![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
arteries |
take oxygenated, high nutrient blood away from the heart |
|
|
veins |
return low oxygen, low nutrient blood to the heart |
|
|
what are the two sets of arteries that supply the brain |
2 internal carotid arteries (one from each hemisphere), and 2 vertebral arteries (which join to form the basilar artery) |
|
|
what vein returns blood to the heart from the brain |
jugular vein |
|
|
anterior circulation is from what artery |
internal carotid artery |
|
|
posterior circulation is from what artery |
vertebral and basilar arteries |
|
|
posterior circulation provides blood to what areas |
brainstem, cerebellum, occipital lobe |
|
|
anterior circulation provides blood to what areas |
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe |
|
|
middle cerebral artery supplies blood to what area? Posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to what area? anterior cerebral artery supplies blood to what area |
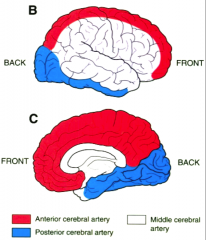
|
|
|
in the motor and sensory homonculus, what areas of the body are supplied by the anterior cerebral artery |
genitals, feet, lets, trunk (lower extremities) |
|
|
in the motor and sensory homonculus, what areas of the body are supplied by the middle cerebral artery |
arms, hands, (upper extremities), face, auditory, and speech |
|
|
inability to recognize faces is probably due to damage to the |
posterior cerebral artery |
|
|
circle of willis allows ______ between the 2 hemispheres except for the area of the _____ |
collateral flow, middle cerebral artery |
|
|
f.a.s.t |
face, arms, speech, time |
|
|
thrombotic stroke |
clot |
|
|
hemorrhagic stroke |
bleed |
|
|
transient ischemic attack (TIA) |
mini stroke that resolves quickly, temporary plug in blood vessel that dissolves quickly |
|
|
aneurysm |
weakening of blood vessels |
|
|
microaneurysm |
develops in small arteries, due to hypertension, most common cause of hemorrhage and vascular dementia |
|
|
berry aneurysm |
congenital (not related to hypertension), common cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage, 90% found in circle of willis |
|
|
subarachnoid hemorrhage |
sudden excruciating headache "worst headache of my life". caused by aneurysm rupture in circle of willis. Lumbar puncture has bloody appearance |
|
|
dural septa |
divide up the brain and help support the weight of the cerebrum |
|
|
falx cerebri |
seperates the 2 cerebral hemispheres and protects brain from lateral movement |
|
|
tentorium cerebellum |
separates cerebellum and cerebrum and protects brain from up/down movement |
|
|
csf circulation |
made from choroid plexus in lateral ventricles, flows to third ventricle, then through the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle and from there it goes to the cisterna magna which surrounds the brain. returns to venous system through arachnoid granulations in the dural sinus |
|
|
circumventricular organs |
tell the brain about blood composition |
|
|
bacterial meningitis |
headache, fever & stiff neck. bacteria block csf reabsorption, but it continues to be made. leads to intracranial pressure
any motion will give them an excruciating headache due to the pressure so patients will be really stiff and not want to move |
|
|
dural sinus are filled with what type of blood |
venous blood |
|
|
subdural hematoma |
tearing of the veins entering dural sinuses, commonly seen in elderly after a fall or through shaken baby syndrome. |
|
|
epidural hemotoma |
results from significant trauma or concussion. blood vessels between bone and dura break and lead to rapidly expanding hemorrhage due to arterial blood. |
|
|
where is the needle inserted in a spinal tap |
L4 & L5 |
|
|
Order of flow of CSF |
start in lateral ventricle, go to third ventricle through interventricular foramen, then through cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle |
|
|
third ventricle is a landmark for the.... |
thalamus and hypothalamus |
|
|
how does csf travel once it is outside brain to jugular |
cisterna magna to subarachnoid space to arachnoid granulations which regurns it to venous system to the jugular vein |
|
|
pineal gland is special because it _____ which lets it sense the hormones in the blood |
a BBB |
|
|
language is exclusively on the ___ hemisphere |
left |
|
|
face recognition is exclusively on the ____ hemisphere |
right |
|
|
right hemisphere dominant tends to be more ___ |
creative, musical/ artistic, spatial and pattern perception, face recognition, emotional part of speech |
|
|
left hemisphere dominant tends to be more ______ |
analytical, spoken and written language numerical and scientific skills, reasoning |
|
|
limbic functions are in the _________ and it tells us _______ |
Prefrontal cortex, emotional brain, personality, emotions |
|
|
somatosensation |
sense of touch and awareness of body |
|
|
primary somatosensory cortex |
initial sensation of touch |
|
|
somatosensory association cortex |
interpretation of sensation |
|
|
primary somatosensory area is in the |
postcentral gyrus |
|
|
in the somatosensory cortex, more area is devoted to the ______ compatered to the motor cortex map |
more area is given to the feet |
|
|
hemineglect happens where |
in the right hemisphere of the somatosensory association cortex in the parietal lobe. This is why they ignore the left side of the world. |
|
|
structures in temporal lobe |
primary auditory cortex, lateral fissure, wernicke's speech area |
|
|
wernicke's speech area is involved with |
understanding of speech. "what" |
|
|
primary auditory cortex |
receives sound information and sorts it by frequency in a tonotopic map. deciphers pitch, rhythm |
|
|
receptive aphasia |
language comprehension affected by damage to Wernicke's area, use wrong words,unaware of deficit, apraxia (can't execute motor activity based on verbal command), nonfluent reading, impaired repetition |

