![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
211 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you find the total magnification of the microscope? |
ocular lense x objective lense
|
|
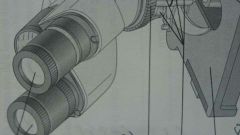
what part is this?
|
ocular lense
|
|

what are these 2 items?
|
on/off switch & light control
|
|
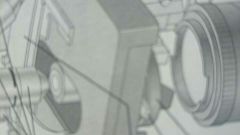
What part is this?
|
mechanical stage
|
|
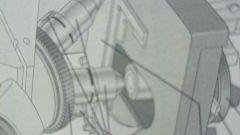
what part is this? |
objective lense
|
|
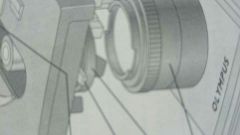
what is the switch under the stage?
|
iris diaphragm lever |
|
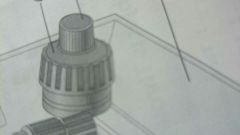
what are these two knobs?
|
coarse adjustment knob
fine adjustment knob |
|
|
what are the 4 kinds of objective lenses?
|
broad field lense
medium(low) power lense high power lense oil immersion lense |
|
|
what's the definition of tissues?
|
similar looking cells with a similar function
|
|
|
what are the 4 kinds of tissue?
|
epithelial tissue
connective tissue muscle tissue nervous tissue |
|
|
what's the definition of epithelial tissue?
|
lines the body surface and body cavities
|
|
|
how do you categorize epithelial tissue?
|
# of layers and the shape of the cells surface
|
|
|
what are the different layers called for epithelial tissue
|
simple
stratified pseudostratified |
|
|
what are the different shapes of epithelial tissue?
|
squamous
cuboidal columnar transitional |
|
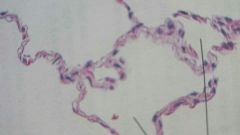
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can it be found? |
simple squamous epithelial
kidney, air sacs of lungs |
|
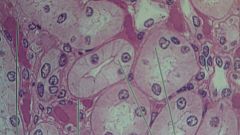
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can this be found? |
simple cuboidal
kidney tubeles, ovary surface |
|
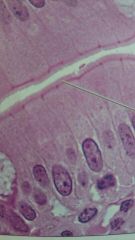
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can it be found? |
simple columnar
lines the stomach and digestive tract |
|
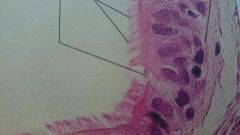
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can it be found in the body? |
ciliated pseudostratified columnar
lining the trachea and bronchi |
|
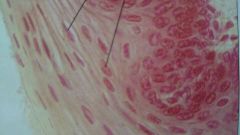
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can it be found? |
stratified squamous
skin, esophagus, and mouth |
|
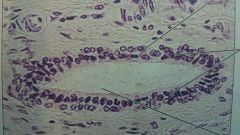
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can it be found? |
stratified cuboidal
sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands |
|
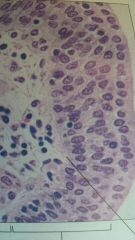
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can you find this? |
stratified columnar
urethra |
|
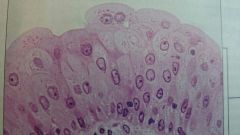
what kind of epithelial is this?
where can you find this? |
transitional
bladder and ureter |
|
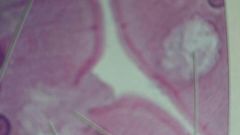
what is this cell?
what does it do? |
goblet cell
secretion |
|
|
what is the definition of connective tissue?
|
connects and holds the body together
|
|
|
how is connective tissue categorized?
|
type of matrix and type of fibers present
|
|
|
what are the 5 kinds of connective tissue?
|
blood
bone cartilage dense connective tissue loose connective tissue |
|
|
what is the fluid of blood called?
|
plasma
|
|
|
what does plasma consist of?
|
erythrocytes leukocytes platelets
|
|
|
what is the periosteum in bone?
|
outer layer of bone
|
|
|
where is the endosteum in bone?
|
inner layer of bone that lines the marrow cavity
|
|
|
what's a compact bone?
|
found along the shaft of long bones and the surface of most bones
|
|
|
what is a osteon? |
the structural and functional units of compact bone
|
|
|
what is the central canal of a osteon?
|
the hollow space in the middle
|
|
|
what are perforating canals?
|
connects one central canal of an osteon to another
|
|
|
what is a lamellae on an osteon? |
rings or layers coming off the the central canal |
|
|
what is lacunae in an osteon? |
tiny space between the lamellae |
|
|
what is canaliculi in an osteon? |
canals that connect one lacunae to another |
|
|
what is a osteoblasts in a osteon? |
cell that makes bone |
|
|
what is a osteocytes in a osteon? |
located in lacunae |
|
|
where is spongy bone located? |
found in the ends of long bones, the body of vertebrae, the middle of cranial bones and the sternum |
|
|
what are the thin boney plates that are the structural and functional units of spongy bone called? |
trabeculae |
|
|
what is cartilage? |
cells spread out in a matrix of chondroitin sulfate
|
|
|
what is a chondroblast?
|
makes cartilage
|
|
|
what is a chondrocytes?
|
mature cartilage cell found is small spaces
|
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
elastic cartilage
outer ear |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this? |
fibrocartilage
intervertebral discs |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
regular dense connective
tendons and ligaments |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
irregular dense connective
fibrous joint capsules |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
elastic dense connective
aorta |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
areolar
found in mucous membranes and dermis of skin |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
adipose
breast tissue |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
reticular connective
lymph nodes and spleen |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where is it found? |
bone (osteon)
bones |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where is it found? |
blood
blood vessels |
|

what kind of connective tissue is this?
where is it found? |
hyaline cartilage
connects ribs to the sternum |
|
|
what is adipose?
|
fat
|
|
|
what's the definition of muscle tissue?
|
cells that can contact
|
|
|
what are the 3 kinds of muscular tissue?
|
skeletal
cardiac smooth |
|
|
what are the characteristics of skeletal muscle?
|
voluntary, multinucleated, striated, long cylindrical cells
|
|

what kind of muscle tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
skeletal muscle
attached to bones |
|
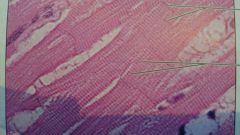
what kind if muscle is this?
where can it be found? |
cardiac muscle
heart |
|
|
what are the characteristics of cardiac muscle?
|
involuntary, uninucleated, striated, branching cells, intercalated discs, gap junctions
|
|
|
what are intercalated discs?
|
thick connections between cardiac muscle cells
|
|
|
what are gap junctions?
|
tiny microscopic hollow tubes that connect two cardiac cells
|
|

what kind of muscular tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
smooth muscle
in walls of hollow organs |
|
|
what are the characteristics of smooth muscle?
|
involuntary, uninucleated, no striations, elongated nuclei
|
|
|
what is the definition of nervous tissue?
|
cells that detect stimuli and transmits electrical impulses throughout the body
|
|
|
what are two things found in nervous tissue?
|
neurons & neuroglia
|
|

what kind of tissue is this?
where can it be found? |
nervous tissue
brain, spinal chord |
|
|
what is the definition of neurons?
|
the structural and functional units of the nervous system
|
|
|
what is the definition of neuroglia?
|
cells that wrap around, insulate, and protect neurons
|
|
|
what is the cell membrane?
|
semipermeable barrier between the inside of the cell and the outside world
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
centrioles
|
|
|
what is the function of the centrioles?
|
involved in cell division anchor cells that the chromosomes are pulled towards when the cell divides.
|
|
|
what is a chromatin?
|
spread out forms of DNA and protein
|
|
|
what is a chromosome?
|
condensed format of DNA and protein
|
|
|
what is cilia?
|
microscopic hair like extensions of the cell membrane that move things along the membrane of the cell
|
|
|
what is cytoplasm?
|
area between the cell membrane and the nucleus
|
|
|
what is cytoskeleton?
|
filament and tubes provides support for the cell and helps transport things, biggest structure in cell
|
|
|
what is cytosol?
|
fluid found in cytoplasm
|
|
|
what is flagellum?
|
structure for locomotion
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
golgi complex
|
|
|
what is the function of the golgi complex?
|
packages things for secretion
|
|
|
what is a lysosome?
|
membrane wrapped around digestive enzymes
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
microvilli
|
|
|
what is the function of microvilli?
|
increases surface area of a cell
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
what is the function of mitochondria?
|
makes most of the ATP
|
|
|
what is the nuclear membrane?
|
outside part of the nucleus (envelope)
|
|
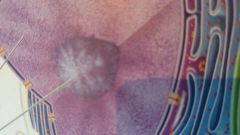
what part of the cell is this?
|
nucleolus
|
|
|
what is the function of the nucleolus?
|
makes RNA
|
|
|
what is the nucleus?
|
part that contains genetic material
|
|
|
what are ribosomes?
|
makes proteins, attached to rough ER and in cytoplasm
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|

what part of the cell is this?
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
what is the function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
|
stores ions
|
|
|
what is mitosis?
|
involved in the growth and repair of a cell
|
|
|
what are the stages of mitosis?
|
interphase
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase |
|
|
what is a diploid cell?
|
contains 2 sets of chromosomes
|
|
|
what is interphase?
|
longest stage of mitosis
|
|
|
what are the 3 parts to interphase?
|
G1 of interphase
S of interphase G2 of interphase |
|
|
what is G1 of interphase?
|
1st growth phase, begins to duplicate organelles, starts to replicate centrosomes
|
|
|
what is S of interphase?
|
DNA replication occurs
|
|
|
what is G2 of interphase?
|
cell growth continues, duplication and replication are completed
|
|
|
what is prophase?
|
chromatin starts to condense into chromosomes, nucleus begins to break down
|
|
|
what is metaphase?
|
chromosomes line up in the middle of a cell
|
|
|
what is anaphase?
|
pulling of genetic material apart, cytokinesis begins late in this stage
|
|
|
what is telophase?
|
cytokinesis completes, nuclear envelope begins to form
|
|
|
what is cytokinesis?
|
division of the cytoplasm
|
|
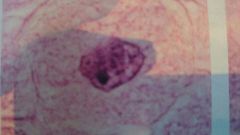
what stage of mitosis is this?
|
interphase
|
|
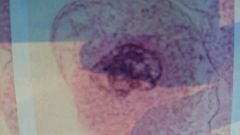
what stage of mitosis is this?
|
prophase
|
|
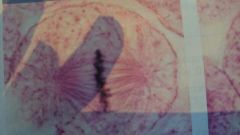
what stage of mitosis is this?
|
metaphase
|
|

what phase of mitosis is this?
|
anaphase
|
|

what stage of mitosis is this?
|
telophase
|
|
|
what is meiosis ?
|
produces sex cells, gamete
|
|
|
what is gamete?
|
eggs and sperm
|
|
|
where does meiosis occur?
|
in the gonads (ovaries & testes)
|
|
|
how does the cell for meiosis begin as
|
1 diploid cell
|
|
|
how does the cell end as after meiosis occurs?
|
4 unique haploid cells
|
|
|
what is the abdominal cavity?
|
the area that houses the stomach, intestines, liver, and other organs
|
|
|
what is the abdominopelvic cavity?
|
the cavity inferior to the diaphragm
|
|
|
what is antebrachial?
|
fore arm
|
|
|
what is antecubital?
|
anterior surface of the elbow
|
|
|
what is anterior?
|
front
|
|
|
what is axillary?
|
armpit
|
|
|
what is brachial?
|
upper arm
|
|
|
what is calcaneal?
|
heal of foot
|
|
|
what is carpal?
|
wrist
|
|
|
what is cephalic?
|
entire head
|
|
|
what is cervical?
|
neck region
|
|
|
what is coronal plane (frontal plane)?
|
plane that divides the body from anterior and posterior
|
|
|
what is cranial?
|
bones that immediately surround the brain, skull
|
|
|
what is cranial cavity?
|
hollow space that contains your brain
|
|
|
what is crural?
|
leg
|
|
|
what is deep?
|
internal, away from the body's surface
|
|
|
what is diaphragm?
|
separates the thoracic cavity from the rest of the ventral cavity
|
|
|
what is distal?
|
away from the main part of the body
|
|
|
what is dorsal
|
back side
|
|
|
what is the dorsal cavity?
|
where the cranial cavity and vertebral or spinal cavity are located
|
|
|
what is epigastric?
|
upper middle abdominal section
|
|
|
what is facial?
|
contains the area from eyes to chin
|
|
|
what is femoral?
|
thigh
|
|
|
what is gluteal?
|
buttocks
|
|
|
what is hallux?
|
big toe
|
|
|
what is hypogastric?
|
middle lower section of abdomen
|
|
|
what is hypochondriac?
|
under the cartilage, under rib cartilage, 2 sides right and left
|
|
|
what is iliac?
|
hip bone region, 2 sides
|
|
|
what is inferior?
|
below other structures
|
|
|
what is lateral?
|
towards the side
|
|
|
what is lumbar? |
either side of bellybutton region, located in both front and back, lower/small of back
|
|
|
What is mammary? |
breast region |
|
|
What is medial? |
towards the midline |
|
|
What is metacarpal? |
makes up the palm |
|
|
What is Mediastinum? |
what divides the thoracic cavity in half |
|
|
What is metatarsal? |
foot |
|
|
What is olecranal? |
posterior side of the elbow |
|
|
What is Parietal pleura? |
membrane on the outer wall of the pleural cavity |
|
|
what is parietal pericardium? |
membrane on the outer wall of the pericardial cavity |
|
|
What is parietal peritoneum? |
membrane on the outer wall of the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
What is patellar? |
knee cap |
|
|
What is pelvic cavity? |
contains the urinary bladder, reproductive, and rectum |
|
|
what is pericardial cavity? |
where the heart is located |
|
|
What is peritoneal cavity? |
same as abdominopelvic cavity usually used when talking about the membranes |
|
|
what is phalangeal? |
fingers |
|
|
What is plantar? |
entire bottom of the foot |
|
|
what is pleural cavity? |
where the lungs are |
|
|
What is pollex? |
thumb |
|
|
What is popliteal? |
back of knee |
|
|
What is posterior? |
back |
|
|
What is proximal? |
closer to the main part of the body |
|
|
What is sagittal plane? |
divides the body into left and right? |
|
|
What is spinal cavity? |
where the spinal chord is located |
|
|
What is superficial? |
bodys surface |
|
|
What is superior? |
above |
|
|
What is sural? |
calf |
|
|
What is tarsal? |
ankle |
|
|
what is thoracic cavity? |
contains heart and lungs |
|
|
What is transverse plane? |
divides the body into superior and inferior |
|
|
What is umbilical? |
belly button middle section of the abdomen |
|
|
What is ventral? |
front side |
|
|
What is ventral cavity? |
contains thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
What is visceral pericardium? |
membrane on the outer surface of the heart |
|
|
What is visceral peritoneum? |
membrane on the outer surface of all the organs in the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
What is visceral pleura? |
membrane on the outer surface of the lungs |
|
|
What is the epidermis? |
consists of stratified squamous epithelial tissue, avascular,cells become keratinized |
|
|
what is keratin? |
a waterproof protein in skin |
|
|
What are the layers of the epidermis? |
Stratum corneum stratum lucidum stratum granulosum stratum spinosum stratum basale |
|
|
What is stratum corneum? |
outer most layer, dead cells |
|
|
What is stratum lucidum? |
Thin translucent layer of dying cells filled with keratin |
|
|
What is stratum granulosum? |
thin dark staining layer of dying cells |
|
|
What is stratum spinosum? |
Varies on thickness, living cells |
|
|
What is stratum basale? |
Single layer, bottom of epidermis contains melanocytes |
|
|
What is melanocytes? |
makes dark pigment called melanin |
|
|
What is the dermis? |
The thickest layer of skin, consist of connective tissue, vascular, has fibroblasts, adipose cells |
|
|
What is fibroblasts? |
cell that makes fibers |
|
|
What are the layers of the dermis? |
Papillary region reticular region |
|
|
What is the papillary region? |
the upper 20% of the dermis |
|
|
What are dermal papillae? |
bumps that extend up into the epidermis, makes up fingerprints and footprints |
|
|
What are corpuscles of touch? |
touch receptors, lite pressure |
|
|
What is the reticular region? |
the other 80% of the dermis |
|
|
What is laminated corpuscles? |
located deep in the dermis, detects heavy pressure |
|
|
What is eccrine sudoriferous gland? |
secretes a watery sweat directly to the surface of the skin |
|
|
What is appocrine sudoriferous gland? |
secretes a thicker and more odiferous secretion are the base of the hairs of the axillary and pubic regions |
|
|
What is the hair shaft? |
part of the hair extending above the skin |
|
|
what is the hair root? |
part of hair under the skin |
|
|
what is the hair follicle? |
layer sounding the root in the dermis |
|
|
What us the hair root bulb? |
rounded bottom of the hair root |
|
|
what is the hair root papilla? |
dome shaped indentation in the hair root bulb |
|
|
What is sebaceous gland? |
secrete an oily secretion around the hair root, waterproofs and lubricates |
|
|
what is a arrector pili muscle? |
smooth muscle makes hair stand up and produces goose bumps |
|
|
What is the hypodermis? |
located between the dermis and the underlying bones or muscle, has large blood vessels, nerves and lots of adipose tissue |

