![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
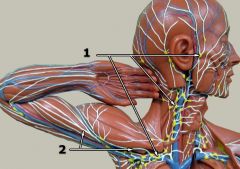
What is #1?
|
Lymph nodes (general)
|
|
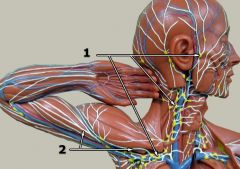
What is #2?
|
Lymph vessels
|
|
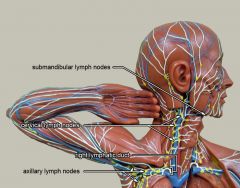
What is #1?
|
Submandibular lymph nodes
|
|
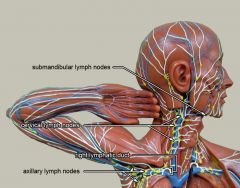
What is #2?
|
Cervical lymph nodes
|
|
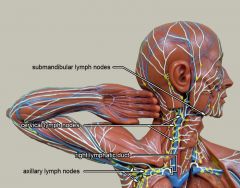
What is #3?
|
Right lymphatic duct
|
|
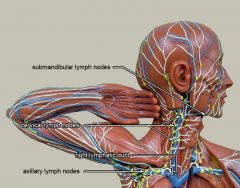
What is #4?
|
Axillary lymph nodes
|
|
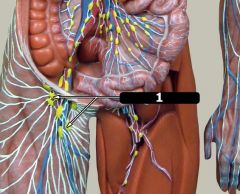
What is #1?
|
Inguinal lymph nodes
|
|
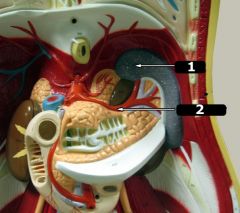
What is #1?
|
Spleen
|
|
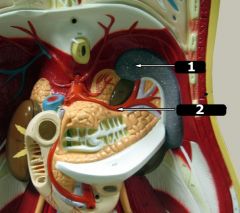
What is #2?
|
Splenic artery
|
|
|
bifurcation
|
branch
|
|
|
Blood moves slowest in which vessels? Why?
|
Capillaries because they have large diameters.
|
|
|
Blood moves fastest in which vessels? Why?
|
Artery because they have the smallest diameters.
|
|
|
Considering a corresponding artery and vein which has a smaller diameter? Why?
|
Arteries have a smaller diameter because they have to pump blood.
|
|
|
volume pulse
|
the change in blood volume with each cardiac cycle
|
|
|
What occurrence in the body is responsible for the dicrotic notch?
|
recoil of aorta
|
|
|
amplitude
|
height of pulse recording
|
|
|
Notice that the slope of the rising edge of the volume pulse is much steeper than the slope of the falling edge. Why?
|
Artery contraction is active [steep rise] and when blood returns, it's passive [not so steep fall].
|
|
|
What changes in the finger are represented by the amplitude changes?
|
The amount of blood going to the finger.
|
|
|
Does the amplitude range increase or decrease when the person stands? Why?
|
Decreases b/c there is less blood going to the finger.
|
|
|
What is the heart rate after the person stands up? Why?
|
73 bpm b/c it had to pump blood to the legs, which is farther.
|
|
|
What is the heart rate when the recording returns to normal?
|
Returns to normal
|
|
|
Explain ALL of the above changes in terms of “homeostasis”.
|
Your heart only works as hard as your body needs it to and will compensate for changes needed.
|
|
|
How much does the heart rate change after exercise?
|
Heart rate increased by 10 bpm.
|
|
|
Does the amplitude range increase or decrease right after exercise? Explain.
|
Amplitude increased b/c more blood was required for muscle contraction.
|
|
|
What does the change in volume pulse amplitude and heart rate indicate about changes in the volume of blood flowing in the finger?
|
More peripheral blood flow during exercise and even for minutes after.
|
|
|
Does your data support the expected need for more energy and blood flow to muscles during exercise?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
How does the amplitude (height) of the volume pulse for the cooled finger compare with the recording at normal room temperature?
|
Decreased amplitude and decreased heart rate
|
|
|
Can you explain this difference in terms of the effect of cold on peripheral blood vessels?
|
Cold elevates pulse pressure, narrows vessels, and increases peripheral resistance
|
|
|
What happens to the volume pulse amplitude when the finger is heated?
|
Increased amplitude and increased heart rate
|
|
|
Can you explain this difference in terms of the effect of heat on peripheral blood vessels?
|
Heat stress induces vasodilation, which increases blood flow to area and reduces resistance.
|
|
|
What receptors does nicotine attach to in the nervous system?
|
Nicotinic cholinergic receptors
|
|
|
Where are these nicotinic cholinergic receptors?
|
Target organs
|
|
|
How is tobacco smoke able to cause such a wide range of effects?
|
Due to acting on receptors of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
|
|
|
radial artery pulse
|
groove medial to styloid process of radius
|
|
|
carotid artery pulse
|
side of the neck
|
|
|
temporal artery pulse
|
on the temple above and to side of eye
|
|
|
brachial artery pulse
|
inner side of biceps
|
|
|
popliteal artery pulse
|
behind knee
|
|
|
What does your heart rate returning to resting rate indicate about cardiovascular condition?
|
The faster your heart returns to resting value after exercise, the healthier you are.
|
|
|
resting (sitting) pulse rate
|
your pulse at rest
|
|
|
What is the class average pulse for males?
|
69
|
|
|
How do the class' heart rates compare to each other?
|
Females have a slightly higher rate than males
|
|
|
How do the class' heart rates compare to expected results?
|
Women are suppose to have a slightly higher rate than men. The rates fit the norm.
|
|
|
sphygmomanometer
|
instrument used to measure peripheral blood pressure indirectly
|
|
|
manometer
|
used to measure the pressure within the cuff in millimeters of mercury
|
|
|
respiration rate
|
how many breaths an individual takes per minute
|
|
|
systolic pressure
|
pressure at the time the first sound is heard
|
|
|
diastolic pressure
|
pressure at the time the sound stops
|
|
|
pulse pressure
|
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
|
|
|
exercise
|
task performed to raise heart rate
|
|
|
A patient has the following symptoms: below normal blood pressure and edema in the hands, legs, and feet. Assume that the patient has damage to one of the ventricles of the heart. On the basis of the symptoms, which ventricle do you believe was damaged, and why?
|
The right ventricle because it pumps blood to the body via the aorta.
|
|
|
Assume a person has a total of 5000 ml. of blood. What sequence of cardiovascular changes would you expect to occur if 500 ml. were suddenly removed from the person, and why?
|
EPO would stimulate the producation of RBCs and facilitate their maturation to replenish blood loss.
|
|
|
In the person from the previous question, suppose the loss of blood continues constantly. What sequence of changes would you expect to occur, and why?
|
Very low blood pressure until the point of death
|
|
|
Nicotine is given to a person who does not normally use the drug. For each of these aspects of cardiovascular physiology, what effect, if any, do you expect, and why?
|
Increased peripheral resistance, heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, and blood pressure.
|
|
|
What is the class average pulse for females?
|
76
|
|
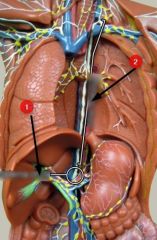
What is #1?
|
Cisterna chyli
|
|
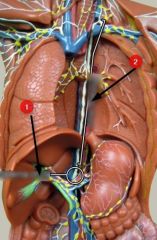
What is #2?
|
Thoracic duct
Note: Leads to cisterna chyli |
|
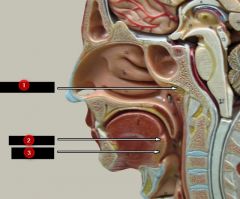
What is #1?
|
Pharyngeal tonsil
|
|
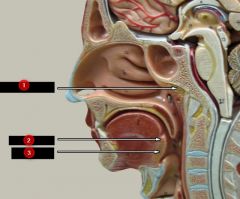
What is #2?
|
Palatine tonsil
|
|
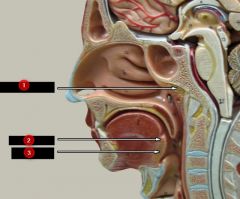
What is #3?
|
Lingual tonsil
Note: At the very bottom |

