![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T/F myofibrils are composed of protein filaments called actin and myosin |
true |
|
|
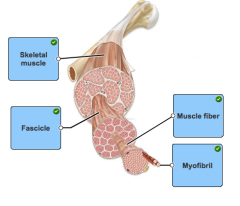
a bundle of muscle fibers is known as a |
fascicle |
|
|
A skeletal muscle fiber (cell) contains a single nucleus (T/F) |
false |
|
|
the muscle cell membrane is called the |
sarcolemma |
|
|
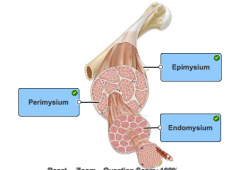
which connective tissue wrapping separates individual muscle fibers |
endomysium |
|
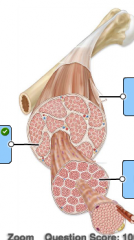
Name the compartments of muscle cells |
|
|
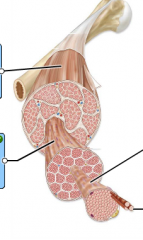
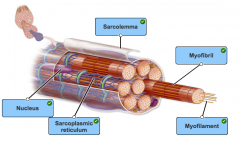
label the parts of a muscle cell |
|
|
|
skeletal muscles are composed of hundreds of muscle cells called |
muscle fibers |
|
|
at the ends of muscles, the connective tissues merge to form a _____ which attaches the muscle to bone |
tendon |
|
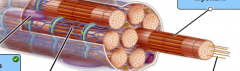
Lable the parts of the skeletal muscle fiber |
|
|
|
An action potential traveling down t-tubules cause calcium ions to diffuse from the ______ into the ______ |
sarcoplasmic reticulum; sarcoplasm |
|
|
which of the following best describes the role of calcium in muscle contraction |
it binds to troponin, moving tropomyosin, so that myosin heads can bind to actin |
|
|
t-tubules are invaginations of the sarcolemma of a muscle cell (T/F) |
true |
|
|
the component of a muscle fiber that allows an action potential to travel quickly from the sarcolemma throughout the entire muscle fiber is called the |
transverse tubule (T-tubule) |
|
|
during contraction of a muscle, calcium ions bind to the |
troponin molecule |
|
|
what is important about the tropomyosin molecule |
tropomyosin blocks the binding sites on actin, unless calcium is bond to troponin |
|
|
the bond beween the actin and myosin head is broken when |
an ATP molecule binds to the myosin head |
|
|
energy is released when |
ATP is broken down into ADP and phosphate |
|
|
the sequence of crossbridge formation and myofilament movement will be repeated as long as calcium ions are present (T/F) |
true |
|
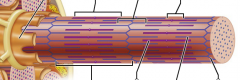
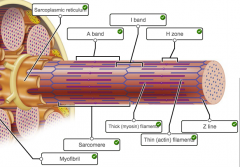
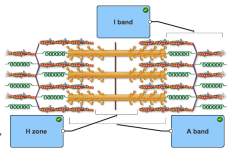
what are the different bands |
|
|
|
Thin filament connect to and extend from either side of a _______. These thin filaments are composed largely of the myofilament______. |
z-disc; actin |
|
|
myosin heads directly use ______ to transition to their _______ conformation, which enables them ready to bind to actin. |
ATP; energized |
|
|
The presence of calcium in the sarcoplasm is directly responsible for ______. |
exposing the binding sites on actin |
|
|
rigor mortis occurs after death because________________. |
detachment of crossbridges does not occur due to the lack of ATP |
|
|
In which region of the muscle fiber do actin and myosin myofilaments overlap |
A band |
|
|
during contraction, the actin myofilaments slide toward the |
H zone |
|
|
the distance from on Z disk to the next Z disk is called a |
sarcomere |
|
|
in a relaxed muscle, the ends of the actin filaments overlap (T/F) |
false |
|
|
troponin and tropomyosin are found on thick or thin filaments |
thin |
|
|
myosin is found on ____ filaments |
thick |
|
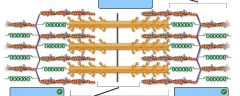
label the bands and sarcomere parts |
|
|
|
During crossbridge cycling, tension is created by |
a change in the shape of the myosin head |
|
|
according tot he sliding filament theory for skeletal muscle contraction, a shortening of the sarcomere is produced by |
an increase in the amount of overlap between the thick and thin filaments |
|
|
maximum tension is produced in skeletal muscle fiber when it is |
at resting length, because this is where there is optimum overlap of thick and thin filaments |
|
|
What occurs when ther is optimum overlap of thick and thin filaments |
this is when the highest number of cross-bridges can form between myosin and actin |
|
|
when the muscle is stretched what happens to the length of the muscle fibers |
the muscle fibers get longer |
|
|
a single contraction produced maximum tension when the muscle was held at |
about 28 mm |
|
|
if maximum tension indicates that the thick and thin filaments are set at optimal overlap to produce a maximum number of crossbridges, in this experiment, further stretching of the muscle beyond 28 mm will |
decrease the amount of thick and thin filament overlap and therefore, the number of crossbridges |
|
|
Since the tension produced by a contracting muscle fiber depends upon the number of crossbridges between the thick and thin filaments, stretching the muscle beyond 28 mm: |
decreases the amount of overlap and decreases the amount of tension produced by a single contraction |
|
|
One factor that influences the amount of tension a muscle can generate when stimulated is the amount of overlap of thick and thin filaments when the muscle begins its contraction is called |
length-tension relationship |
|
|
In the gluteus maximus, each motor unit controls a ______ amount of muscle fibers than a motor unit controlling muscles of the eye |
greater |

