![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
211 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Set point (def) |
The level or range of levels at which a variable is to be maintained. |
|
|
What is a stimuli/ stimulus |
Changes/ produces change in a variable |
|
|
A variable is |
The factor or event being regulated |
|
|
What are the 3 components of all homeostatic control mechanisms that work together to regulate the variable? |
Receptor, control center, effector |
|
|
The ___ is the sensor that monitors the environment. It responds to a stimuli. |
Receptor |
|
|
A ____ responds to a stimuli by sending info along the afferent pathway to the control center |
Receptor |
|
|
The ___ determines the set point. |
Control center |
|
|
The control center... |
Analyzes the input it receives by comparing it to the set point and determines the appropriate response |
|
|
Remember: "afferent" pathway means info "approaches" the control center, "efferent" info "exists" the control center. |
Tip |
|
|
The ___ carries out the control centers response to the stimulus. |
Effector |
|
|
Most homeostatic control mechanosms are... |
Negative feedback mechanisms |
|
|
The response of effector.. |
Feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level |
|
|
In _____ feedback mechanisms, the output shuts off the original effect of the stimulus or reduces its intensity. |
Negative |
|
|
These negative feedback mechanism cause the variable to change in a direction ______ to that of the initial change. |
Opposite |
|
|
Your body thermostat |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
All negative feedback mechanisms have the same goal: |
Preventing severe changes within the body |
|
|
In ____ feedback mechanisms, the initial response enhances the original stimulus so that further responses are even greater |
Positive |
|
|
The positive feedback mechanisms cause the results the change in the ___ direction as the initial change |
Same |
|
|
_____ feedback controls maintain some physiological function or keep blood chemicals within a narrow range. |
Negative |
|
|
____ feedback mechanisms usually control infrequent events that no do require continuous adjustments |
Positive |
|
|
Positive feedback mechanisms are often referred to as |
Cascades |
|
|
The anatomical reference point is a standard body position called |
Anatomical position |
|
|
Anatomical position |
The anatomical reference point is a standard body position called |
|
|
_____ _____ allow us to explain where one body structure is in relation to another |
Directional terms |
|
|
What are the two fundamental divisions of the body |
Axial and appendicular |
|
|
The axial part is |
Head, neck, trunk |
|
|
The appendicular part consists of |
Appendages (limbs) which are attached the the bodies axis. |
|
|
Regional terms are used to |
Designate specific areas within major body divisions |
|
|
What are the most frequently used body planes? |
Sagittal, frontal, transverse |
|
|
The sagittal plane is the vertical plane that divides the body |
Into right and left parts |
|
|
A sagittal plane that lies exactly jn the midline is... |
The median plane (aka midsagital planes) |
|
|
Sagittal planes, other then the median plane, are called ____ are offset from the midline |
parasagittal planes |
|
|
Frontal planes (aka coronal plane) lie _____ and .. |
Vertically. Divide the body into anterior and posterior parts. |
|
|
Coronal plane aka |
Frontal plane |
|
|
A _____ (aka horizontal plane) runs horizontal from left to right, dividing the body into ____ and ____ parts. |
Transverse. Superior and inferior |
|
|
Transverse (aka ___) |
Cross section |
|
|
Oblique sections are cuts made... |
Diagonally between the horizontal and the vertical planes |
|
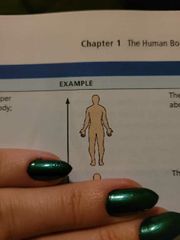
(Def) toward the head end or upper partt of a structure or the body, above |
Superior (cranial) |
|
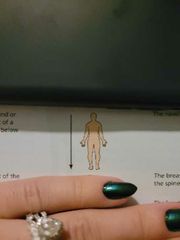
(Def) away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body, below |
Inferior (caudal) |
|

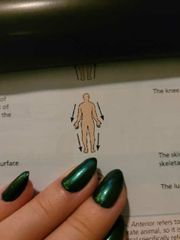
(Def) toward or at the front of the body in front of |
Anterior (ventral) |
|

(Def) towards or at the back of the body, behind |
Posterior (dorsal) |
|

(Def) towards or at the midline of the body, on the inner side of |
Medial |
|

(Def) away from the midline of the body, in the outer side of |
Lateral |
|

(Def) between a more medial and a more lateral structure |
Intermediate |
|
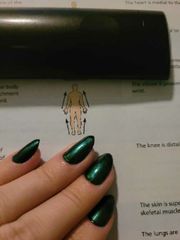
(Def) closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a liml to the body truck |
Proximal |
|
(Def) farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a liml to the body trunk |
Distal |
|

(Def) toward or at the body structure |
Superficial (external) |
|

(Def) away from the body surface, more internal |
Deep (internal) |
|
|
Two sets of internal body cavities: |
Dorsal and ventral |
|
|
Dorsal body cavity protects |
The fragile nervous system organs |
|
|
The Doral body cavity has two subdivisions: |
The cranial cavity and the vertebral/spinal cavity |
|
|
Cranial cavity is |
In the skull, encases the brain |
|
|
The vertebral (or _____ ) cavity runs |
Spinal. Runs within the bony vertebral column encloses the delicate spinal cord |
|
|
Meninges are |
Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
The two subdivisions of the ventral body cavity is: |
The thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
The ventral body cavity houses |
Internal organs collectively called the viscera |
|
|
Viscera (def) |
An organ in a body cavity |
|
|
The ____ ( the superior subdivision) is surrounded by the ribs and muscles of the chest |
The thoracic cavity |
|
|
The thoracic cavity has subdivisions: |
Lateral pleural cavities, medial mediastinum ( mediastinum contains pericardial cavity ) |
|
|
The pleural cavities enclose the... |
Lung |
|
|
The pericardial cavity encloses... |
The heart, esophagus, trachea, etc. |
|
|
The _____ separates the thoracic and the abdominopelvic cavities |
The diaphragm |
|
|
The abdominopelvic cavity has to parts: |
The abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity |
|
|
The abdominal cavity (superior part) contains |
The stomach, intestines, spleen, liver, and others |
|
|
The pelvic cavity (inferior part) contains ... |
Urinary bladder, some reproductive organs, and rectum |
|
|
What is the serosa (aka serous membrane) |
A thin, double layered membrane that covers outer surface of organs and walls in the ventral body cavity |
|
|
Parietal serosa is the part of the membrane |
lining the cavity walls |
|
|
The visceral serosa covers |
The organs in the cavity |
|
|
The serous membranes are named for .. |
The specific cavity and organs with which they are associated |
|
|
The serous membranes are separated by a thin layer of lubricating fluid called |
Serous fluid |
|
|
What are the 4 quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity: |
The right upper quadrant (RUQ), left upper quadrant (LUQ), right lower quadrant (RLQ), and left lower quadrant (LLQ) |
|
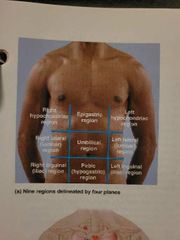
Study this chart |
See chart |
|
|
Another division method of dividing the abdominopelvic cavity into 9 regions: |
Umbilical region, epigastric region, public (hypogastric) region, right/left inguinal (iliac regions), right/left lateral (lumbar)regions, right/left hypochondriac regions. |
|
|
The _____ region is the center most region deep to and surrounding the umbilicus (navel) |
Umbilical |
|
|
The ____ region Is located superior to the umbilical region |
Epigastric |
|
|
The____ (______) region Is located inferior to the umbilical region |
Pubic or hypograstric |
|
|
The right/left _____ or ____ region Are located lateral to the hypogastric region |
Inguinal, iliac |
|
|
The right/left _____ (____) region. Live lateral to the umbilical region |
Lateral. Lumbar |
|
|
The right/left ____ region Lie lateral to the epigastric region and deep to the ribs |
Hypochondriac |
|
|
The oral cavity contains |
The teeth and tongue |
|
|
The oral cavity is part off the |
Digestive organs |
|
|
Nasal cavity is located |
Within and posterior to the nose |
|
|
Oribital cavities in the skull house the.. |
Eyes and present them in an anterior position |
|
|
The middle ear cavities in the skull lie |
Just medial to the eardrum |
|
|
Synovial cavities are |
Joint cavities |
|
|
Homeostasis def |
Bodies ability to maintain relatively sta le i tetnal conditions even though the outside world changes continuously |
|
|
What are some Survival needs of living things |
Nutritents, oxygen, water, appropriate body temperature, atmospheric pressure |
|
|
______ are the major engery fuel for body cells |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
_____ and to a lesser extent _____ are essential for building cell structures. |
Proteins, fats |
|
|
____ provides a reserve of energy rich fuel |
Fats |
|
|
Normal body temperature |
98.6 F |
|
|
________ is the force that air exerts on the surface of the body. |
Atmospheric pressure |
|
|
For true growth to occur, ____ activities must occur at a faster rate then _____ activities |
Constructive, destructive |
|
|
______ system: forms the external body covering and protects deeper tossues from injury. Synthesizes vitamin d and houses cutaneous receptors and sweat and oil glands. |
Integumentary system |
|
|
Cutaneous receptors are |
Pain, pressure, etc |
|
|
_____ system: protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement. Blood cells are formed within bones. Bones store minerals |
Skeletal system |
|
|
______ system: allows manipulation if the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture and produces heat. |
Muscular system |
|
|
_____ system: as the fast acting control system of the body, it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands |
Nervous system |
|
|
______ system: glands secrete hormones es that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells. |
Endocrine system |
|
|
______ system: blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients waste, etc. The heart pumps blood |
Cardiovascular system |
|
|
_____ system : picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels admbd returns it to the blood. Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream. Houses white blood cells involved in immunity. The immune e response mounts the attack against foreign substances within the body |
Lymphatic system |
|
|
____ system: Keeps flood constantly supplied with oxygen and moves carbon dioxide. These exchanges occur through the walls of the air sacs of lungs |
Respiratory system |
|
|
_____ system: Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells. Indigestible food stuffs are eliminated as feces |
Digestive system |
|
|
______ system: Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electryte, and acid base balance of the blood |
Urinary system |
|
|
_________ system: overall function is production of offspring. Testes produce sper. And male sex hormones. Male ducts and glands aid in delivery of supermarket to female reproductive tract. |
Male reproductive system |
|
|
________ system: ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones. The remaining female structures serve as sites for fertilization and development of the fetus. Mammary glands of the female breasts produce milk to nourish the newborn. |
Female reproductive system |
|
|
Excretion is the process of |
Removing wastes (excreta) from the body |
|
|
Lymphocytes are |
White blood cells |
|
|
______ is a broad term that includes all chemical reactions that occur within body cells |
Metabolism |
|
|
Metabolism includes |
Breaking down substances into simpler building blocks, synthesising more complex substances from simpler building blocks, and using nutrition and oxygen to produce ATP |
|
|
What is ATP? |
Organic molecule that stores and releases chemical energy for use in body cells |
|
|
What does metabolism depend on to make nutrition and oxygen available to the blood? |
Digestive and respiratory systems |
|
|
What is metabolism regulated by? |
hormones secreted by the endocrine system glands |
|
|
________ is the breaking down of ingested foods to simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood |
Digestion |
|
|
______ or ______ is the ability to sense changed in the environment and then respond to them. |
Responsiveness or excitability |
|
|
The muscle cells ability to move by shortening is more precisely called |
Contractility |
|
|
Activities promotes by the muscular systems have as propelling ourselves from one place to another. |
Movement |
|
|
All body cells are surrounded by a selectively permeable _____ _____ |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
The plasma membrane separates the: |
Intracellular fluid inside cells from the extracelluar fluid outside |
|
|
Extracelluar fluid aka... |
Blood plasma |
|
|
The interstitial fluid ... |
Surrounds and bathes all of our cells |
|
|
Part of the extracellular fluid is enclosed in... |
Blood vessels |
|
|
Study this picture |
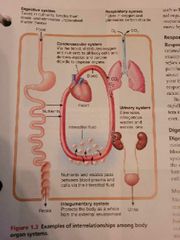
|
|
|
All body cells are... |
Interdependent |
|
|
The body cells interdependence is due to the fact that humans are |
Multicellular organisms and our bodys vital functions are parceled out among different cells. |
|
|
The organismal level represents the |
Sum total of all structural levels working together to keep us alive |
|
|
_____ is a discrete structure composed of at least two tissue type (Four is more common) that performs a specific function for the body. |
Organ |
|
|
The principal of complementarity of structure and function |
What a structure can do depends on its specific form. |
|
|
The simplest level of the structural hierarchy is |
The chemical level |
|
|
Name some of the structural organization levels of the body: |
Chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organismal level, organ system level. |
|
|
Organelles are |
The basic components of cells |
|
|
Cells are |
The smallest units of living things |
|
|
______ are groups of similar cells that have a common function |
Tissues |
|
|
Renal physiology concerns |
Kidney function and urine production |
|
|
Neurophysiology explains the workings of |
The nervous system |
|
|
_____ means feeling organs with your hands |
Palpation |
|
|
_____ means listening to organ sounds with a stethoscope |
Auscultation |
|
|
________ anatomy studies internal structures as visualized by x-ray images or specialized scanning procedures. |
Radiographic |
|
|
Pathological anatomy studies |
Structural changes caused by disease |
|
|
________ anatomy traces Structural changes that occur throughout the lifespan |
Developmental |
|
|
______ Is a subdivision of developmental anatomy concerning developmental changes that occur before birth |
Embryology |
|
|
_______ Anatomy deals with structures to smalle to be seen with the naked eye |
Microscopic anatomy |
|
|
_______ Is a subdivision of microscopic anatomy and considers the cells of the body |
Cytology |
|
|
______ Is a subdivision of microscopic anatomy and is interested in the study of tissues |
Histology |
|
|
Anatomy studies the |
Structure of body parts and their relationships to one another |
|
|
Physiology concerns the |
The function of the body and have a body parts work and carry out their life sustaining activities |
|
|
______ or _____ Anatomy is the study of large body structures visible to the naked eye such as the heart lungs and kidney. |
Gross or macroscopic anatomy |
|
|
In regional anatomy Look at structures.. |
Such as mussels, bones, blood vessels, nerves, in a particular region of the body such as the abdomen or leg. |
|
|
In systemic anatomy, body structure is studied |
System by system |
|
|
What is anything that occupy space and has Mass |
Matter |
|
|
The mass of an object = |
The actual amount of matter in the object and it remains constant wherever the object is |
|
|
Compared to matter energy is more or less tangible? |
Less tangible |
|
|
How can we measure energy? |
We can measure it only by its affects on matter |
|
|
_______ is The capacity to do work or to put matter in to motion |
Energy |
|
|
Kinetic energy is ______ and potential energy is _____ |
Energy in action, stored energy |
|
|
______ energy Is the form stored in the bonds of chemical substances |
Chemical energy |
|
|
What does ATP stand for? |
Adenosine triphosphate |
|
|
What type of energy results from the movement of charged particles? |
Electrical energy |
|
|
The nervous system uses electrical currents called… |
Nerve impulses or action potentials |
|
|
What type of energy is directly involved in moving matter |
Mechanical energy |
|
|
What type of energy is energy that travels in waves |
Radiant energy or electromagnetic radiation |
|
|
All matter is composed of ____ |
Elements |
|
|
What are common elements that make up the human body? |
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, Phosphorus, potassium, Sulfur, sodium, chlorine, magnesium iodine, iron |
|
|
What are common elements that make up the human body? |
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, Phosphorus, potassium, Sulfur, sodium, chlorine, magnesium iodine, iron |
|
|
The orbital model of atoms represents |
Electrons as a cloud of negative charge |
|
|
The orbital model of atoms represents |
Electrons as a cloud of negative charge |
|
|
The planetary model shows |
A more simplified version, shows electrons as two small spheres on a circle around the nucleus |
|
|
The atomic weight is an average of |
The weights (mass numbers) of all the isotopes of an element taking into account their relative abundance in nature |
|
|
Avogadros number |
6.02 x 10^23 |
|
|
_____ (aka emulsions) are heterogeneous mixtures, appear milky or translucent, and scatter light. |
Colloids |
|
|
Sol-gel transformations mean |
To change reversible from a fluid (sol) state to a more solid (gel) state (jello) |
|
|
______ are homogeneous mixtures with large often visible solids that tend to settle out (blood plasma) |
Suspensions |
|
|
______ Regions around the nucleus in which a given electron is likely to be found most of the time |
Orbitals |
|
|
When atoms are stable they are chemically inert which means they are |
Unreactive |
|
|
The rule of Eights is also called |
Octet rule |
|
|
What are the 3 major types of chemical bonds |
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen |
|
|
What is the strongest chemical bond? |
Covalent |
|
|
What is considered to be the Weakest type of chemical bond |
Hydrogen |
|
|
An anion is an electron ____ |
Acceptor |
|
|
A cation is an electron ____ |
Donor |
|
|
____ are large arrays of cations and anions held together by ionic bonds |
Crystals |
|
|
A molecules _____ helps determine what other molecules or atoms it can interact with. |
Shape |
|
|
Most chemical reactions are one of 3 type... |
Synthesis, decomposition, exchange |
|
|
In synthesis reactions, smaller particles are bonded to form |
Larger more complex molecules. |
|
|
In _____ reactions, bonds are broken in larger molecules, resulting in smaller less complex molecules. |
Decomposition |
|
|
In _____ reactions, bonds are both make and broken |
Exchange |
|
|
What is a Process in which living cells break down substances into simpler substances |
Catabolic/ catabolism |
|
|
What is energy requiring building phase of metabolism in which simpler substances are combined to forn more complex substances |
Anabolic/Anabolism |
|
|
Oxidation- reduction reactions aka... |
Redox reactions |
|
|
______ reactions are decomposition reactions, the basis of all reactions in which food fuels are broken fownfor energy |
Oxidation reduction reactions |
|
|
____ are proteins and other types of molecules that helps regulate homeostasis of acid base balance |
Buffers |
|
|
____ resist abrupt Bd large swings in the pH of body fluids by releasing hydrogen ions when pH rises and binds hydrogen ions when pH drops |
Buffers |
|
|
The ______ buffer system is the major buffer system. The weak acid is carbonic acid (H2CO3), dissociated reversibly, releasing its corresponding qeak base, bicarbonate ions (HCO3) and protons (H+) |
Bicarbonate |
|
|
Carbohydrates, liquids (fats), proteins and nucleic acid all contain _____ |
Carbon |
|
|
Electroneutral means |
Neither loses.or gains electrons |
|
|
Macromolecules are |
Large complex molecules containing thousands of atoms |
|
|
Most macromolecules are |
Polymers |
|
|
______ are chainlike molecules made of many smaller, identical or similar subunits |
Polymers |
|
|
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer is ____ |
Monomers |
|
|
Monomers are joined together by a process called _____ |
Dehydration synthesis |
|
|
_______ ______ process by which large molecule is synthesized by removing water and covalently bonding smaller molecules together |
Dehydration synthesis |
|
|
Hydrolysis aka |
Water splitting |
|
|
_______ is process in which water is usedd to split a substance into smaller parts |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
____ A group of molecules that includes sugars and starches |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates are |
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides |
|
|
Monosaccharides are the _____, or building blocks of the other carbohydrates |
Monomers |
|
|
_______ or simple sugars, are single chain or single ring structures containing from 3-7 carbon atoms |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
For monosaccharides, carbon, 0xygen, hydrogen atoms occurs in a ratio of |
1:2:1 |
|
|
Monosaccharides ate generally named according to the ... |
Number of carbon atoms they contain |
|
|
_____ have the same molecular formula but their atoms are arranged differently, giving them different chemical properties |
Isomers |
|
|
______ or double sugar, is formed when two monosaccharides are joined by dehydration synthesis. |
Disaccharides |

