![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the study of the structure of an organism and the relationship of its parts
|
anatomy
|
|
|
cutting apart the body to isolate and study its structural components
|
dissection
|
|
|
the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts
|
physiology
|
|
|
the balance the body tries to maintain by keeping its internal environment "staying the same"
|
homeostasis
|
|
|
an outstanding characteristic of body structure
|
organization
|
|
|
a unit constructed of cells, tissues, organs and systems
|
the body
|
|
|
the smallests structural units; organizations of various chemicals
|
cells
|
|
|
organizations of similar cells
|
tissues
|
|
|
organizations of different kinds of tissues
|
organs
|
|
|
organizations of many different kinds of organs
|
systems
|
|
|
standing erect with the arms at the sides and palms turned forward
|
anatomical position
|
|
|
toward the head, upper, above
|
superior
|
|
|
toward the feet, lower, below
|
inferior
|
|
|
front, in front of
|
anterior
|
|
|
same as ventral in humans
|
anterior
|
|
|
back, in back of
|
posterior
|
|
|
same as dorsal in humans
|
posterior
|
|
|
toward the midline of a structure
|
medial
|
|
|
away from the midline or toward the side of a structure
|
lateral
|
|
|
toward or nearest the trunk, or nearest the point of origin of a structure
|
proximal
|
|
|
away from or farthest from the trunk, or farthest from a structure's point of origin
|
distal
|
|
|
nearer the body surface
|
superficial
|
|
|
farther away from the body surface
|
deep
|
|
|
lengthwise plane that divides a structure into right and left sections
|
sagittal plane
|
|
|
sagittal plane that divides the body into two equal halves
|
midsagittal
|
|
|
also known as coronal plane
|
frontal plane
|
|
|
lengthwise plane that divides a structure into anterior and posterior sections
|
frontal plane
|
|
|
horizontal plane that divides a structure into upper and lower sections
|
transverse plane
|
|
|
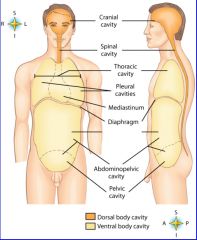
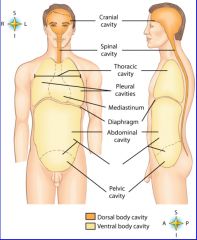
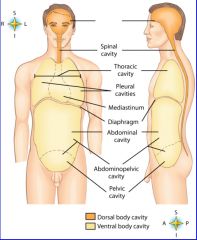
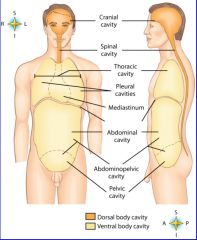
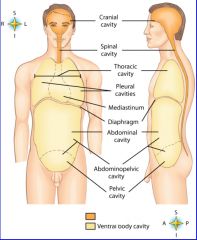
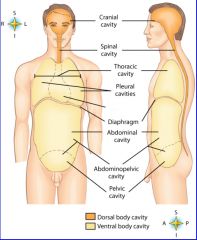
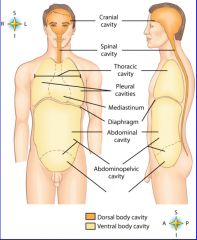
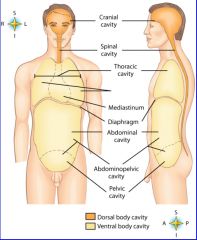
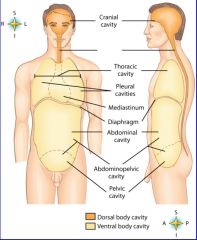
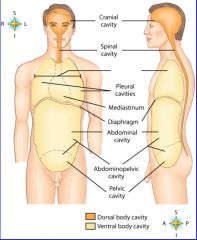
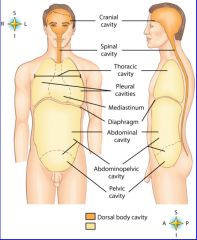
midportion of thoracic cavity; heart and trachea located here
|
mediastinum
|
|
|
the two major body cavities
|
ventral, dorsal body cavities
|
|
|
cavity location of the right lung
|
right pleural cavity
|
|
|
cavity location of the left lung
|
left pleural cavity
|
|
|
contains stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
cavity that contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and lowest part of intestine
|
pelvic cavity
|
|
|
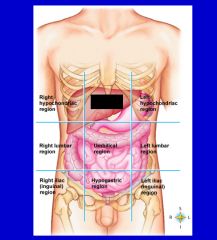
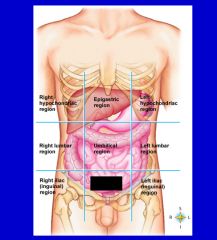
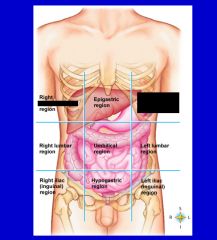
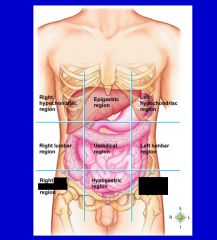
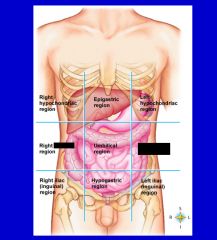
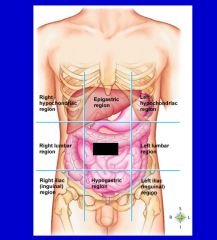
cavity that consists of nine regions and four quadrants
|
Abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
cavity that contains the brain
|
cranial cavity
|
|
|
cavity that contains the spinal cord
|
spinal cavity
|
|
|
body region encompassing the head, neck, and torso or trunk
|
axial region
|
|
|
body region including the upper and lower extremities
|
appendicular region
|
|
|
survival depends on the maintenance of this; relative constancy of the internal environment
|
homeostasis
|
|
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
cranial cavity
|
|
|
diaphragm
|
|
|
dorsal body cavity
|
|
|
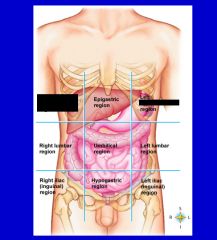
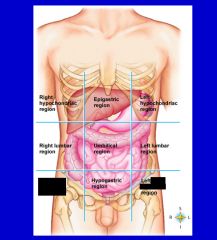
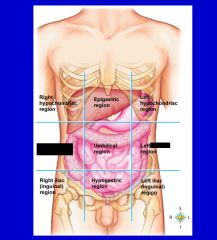
epigastric region
|
|
|
hypogastric region
|
|
|
left hypochondriac region
|
|
|
left iliac (inguinal) region
|
|
|
left lumbar region
|
|
|
mediastinum
|
|
|
pelvic cavity
|
|
|
pleural cavities
|
|
|
right hypochondriac region
|
|
|
right iliac (inguinal) region
|
|
|
right lumbar region
|
|
|
spinal cavity
|
|
|
thoracic cavity
|
|
|
umbilical cavity
|
|
|
ventral body cavity
|
|
|
midportion of the thoracic cavity
|
mediastinum
|
|
|
toward the midline of a structure
|
medial
|
|
|
feedback which is temporary and tends to bring about a rapid conclusion
|
positive feedback
|
|
|
homeostasis is usually maintained by this type of feedback
|
negative feedback
|
|
|
When a person's blood pressure drops below normal temporarily and then returns to normal after a few minutes, this might be an example of __________.
|
negative feedback
|
|
|
A degenerative process; a wasting away of tissue
|
atrophy
|
|
|
study of body structure
|
anatomy
|
|
|
study of how the body function
|
physiology
|
|
|
study of disorders of functioning
|
pathophysiology
|
|
|
the smallest fundamental substance known to man
|
element
|
|
|
another name for an element (unit of an element)
|
atom
|
|
|
a listing of all elements known to man
|
periodic table
|
|
|
molecules that make up all matter, living and non-living
|
chemicals
|
|
|
simple molecules made of one or two elements
|
inorganic chemicals
|
|
|
complex molecules that contain carbon
|
organic chemicals
|
|
|
examples: water (H20), sodium chloride (NaCl), oxygen (02)
|
inorganic chemicals
|
|
|
carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids
|
organic chemicals
|
|
|
smallest living units of structure & function
|
cells
|
|
|
a group of cells with similar structure and function
|
tissues
|
|
|
four types of tissues
|
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
|
|
|
these cover or line body surfaces
|
epithelial tissues
|
|
|
capable of producing secretions e.g. sweat glands in skin, salivary glands in mouth
|
epithelial tissues
|
|
|
these connect and support parts of the body, e.g. bones
|
connective tissues
|
|
|
some transport and store materials such as blood and fat (adipose tissue)
|
connective tissues
|
|
|
these are specialized for contraction & movement, e.g. skeletal ..., heart...
|
muscle tissues
|
|
|
specialized to generate and transmit electrochemical impulses to regulate body functions e.g. brain, optic...
|
nerve tissues
|
|
|
a group of tissues precisely arranged to perform a specific function
|
organ
|
|
|
examples include stomach, kidneys, liver, lungs, skin, hair
|
organ
|
|
|
group of organs that contribute to a particular function
|
organ system
|
|
|
standing erect with arms at sides and palms forward
|
anatomical position
|
|
|
formed by ribcage in chest
|
thoracic cavity
|
|
|
contains lungs and heart
|
thoracic cavity
|
|
|
separated from thoracic cavity by diaphragm
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
located between thoracic cavity and pelvic cavity
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
contains kidneys, liver, stomach, spleen, intestines
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
has nine regions and four quadrants
|
abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
formed by pelvic bone
|
pelvic cavity
|
|
|
contains urinary bladder, ovaries (female), uterus (female), prostate gland (male)
|
pelvic cavity
|
|
|
head, neck, torso
|
axial region
|
|
|
upper and lower extremities
|
appendicular region
|
|
|
body's ability to adapt to subtle changes in both the internal and external environment in order to maintain stability
|
homeostasis
|
|
|
aka equilibrium
|
homeostasis
|
|
|
compensatory mechanism
|
negative feedback mechanism
|
|
|
body responses that reverse a negative stimulus to put all body systems back into normal range
|
negative feedback
|
|
|
five parts of negative feedback loop
|
disturbance > sensor > control center > effector > controlled condition
|
|
|
anterior torso below diaphragm (region)
|
abdominal
|
|
|
forearm (region)
|
antebrachial
|
|
|
armpit (region)
|
axillary
|
|
|
depressed area just in front of elbow
|
antecubital
|
|
|
arm (region)
|
brachial
|
|
|
cheek (region)
|
buccal
|
|
|
wrist (region)
|
carpal
|
|
|
head (region)
|
cephalic
|
|
|
neck (region)
|
cervical
|
|
|
skull (region)
|
cranial
|
|
|
leg (region)
|
crural
|
|
|
elbow (region)
|
cubital
|
|
|
skin (or body surface) region
|
cutaneous
|
|
|
(referring to) fingers or toes
|
digital
|
|
|
(referring to) the back
|
dorsal
|
|
|
(referring to) the face
|
facial
|
|
|
(referring to) the forehead
|
frontal
|
|
|
(referring to) the nose
|
nasal
|
|
|
(referring to) the mouth
|
oral
|
|
|
(referring to) the eyes
|
orbital or ophthalmic
|
|
|
leg (region)
|
crural
|
|
|
elbow (region)
|
cubital
|
|
|
skin (or body surface) region
|
cutaneous
|
|
|
(referring to) fingers or toes
|
digital
|
|
|
(referring to) the back
|
dorsal
|
|
|
(referring to) the face
|
facial
|
|
|
(referring to) the forehead
|
frontal
|
|
|
(referring to) the nose
|
nasal
|
|
|
(referring to) the mouth
|
oral
|
|
|
(referring to) the eyes
|
orbital or ophthalmic
|
|
|
(referring to) upper cheek
|
zygomatic
|
|
|
(referring to) thigh
|
femoral
|
|
|
(referring to) buttock
|
gluteal
|
|
|
(referring to) groin
|
inguinal
|
|
|
(referring to) lower back between rib cage and pelvis
|
lumbar
|
|
|
(referring to) breast
|
mammary
|
|
|
(referring to) back of lower skull
|
occipital
|
|
|
(referring to) back of elbow
|
olecranal
|
|
|
(referring to) palm of hand
|
palmar
|
|
|
(referring to) foot
|
pedal
|
|
|
(referring to) lower portion of torso
|
pelvic
|
|
|
(referring to) area between anus and genitals
|
perineal
|
|
|
(referring to) sole of foot
|
plantar
|
|
|
(referring to) area behind knee
|
popliteal
|
|
|
(referring to) area above clavicle
|
supraclavicular
|
|
|
(referring to) ankle
|
tarsal
|
|
|
(referring to) side of skull
|
temporal
|
|
|
(referring to) chest
|
thoracic
|
|
|
(referring to) area around navel
|
umbilical
|
|
|
(referring to) palm or sole
|
volar
|

