![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
two main flexors in the compartment of the arm |
biceps brachii (inserts into the radius on thumb side of forearm), brachialis (from humerus into the ulna) |
|
|
superficial muscles in forearm (anterior) work on the |
wrist |
|
|
deep muscles in the forearm (anterior) work on the |
fingers |
|
|
hypothenar |
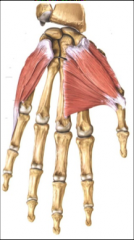
pinky side of hand Include abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi, opponens digiti minimi
Help to abduct fingers, flex fingers, |
|
|
thenar |
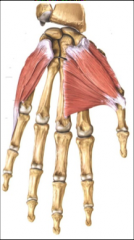
thumb side of hand abductor pollicis brevis flexor pollics brevis opponens pollicis
Abducts and flexes thumb |
|
|
extensors of arm are in the _____ compartment |
posterior |
|
|
triceps |
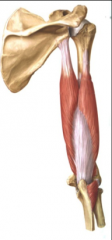
posterior. extension at elbow joint |
|
|
all nerves innervating upper limb come from |
brachio plexus |
|
|
four terminal nerves of brachioplexus and what they innervate |
musculocutaneous nerve (anterior compartment of arm, i.e. biceps and brachialis), median nerve (most muscles in anterior compartment of forearm plus the thenar muscles (thumb)), ulnar nerve (1.5 muscles in forearm and all other muscles in hand that aren't innervated by median nerve), radial nerve (posterior compartment of arm and forearm (extensors in arm)) |
|
|
intercostal muscles |
between the ribs. three layers. include external intercostal, inner intercostal, innermost intercostal. |
|
|
abdominal muscles |
external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis side muscles |
|
|
what makes up "six pack abs" |
rectus abdominis |
|
|
arm bones |
humerus, radius, ulna |
|
|
leg bones |
femur, tibia, fibula |
|
|
anterior muscles in leg are |
extensors |
|
|
posterior muscles in leg are |
flexors (opposite than arms because the leg is rotated 180 degrees) |
|
|
sartorius muscle |
crosses thigh and inserts into the tibia on the medial side. Landmark between anterior and medial thigh. |
|
|
anterior thigh includes |
quadriceps which include the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, and vastus medialis |
|
|
medial thigh muscles include |
adductor muscle group which includes the pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, adductor magnus, and gracilis |
|
|
what two muscles make up the hip |
iliacus and psoas major |
|
|
lifting thigh up works what muscle |
illeus soleus |
|
|
sartorius muscle allows |
lateral rotation at the thigh. (crossing your leg) Hip flexion, knee flexion, lateral rotation |
|
|
quadricep muscles form tendon that |
envelop the patella (knee cap) and then extend onward to form the patella tendon |
|
|
quadricep muscles do what action |
kicking or things that bend the knee (kicking soccer ball movement). knee extension. also can cause hip flexion |
|
|
thigh adductors do what |
adduct the thigh |
|
|
iliotibial tract is in what compartment |
lateral compartment. |
|
|
what muscle is found in the iliotibial tract and what action does it do |
tensor fascia latae, abducts leg at hip joint, locks the knee by pushing on tibia so it rests above the femur |
|
|
posterior part of thigh |
gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, hamstring muscles (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris) |
|
|
gluteus maximus muscle allows |
extension at hip joint (most powerful extensor at hip joint), also allows lateral rotation of thigh |
|
|
gluteus medius and gluteus minimus |
analogous to rotators cuff. allow for abduction at high joint and medial rotation |
|
|
hamstrings include |
semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris |
|
|
hamstring muscles do what |
extension at hip joint and flexion at knee joint. necessary for running |
|
|
anterior leg compartments |
extensor digitorum longus, tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus |
|
|
lateral leg compartments |
fibularis longus and fibularis brevis |
|
|
posterior leg compartments |
gastrocnemius, soleus (deep to gastrocnemius), flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
extensor digitorum longus, tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus are important for |
dorsiflexion, inversion, toe extension. |
|
|
fibularis longus and fibularis brevis are important for |
plantarflexion and eversion |
|
|
gastrocnemius and soleus are important for |
plantar flexion of foot, gastrocnemius also does knee flexion |
|
|
gastrocnemius and soleus form the _______ at the calcaneal bone |
achilles tendon |
|
|
superficial posterior compartment of leg contains |
gastrocnemius and soleus |
|
|
deep posterior leg muscles in posterior compartment |
flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, and flexor hallucis longus do what |
plantar flexion, inversion, toe flexion |
|
|
femoral nerve innervates |
muscles in anterior thigh |
|
|
obturator nerve innervates |
all muscles in medial thigh (does adduction of thigh) |
|
|
sciatic nerve innervates |
posterior thigh (hamstring) divides into common fibular and tibial nerve |
|
|
tibial nerve innervates |
muscles of posterior compartment of leg and of foot |
|
|
common fibular nerve innervates |
muscles in anterior/ lateral compartments of let |

