![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
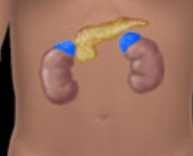
Adrenal gland |
|
|
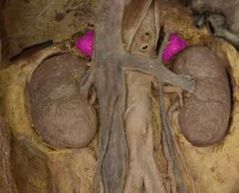
Adrenal gland |
|
|
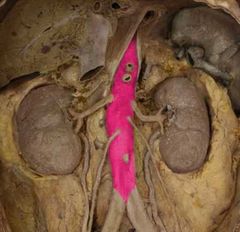
Abdominal aorta |
|
|
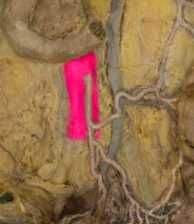
Abdominal aorta |
|
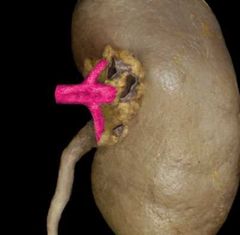
|
Renal artery |
|
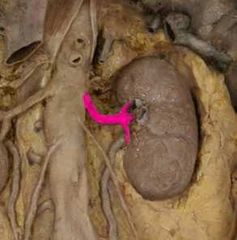
|
Renal artery |
|
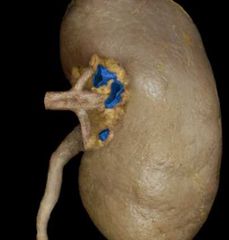
|
Renal vein |
|
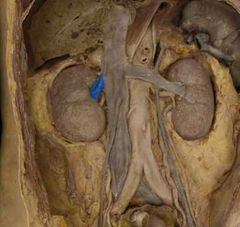
|
Renal vein |
|
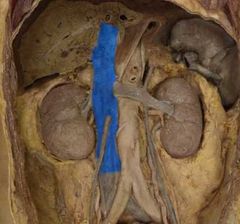
|
Inferior vena cava |
|
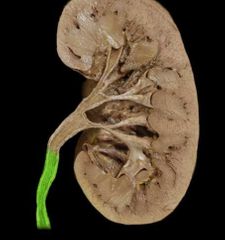
|
Ureter |
|
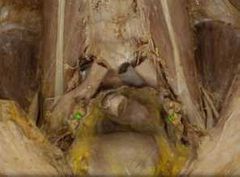
|
Ureter |
|
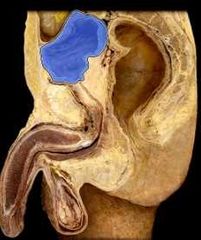
|
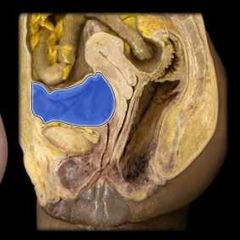
Urinary bladder |
|
|
Urinary bladder |
|
|
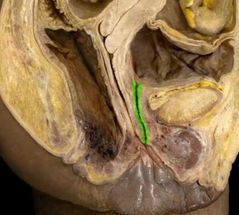
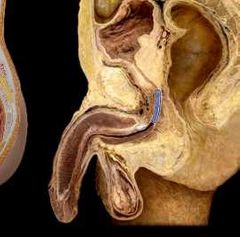
Urethra |
|
|
Urethra |
|
|
Ureteral openings |
|
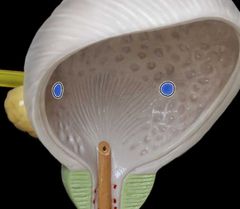
|
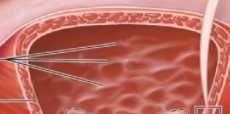
Ureteral openings |
|
|
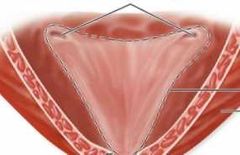
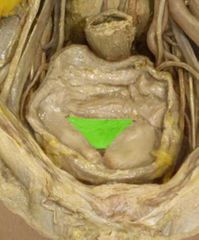
Trigone |
|
|
Trigone |
|
|
Rugae |
|

|
Rugae |
|
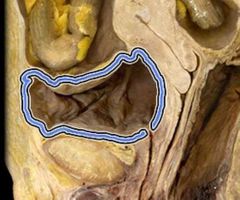
|
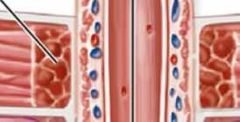
Detrusor muscle |
|
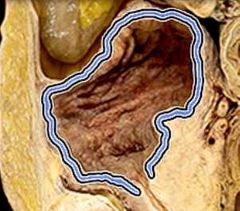
|
Detrusor muscle |
|
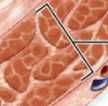
|
Detrusor muscle |
|
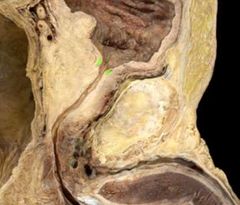
|
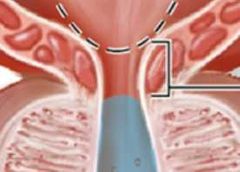
Internal urethral sphincter |
|
|
Internal urethral sphincter |
|
|
Internal urethral sphincter |
|
|
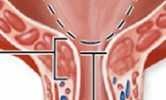
External urethral sphincter |
|
|
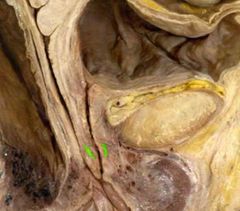
External urethral sphincter |
|
|
External urethral sphincter |
|
|
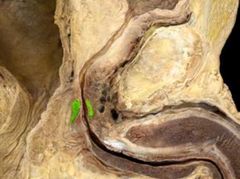
External urethral sphincter |
|
|
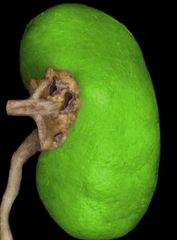
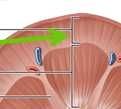
Fibrous (renal) capsule |
|
|
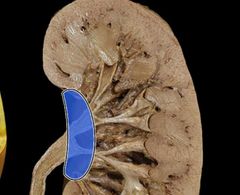
Renal hilum |
|
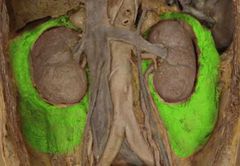
|
Perinephric fat capsule |
|
|
Renal cortex |
|
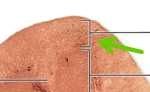
|
Renal cortex |
|
|
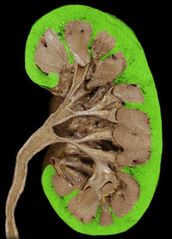
Renal cortex |
|
|
Renal cortex |
|
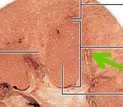
|
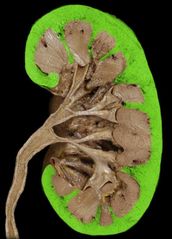
Renal medulla |
|
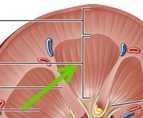
|
Renal medulla |
|
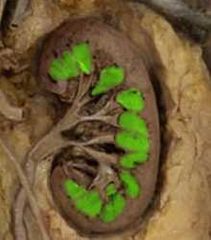
|
Renal (medullary) pyramid |
|

|
Renal (medullary) pyramid |
|
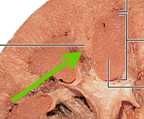
|
Renal column |
|
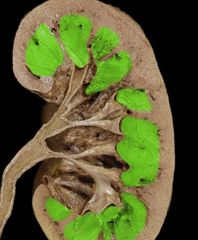
|
Renal medulla |
|
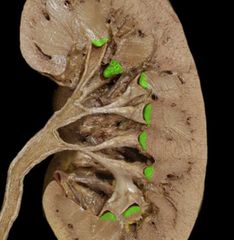
|
Renal apex/papilla |
|
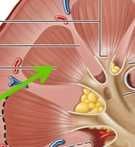
|
Renal (medullary) pyramid |
|
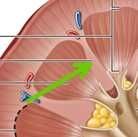
|
Renal column |
|
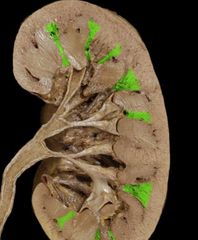
|
Renal column |
|
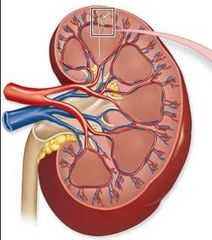
|
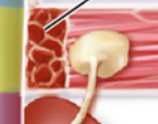
Nephron |
|
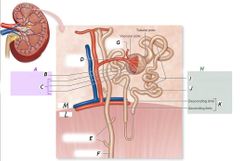
E |
Collecting tubules |
|
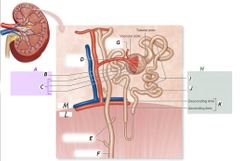
B |
Glomerulus |
|
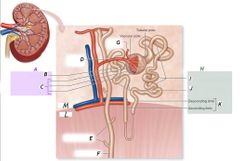
C |
Glomerular capsule |
|
|
What are renal sinuses?
|
Urine drainage areas containing major & minor calyces and the renal pelvis
|
|
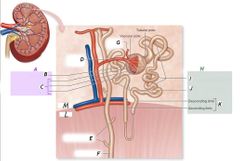
G |
Efferent arteriole |
|
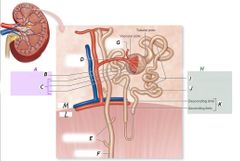
F |
Collecting duct |
|
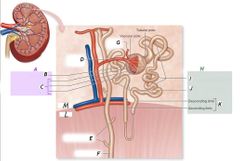
H |
Renal tubule |
|
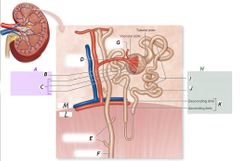
J |
Distal convoluted tubule |
|
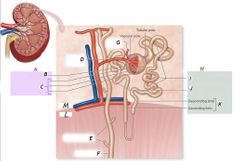
K |
Nephron loop |
|
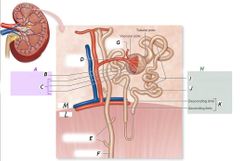
L |
Medulla |
|
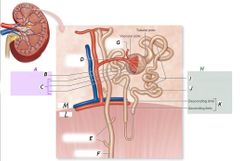
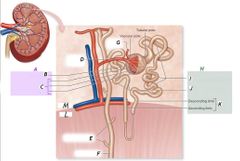
I |
Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
B |
Renal corpuscle |
|
A |
Nephron |
|
|
Which has a higher specific density - urine or water? Why?
|
Urine, because of the solutes
|
|
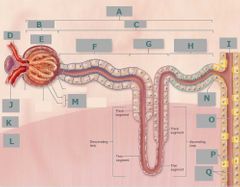
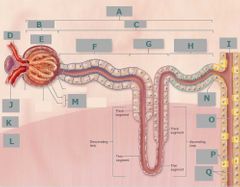
M |
Cortex |
|
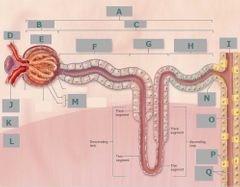
G |
Nephron loop |
|
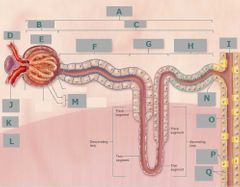
J |
Afferent arteriole |
|
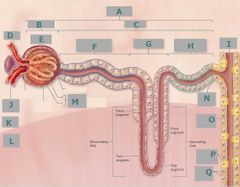
E |
Glomerulus |
|
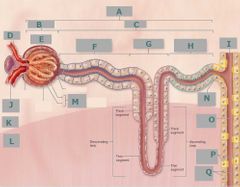
L |
Medulla |
|
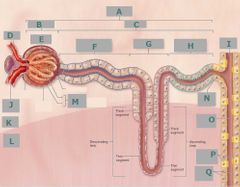
F |
Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
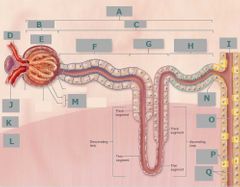
C |
Renal tubule |
|
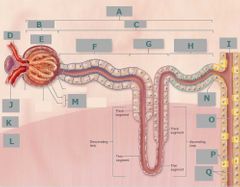
D |
Efferent arteriole |
|
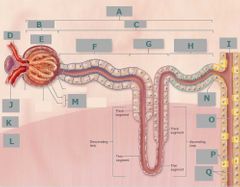
H |
Distal convoluted tubule |
|
M |
Glomerular capsule |
|
Q |
Principal cells |
|
K |
Cortex |
|
|
Which layer of the glomerular capsule is impermeable?
|
Parietal
|
|
P |
Intercalated discs |
|
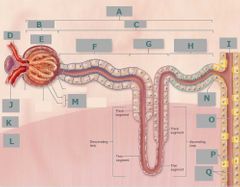
N |
Collecting tubule |
|
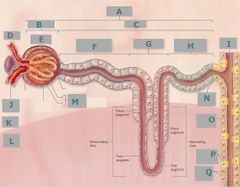
I |
Collecting duct |
|
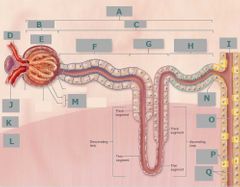
O |
Collecting duct |
|
|
What forms the renal pelvis?
|
Merging major calyces
|
|
|
What kind of epithelium lines the renal tubules? |
Simple cuboidal
|
|
|
What are the three layers of a glomerular capsule?
|
Visceral, capsular space, and parietal
|
|
|
What is urinoid?
|
Smell of fresh urine
|
|
|
What are the two regions of functional tissue in the kidney?
|
Outer renal cortex and inner renal medulla
|
|
|
Which part of the renal tubules appears clear when viewed under a light microscopic?
|
Distal convoluted tubule
|
|
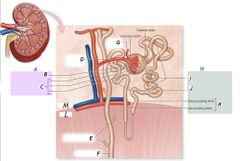
A |
Renal corpuscle |
|
|
What is specific gravity?
|
Density of a substance compared to the density of water
|
|
|
Which part of the renal tubules has microvilli?
|
Proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
Which layer of a glomerular capsule is permeable?
|
The visceral layer that directly overlies the glomerular capillaries
|
|
|
Where do the afferent and efferent arterioles attach to the glomerulus?
|
Vascular pole
|
|
|
What are renal columns?
|
Extensions of the cortex projecting into the medulla
|
|
|
What is perinephric fat?
|
Adipose connective tissue outside of the fibrous capsule that cushions & supports the kidney
|
|
|
What is the normal pH of urine?
|
4.5 - 8
|
|
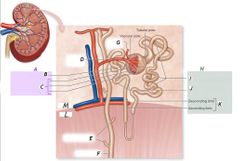
D |
Afferent arteriole |
|
|
Which part of the kidney protects it from pathogens?
|
Fibrous capsule
|
|
|
How much urine is made in a day?
|
1-2 liters
|
|
|
What are the solutes in urine?
|
Salts, nitrogenous wastes, hormones, drugs, ketone bodies
|
|
|
What is the capsular space responsible for?
|
It receives the filtrate and modifies it to form urine
|
|
|
What causes urine to smell fruity?
|
Diabetes
|
|
|
What is the tubular pole of the glomerulus?
|
Origin of the renal tubule
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the parietal layer of a glomerular capsule?
|
Simple squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What are the components of a renal lobe?
|
Renal pyramid & portions of adjacent renal columns
|
|
|
What are renal pyramids? |
Portions of medulla between the renal columns
|
|
|
What impacts the pH of urine?
|
Metabolism and infection
|
|
|
Where are nephrons located?
|
Renal cortex
|
|
|
What connects at the hilum?
|
Nerves, vessels, and ureters
|

