![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
4 purposes of tissue.
|
1. Covering
2. Support 3. Movement 4. Control |
|
|
|
Functions of epithelium.
|
1. Protection
2. Absorption 3. Filtration 4. Excretion 5. Secretion 6. Sensory reception |
|
|
|
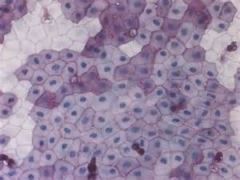
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
Thin and often permeable, allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae.
|
|
|
|
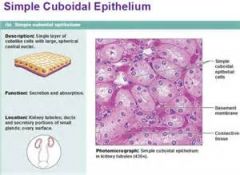
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
Secreation and absorption. Found in kidney tubules; sucts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface.
|
|
|
|
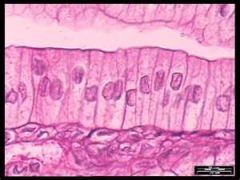
simple columnar epithelium
|
Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action. Lines most of the digestive tract. Gallbladder ducts of some glands. ciliated lines the bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
|
|
|
|
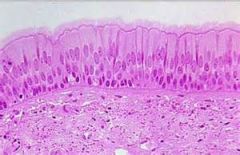
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
|
Secretion, particularly of mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action. Non ciliated type found in ducts of large glands, parts of male urethra; ciliated variety lynes the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract.
|
|
|
|
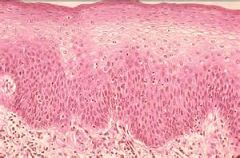
Stratified squamous epithelium
|
Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion. Forms most linings of the esophagus, mouth and vagina; keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane
|
|
|
|
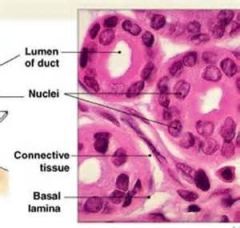
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
|
Protection. Found in the largest ducts of the sweat glands, mammary glands and salivary glands.
|
|
|
|
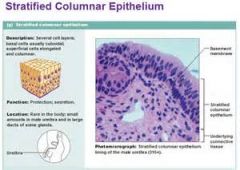
stratified columnar epithelium
|
Protection; and secretion. Rare in the body, small anounts in the male urethra and in larges ducts of some glands
|
|
|
|
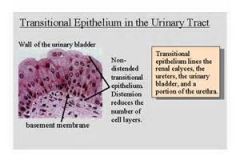
transitional epithelium
|
Stretches readily and permits distention of urinary organ by contained urine. Lines the ureturs, bladder, andpart of the urethra.
|
|
|
|
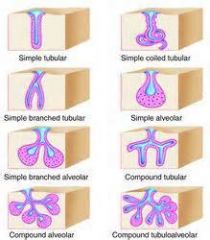
multicellular exocrine glands
|
1. simple tubular
2. simple branched tubular 3. simple alveolar 4. simple branched alveolar 5. compound tubular 6. compound alveolar 7. compound tubuloalveolar 8. simple coiled |
|
|
|
Simple tubular
|
single unbranched duct (intestinal gland)
|
|
|
|
simple branched tubular
|
Stomach (gastric) glands
|
|
|
|
simple branched alveolar
|
sebaceous (oil) glands
|
|
|
|
compound tubular
|
brunners flands of small intestine
|
|
|
|
compound alveolar
|
mammary glands
|
|
|
|
compound tubuloalveolar
|
salivary glands
|
|
|
|
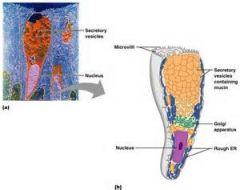
Unicellular Exocrine Glands
|
In humans, all such glands produce mucin, mixed with water forms mucus. the only important one is the goblet cells.
|
|

