![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
229 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pH less than 7 is
|
Acidic
|
|
|
pH over 7 is
|
Alkaline
|
|
|
Blood pH
|
7.35 - 7.45
|
|
|
Organs that regulate pH |
Lungs, Kidneys, and Buffers
|
|
|
Purpose of glucose
|
Most important energy source. A monosaccharide, or simple sugar, that servers as the principal fuel for the cells of the body. Used by cells as an immediate source of energy. Stored as fat and burned as fuel at a later time.
|
|
|
Where are triglycerides derived?
|
Are ester derived from glycerol and 3 fatty acids
|
|
|
Where is cholesterol derived?
|
Steroid, lipid- is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell membrane
|
|
|
Smallest pathogen
|
Virus
|
|
|
Largest pathogen
|
Bacteria
|
|
|
Epidemiology
|
The study of the occurrence and distribution of disease in a population
|
|
|
Resistance
|
The ability to ward off disease
|
|
|
Susceptibility
|
A lack of resistance
|
|
|
Reservoir of infection
|
A continual source of infection. Can be living organisms such as humans and other animals. Can be a non-living vector. Contaminated soil and water also serve as inanimate reservoirs.
|
|
|
Fomite
|
Non-living vector
|
|
|
Normal Flora
|
A group of microorganisms that colonize a host without causing diease
|
|
|
Sterilization
|
A process that destroys all living organisms
|
|
|
Vector
|
A carrier of pathogens from host to host. The mosquito is the animal vector carrying the plasmodium (malaria) to humans. A contaminated syringe is a non-living vector.
|
|
|
Antibiotic
|
Chemical used to treat bacterial infections. A broad - spectrum one destroys many different types of bacteria, whereas a narrow-spectrum one only destroys a few types.
|
|
|
Disease
|
A failure of the body to function normally
|
|
|
Nosocomial
|
Hospital acquired infection that is most often transmitted from patient to patient by direct contact. Today, they are caused by health care professionals not washing their hands.
|
|
|
Purpose of mucus membranes
|
Sheets of tissue that cover surfaces, line body cavities, and support organs.
|
|
|
4 major types of tissues
|
Epithelial, Connective, Nervous, Muscular.
|
|
|
Also called the epithelium
|
Epithelial tissue
|
|
|
Most abundant tissue
|
Connective tissue
|
|
|
3 types of muscular tissue
|
Skeletal, Smooth (visceral), and Cardiac.
|
|
|
Types of epithelial membranes
|
Cutaneous, Mucous, Serous.
|
|
|
Types of serous membranes
|
Pleurae, Pericardium, Peritoneum
|
|
|
Types of connective tissue
|
Synovial, Periosteum, Perichondrium, Meninges, Fascia
|
|
|
Lines joint cavities, secretes synovial fluid
|
Synovial
|
|
|
Covers bones; contains the blood vessels that supply the bone
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
Covers cartilage; contains capillaries that nourish the cartilage
|
Perichondrium
|
|
|
Covers the brain and spinal cord
|
Meninges
|
|
|
Appears throughout the body
|
Fascia
|
|
|
Classification of epithelial membranes
|
Cutaneous, mucous, and serous.
|
|
|
Classification of connective tissues
|
Synovial, periosteum, perichondrium, meninges, fascia
|
|
|
Functions of the skin
|
Serves as a mechanical barrier, protects internal structures, participates in the immune system, acts as a gland for vitamin D synthesis, performs excretory function, performs sensory role, helps regulate body temperature.
|
|
|
Integumentary glands that secrete earwax
|
Ceruminous glands
|
|
|
Cerumen
|
Ear wax
|
|
|
Cerumen is found in
|
The external auditory canal of the ear
|
|
|
Mottled pigmentation
|
Discolored areas of the skin
|
|
|
Sallowness
|
A yellow discoloration of the skin
|
|
|
Telangiectasis
|
The dilation of small blood vessels under the skin
|
|
|
Elastosis
|
The destruction pf the elastic and collagen tissue (causing lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin)
|
|
|
Most common type of skin cancer for fair skin
|
Basal cell
|
|
|
Most common type of skin cancer for dark skin
|
Squamous cell
|
|
|
Cancer that is rare in dark skin
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
Types of cancer
|
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma
|
|
|
Exposure to the sun causes
|
Precancerous and cancerous skin lesions, benign tumors, fine and coarse wrinkles, freckles, mottled pigmentation, sallowness, telangiectasis, elastosis, common skin cancer.
|
|
|
Skin color is determined by
|
Genes, physiology, and sometimes pathology
|
|
|
Dark pigment
|
Melanin
|
|
|
Melanocyte malfunctions
|
Albinism, vitiligo, moles
|
|
|
Blushing
|
Blood vessel dilation
|
|
|
Pallor
|
Blood vessel constriction
|
|
|
Cyanosis
|
Poor oxygenation ; bluish tint
|
|
|
Jaundice
|
Bilirubin deposition ; yellowing
|
|
|
Bronzing
|
Melanin overproduction
|
|
|
Ecchymosis
|
Black and blue bruising
|
|
|
Nonmelanomas
|
Neoplasms that arise from the epithelial tissue and most commonly occurs on sun exposed areas of the body
|
|
|
Malignant melanoma
|
Malignant neoplasm of the melanocytes
|
|
|
Pustule
|
A small pus-containing elevation of the skin that is seen in conditions such as acne and impetigo
|
|
|
A pimple is a
|
Small pustule
|
|
|
Macule
|
Flat lesion, also called a blemish. Include freckles, flat mole (nevus), vitiligo, measles, smallpox, and petechial
|
|
|
Papule
|
Elevated lesion that looks like a solid blister.
|
|
|
Vesicle
|
A blister- round lesion filled with serous fluid.
|
|
|
Examples of papules
|
Insect bites, some skin cancers, wart.
|
|
|
Examples of vesicles
|
Herpes zozster (shingles) contact dermatitis
|
|
|
Wheal
|
A hive / urticarial: multiple hives, itching skin eruption
|
|
|
Ulcer
|
Crater-like lesion formed by the loss of the epidermis and the dermis
|
|
|
Types of joints
|
Immovable, slightly movable, freely movable, hinge, ball-and-socket, pivot, saddle, gliding, condyloid.
|
|
|
Immovable joints
|
Cranial bones
|
|
|
Slightly movable joints
|
Intervertebral disc; symphysis pubis
|
|
|
Hinge joints
|
Elbows, knees, fingers.
|
|
|
Ball-and-socket joints
|
Shoulders, hips
|
|
|
Pivot joints
|
Atlas-axis joint (side to side movement) ; head saying "no"
|
|
|
Saddle joints
|
Carpometacarpal , thumb
|
|
|
Gliding joints
|
Wrist (carpals)
|
|
|
Condyloid joints
|
Knuckles, temporal bone, and mandible (jaw)
|
|
|
Tendons
|
Cordlike structures that attach muscles to bones
|
|
|
Ligaments
|
Cross joints and attach bone to bone
|
|
|
Flexion
|
Bending of joints; decrease the angle.
|
|
|
Extension
|
Straightening a joint to increase angle
|
|
|
Adduction
|
Movement toward the midline of the body
|
|
|
Abduction
|
Movement away from the midline of the body
|
|
|
Planter flexion
|
Bending the foot down, as in toe dancing
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion
|
Bending the foot up toward the leg
|
|
|
Pronation
|
Turning the palm of the hand so that it faces down
|
|
|
Circumduction
|
Combination movement, as in circling the arm
|
|
|
Supination
|
Turning the hand so that the palm faces upward
|
|
|
Structures of the brain
|
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brain Stem
|
|
|
Parts of the cerebrum
|
Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
|
|
|
Parts of the diencephalon
|
Thalamus, hypothalamus
|
|
|
Parts of the brain stem
|
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum
|
|
|
Frontal Lobe "Executive"
|
Motor area, personality, behavior, emotional expression, intellectual functions, memory storage
|
|
|
Parietal lobe
|
Somatosensory area (especially skin, muscle, taste, speech, reading
|
|
|
Occipital lobe
|
Vision, vision-related reflexes and function
|
|
|
Temporal lobe
|
Hearing (auditory area), smell (olfactory), taste, memory storage, part of speech area
|
|
|
Thalamus
|
Relay structure and processing center for most sensory information going to the cerebrum
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
Autonomic nervous system; regulation of temperature, water balance, sex, thirst, appetite, some emotions (pleasure and fear) regulates the pituitary gland and controls endocrine function
|
|
|
Midbrain
|
Relays information (sensory and motor) associated with visual and auditory reflex
|
|
|
Pons
|
Relays information (sensory and motor) plays a role in respirations
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
Vital function (regulation of heart rate, blood flow, blood pressure, respiratory centers), reflex center for coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting
|
|
|
Cerebellum
|
Smooth out and coordinates voluntary muscle activity; helps in maintaining balance and muscle tone
|
|
|
How many pairs of cranial nerves?
|
12
|
|
|
CN I
|
Olfactory nerve (smell)
|
|
|
CN II
|
Optic nerve (sight)
|
|
|
CN III
|
Oculomotor (most movements of eyeball, eyelid, and pupil size)
|
|
|
CN IV
|
Trochlear (movement of eyeball)
|
|
|
CN V
|
Trigeminal (chewing; sensations in face, scalp, cornea, teeth)
|
|
|
CN VI
|
Abducens (eyeball movement)
|
|
|
CN VII
|
Facial nerve (facial expression, salivation, taste, tearing, and blinking)
|
|
|
CN VIII
|
Vestibulocochlear (hearing, balance)
|
|
|
CN IX
|
Glossopharyngeal (swallowing, secretion of saliva; taste)
|
|
|
CN X
|
Vagus ("wanderer nerve") innervates many thoracic and abdominal organs and voice box; sensory arm of baroreceptor reflex
|
|
|
CN XI
|
Accessory (head movement and shrugging shoulders, swallowing)
|
|
|
CN XII
|
Hypoglossal (speech and swallowing)
|
|
|
12 cranial nerves
|
Olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocohlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal
|
|
|
Types of neurons
|
Afferent, Efferent, and Interneuron
|
|
|
Sensory neurons. Carries information from the periphery toward the CNS
|
Afferent
|
|
|
Motor neurons. Carries information from the CNS toward the periphery
|
Efferent
|
|
|
Only found in the CNS. Forms connections between sensory and motor neurons. Play a role in thinking, learning, and memory
|
Interneuron
|
|
|
Parts of the Central Nervous System
|
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
|
|
|
Function of the eye
|
Sense of sight (vision).
|
|
|
The organ of hearing
|
Ear
|
|
|
Master gland of the ear
|
Anterior pituitary - controlled by the hypothalamus
|
|
|
Structure of the ear
|
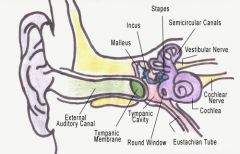
|
|
|
How the ear hears
|
Sound waves enter through the external part causing vibrations. Contains the receptors for balance.
|
|
|
Hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex. Acts primarily on the upper collection duct of the nephron unit.
|
Aldosterone
|
|
|
Red Blood Cells (RBC) count for men
|
4.5 - 6.0 million/uL
|
|
|
Red Blood Cells (RBC) count for women
|
4.2 - 5.4 million/uL
|
|
|
Hemoglobin (Hgb) count for men
|
13.5 - 17.5 g/100 mL
|
|
|
Hemoglobin (Hgb) count for women
|
12 - 16 g/100 mL
|
|
|
Hematocrit (Hct) count for men
|
40% - 50%
|
|
|
Hematocrit (Hct) count for women
|
37% - 47%
|
|
|
White Blood Cells (WBC) count for men and women
|
5,000 - 10,000/uL
|
|
|
Platelet (thrombocytes) count for men and women
|
150,000 - 450,000/uL
|
|
|
Both A & B antigens on RBC. Neither anti-A nor anti-B antibodies in plasma
|
Type AB blood
|
|
|
Neither A nor B antigen on RBC. Both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in plasma
|
Type O blood
|
|
|
What is a cardiac cycle?
|
A sequence of events that occurs during one heartbeat. It is the contractions (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the chambers of the heart
|
|
|
Relaxation of the myocardium; blood fills a chamber during it
|
Diastole
|
|
|
Contraction of the heart muscle; contractions of the heart muscle ___ pumps blood out of a chamber
|
Systole
|
|
|
Carries blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs and back to the left atrium of the heart. Transports unoxygenated blood to the lungs, where oxygen is located and carbon dioxide is unloaded
|
Pulmonary circulation
|
|
|
The largest circulation. Provides the blood supply to the rest of the body. Carries oxygen and other nutrients to the cells and picks up carbon dioxide and other waste.
|
Systemic circulation
|
|
|
Purpose of valves
|
Only in veins
|
|
|
What do one way valves do?
|
Keeps the blood flowing toward the heart
|
|
|
Artery
|
Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
|
|
|
Arteriole
|
Small artery that is composed largely of smooth muscle, found between the large artery and the capillaries; also called resistance vessel
|
|
|
Capillary
|
Smallest and most numerous of the blood vessels; site of exchange of nutrients and waste between blood and tissue; also called exchange vessels
|
|
|
Venule
|
Tiny veins that connect capillaries to a larger vein
|
|
|
Vein
|
Blood vessel that takes blood toward the heart
|
|
|
Aorta
|
Largest artery that conducts blood from the left ventricle of the heart
|
|
|
Capacitance vessels
|
Refers to the veins and specifically to their ability to store blood
|
|
|
Conductance vessels
|
Blood vessels that are primarily concerned with carrying blood to smaller blood vessels; functional name for arteries
|
|
|
Splanchnic circulation
|
Blood supply of the abdominal organs
|
|
|
Vena cava
|
Large veins that take unoxygenated blood to the right atrium; superior and inferior
|
|
|
3 main functions of lymphatic organs
|
Returns interstitial fluid to the blood, absorbs fats and fat-soluble vitamins, helps the body defend itself against infection.
|
|
|
35% right lymphatic duct, 65% thoracic duct
|
Lymphoid organs
|
|
|
Lymph nodes
|
Lymphatic vessels drain most of the body
|
|
|
Tonsil
|
Filter tissue fluid contaminated by pathogens that enter the body through the nose, mouth, or both.
|
|
|
Often the target of tonsillectomy
|
Palatine tonsils
|
|
|
Assists development of immune system before puberty, secreted thymosins, produces T cells
|
Thymus glands
|
|
|
Red pulp: venous sinuses filled with blood and phagocytes. White pulp: contains lymphocyes. Stores RBCs and platelets. Removes old RBCs and platelets.
|
Spleen
|
|
|
Lower respiratory system
|
Lower trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, lungs, pleural membrane, muscles of respiration
|
|
|
Upper respiratory system
|
Nose and nasal passages, pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe)
|
|
|
Conduct air to bronchioles
|
Bronchi
|
|
|
Bronchioles
|
Smooth muscle determines diameter, regulates air flow to the alveoli
|
|
|
Alveoli
|
Small grapelike structures; air sacs that exchange O2 and CO2 with blood in pulmonary circulation
|
|
|
How many lobes does the right lung have?
|
3; superior, middle, inferior.
|
|
|
How many lobes does the left lung have?
|
2; superior, inferior
|
|
|
Parietal pleura
|
Outer serous membrane
|
|
|
Visceral pleura
|
Lines inside of lungs
|
|
|
Intrapleuralspace
|
Located between parietal and visceral pleurae
|
|
|
2 factors that oppose lung expansion
|
Elastic recoil & surface tension
|
|
|
Eupnea
|
Normal, quiet breathing
|
|
|
Apnea
|
Temporary cessation of breathing
|
|
|
Dyspnea
|
Difficult or labored breathing
|
|
|
Tachypnea
|
Rapid breathing
|
|
|
Orthopnea
|
Difficulty in breathing relieved by sitting up
|
|
|
Hyperventilation
|
Increase in rate and depth
|
|
|
Hypoventilation
|
Decrease in rate and depth
|
|
|
Hypoxemia
|
Abnormally low concentration of O2 in the blood
|
|
|
Hypercapnia
|
Abnormally high concentration of CO2 in the blood
|
|
|
Hypocapnia
|
Abnormally low concentration of CO2 in the blood
|
|
|
Purpose for surfactant
|
Keeps the alveoli from collapsing
|
|
|
Functional unit of the urinary system
|
Nephron
|
|
|
Normal constituents of urine
|
Water, urea, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, phosphates, uric acid, organic salts, and the pigment urobilin
|
|
|
Abnormal constituents of urine
|
Keytone bodies, protein, bacteria, blood, glucose, pus, and certain crystals
|
|
|
Parts of a nephron
|
Tubular component (renal tubules) and a vascular component (blood vessels)
|
|
|
Fluid balance
|
Intake and output should be the same
|
|
|
Fluid regulation
|
The control of the amount of fluids a body needs to survive; essential to homeostasis
|
|
|
First line of defense in the regulation of pH
|
Buffer system
|
|
|
Intracellular compartment
|
63% of water is located here. It includes all the water located in all the cells of the body
|
|
|
Extracellular compartment
|
Includes the fluid located outside all the cells and represents about 37% of the total body water. Includes the water located between cells, called interstitial fluid, water within the blood vessels (plasma), and water within lymphatic vessels (lymph)
|
|
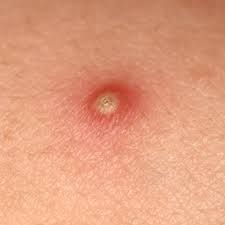
|
Pustule
|
|
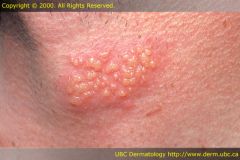
|
Vesicle
|
|
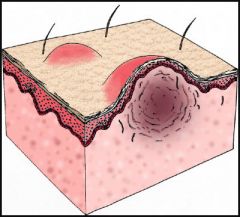
|
Papule
|
|
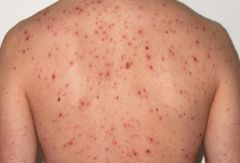
|
Macule
|
|
|
Ulcer
|
|
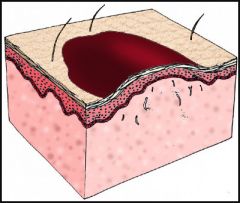
|
Wheal
|
|
|
Hydrochloric acid pH
|
0
|
|
|
Lemon juice pH
|
2
|
|
|
Stomach contents pH
|
1-4
|
|
|
Vinegar, wine pH
|
3
|
|
|
Black coffee pH
|
5
|
|
|
Pure H2O pH
|
7
|
|
|
Intestinal contents pH
|
8-10
|
|
|
Soap solutions pH
|
10
|
|
|
Household ammonia pH
|
12
|
|
|
Sodium hydroxide pH
|
14
|
|
|
Has a bitter taste and is slippery like soap
|
Base
|
|
|
An electrolyte that dissociates into a hydrogen ion (H+) and an anion
|
Acid
|
|
|
The ability to perform work
|
Energy
|
|
|
How pathogens are spread
|
Droplet infection, direct contact, contaminated food, contaminated water, body fluids, vectors
|
|
|
Major bones of the body
|
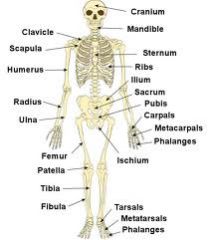
|
|
|
Gland that is both exocrine and endocrine
|
Pancreas
|
|
|
Most common blood type
|
O
|
|
|
Least common blood type
|
AB
|
|
|
Blood types
|
A, B, AB, O
|
|
|
Digestion from mouth to anus
|
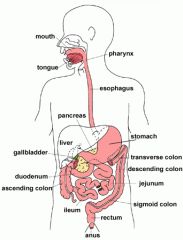
|
|
|
External genitalia of the male
|
Penis, scrotum
|
|
|
Accessory or supportive sex glands of the male
|
Seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral (Cowper's) glands
|
|
|
Reproductive ducts of the male
|
Ductus (vas) deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
|
|
|
Essential organs of the male
|
Gonads or testes
|
|
|
Male reproductive fluid
|
Semen
|
|
|
Essential organs of the female
|
Gonads or ovaries
|
|
|
Reproductive ducts of the female
|
Uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
|
|
|
Accessory or supportive sex glands of the female
|
Bartholin’s glands and breasts
|
|
|
External genitalia of the female
|
Vulva
|
|
|
During a 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation would be most likely to occur on day ___ of the cycle
|
14
|
|
|
Shortly before menstruation....
|
Blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
|

