![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
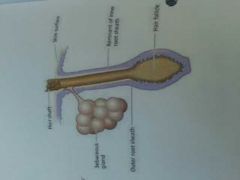
Sebaceous gland |
Holocrine gland produces oil to lubricate hair and skin |
|
|
|
types of Sudoriferous glands |
Two types apocrine and eccrine |
|
|
|
Aporine glands |
Attached to hair follicles in genitals and armpits, has odor as it breaks down, secrets a milky fluid that contains pheromones and under nervous and hormonal control |

|
|
|
Eccrine glands |
All over body, extend to surface (forming pores), nervous control and cools body |
|
|
|
What are sweat glands called |
Sudoriferous |
|
|
|
What are oil glands |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Examples of stratified squamous keratinised epithelial tissue |
Skin, hair and nails |
|
|
|
Examples of non keratinised stratifed squamous epithelial tissue |
Eyes mouth |
|
|
|
What are the uses of epithelial tissue |
Protection, secretion, absorption |
|
|
|
Does epithelial tissue have a central nucleus |
Yes |
|
|
|
Types of simple epithelial |
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar and ciliated columnar |
4 types |
|
|
Types of stratified epithelial tissue |
Stratified squamous and transitional |
2 types |
|
|
Examples of transitional stratified epithelial tissue |
Stomach, lungs, bladder and uterus |
|
|
|
Functions of epithelial tissue |
Lines the outer surfaces of our body (skin) lines the inner surfaces of the bodys major cavities, lines all tubular organs, forms glands and forms membranes |
|
|
|
What is a gland |
A group of epithelial cells which produce a specialized secretion |
|
|
|
Term for expelling waste products eg sweat fron sweat gland |
Excretion |
|
|
|
Term for release of substances for further use eg sebum from sebaceous gland |
Secretion |
|
|
|
What gland controls the endocrine and exocrine |
Pituitary |
|
|
|
How apocrine glands work |
They accumulate secreted material near the free surface of the cell, that part is then pinched off and cell is discharged |
|

