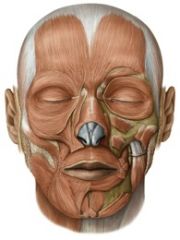
Facial muscles: (10)
|
orbicularis oris
risorius zygomatic levator labii superioris levator labii superioris alaeque nasi levator anguli oris depressor labii inferioris depressor anguli oris mentalis buccinator |
|
|
Jaw muscles: (7)
|
temporalis
masseter medial pterygoid lateral pterygoid anterior belly of digastric mylohyoid geniohyoid |
|
|
Action: orbicularis oris
(superior & inferior) |
Round, Protrude, & Compress Lips
|
|
|
Action: Retract Lips (smile)
|
risorius
zygomatic |
|
|
action: Elevate Upper Lip
|
levator labii superioris
levator labii superioris alaeque nasi levator anguli oris |
|
|
action: Depress Lower Lip
|
depressor labii inferioris
depressor anguli oris |
|
|
action: mentalis
|
Protrude Lower Lip & Wrinkle Chin (Pout)
|
|
|
action: buccinator
|
Compress Cheeks
|
|
|
action: Elevate Mandible (Close Mouth)
[Must work against gravity & apply force to chew food] |
temporalis
masseter medial pterygoid |
|
|
action: lateral pterygoid
|
Protrude Jaw (when bilaterally contracted)
Lateralize Jaw (when unilaterally contracted) |
|
|
action: Actively Depress Mandible (Open Mouth)
(*When hyoid is anchored down by infrahyoid muscles*) |
anterior belly of digastric
mylohyoid geniohyoid |

