![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
The branch of science that deals with the structure of body parts |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Branch of science that deals with function of body parts |
|
|
|
Requirements for Life |
Water, Food, Oxygen, Heat, and Pressure |
|
|
|
Append |
[to hang something] appendicular: pertaining to the limbs |
|
|
|
Append |
[to hang something] |
appendicular: pertaining to the limbs |
|
|
Cardi |
[heart] |
pericardium: membrane that surrounds that heart |
|
|
Cran |
[helmet] |
Cranial: pertaining to the portion of the skull that surrounds the brain |
|
|
-tomy |
[cutting] |
Anatomy: study of a structure, which often in ok ex. Urging or removing body parts |
|
|
Atoms |
Microscopic particles that make up chemicals |
|
|
|
Macromolecules |
Small molecules combine in complex ways to form larger _______ |
|
|
|
Cell |
The basic unit of structure and function |
|
|
|
Organelles |
All cells of humans and other complex organisms contain ______ |
|
|
|
Movement |
Change in position of the body or of a body part; motion of an internal organ |
|
|
|
Responsiveness |
Reaction to a change inside or outside the body |
|
|
|
Growth |
Increase in body size without change in shape |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Production of new organisms and new cells |
|
|
|
Respiration |
Obtaining oxygen, removing Cain dioxide and releasing energy from foods |
(Some forms of life so not use oxygen in respiration) |
|
|
Dors |
[back] |
Dorsal: position towards the back |
|
|
Digestion |
Breakdown of foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used |
|
|
|
Circulation |
Movement of nutrients and waste products between blood and body tissues |
|
|
|
Assimilation |
Changing absorbed substances into chemist different forms |
|
|
|
Excretion |
Removal of wastes production by metabolic reactions |
|
|
|
Receptors |
Provide info about specific conditions in the internal environment (stimuli) |
|
|
|
Set point |
Tells what a particular value should be (Example: such as a body temperature at 98.6 Fahrenheit or 37 Celsius) |
|
|
|
Effectors |
Bringing about responses that can alter conditions in the internal environment |
|
|
|
Respiration |
Obtaining oxygen, removing carbon dioxide and releasing energy from foods |
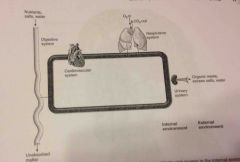
(Some forms of life do not use oxygen in respiration) |
|
|
Appendicular portion |
Upper and lower limbs |
|
|
|
Circulation |
Movement of blood through blood vessels as result of the heart's pumping action |
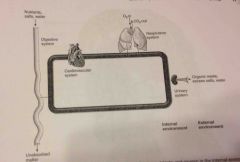
|
|
|
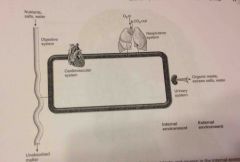
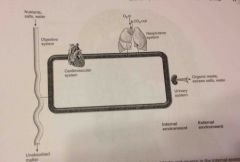
Homeo |
[same] |
Homeostasis: maintenance of a stable internal environment |
|
|
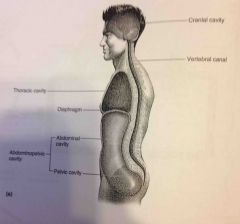
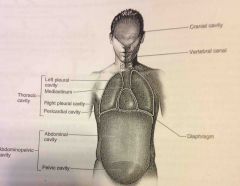
Vertebral canal |
Spinal cord and sections of the backbone |
|
|
|
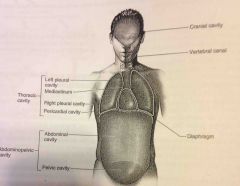
Abdominopelvic and Thoracic cavity |
Viscera |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
Thin skeletal voluntary muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Effectors |
Bringing about responses that can alter conditions in the internal environment |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Enclosed by the hip bones is portion of the abdominopelvic cavity. Contains the terminal portion of the large intestine, urinary bladder and internal reproductive organs. |
|
|
|
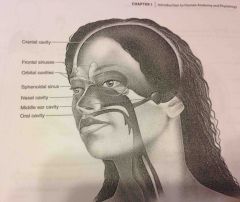
Oral cavity |
The teeth and tongue |
|
|
|
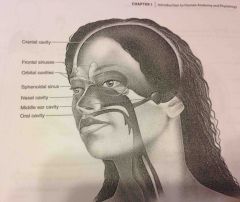
Cranial cavity |
(Within axial portion) houses the brain |
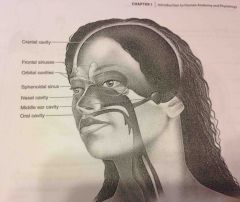
|
|
|
Vertebral canal |
Spinal cord and sections of the backbone |
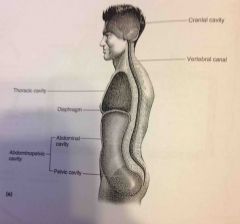
|
|
|
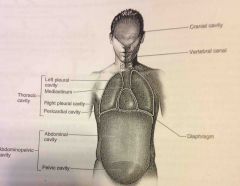
Abdominopelvic and Thoracic cavity |
Viscera |
|
|
|
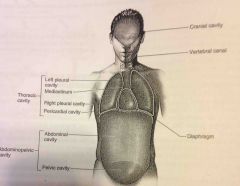
Diaphragm |
Thin skeletal voluntary muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
-logy |
[study of] |
Physiology: study of the body functions |
|
|
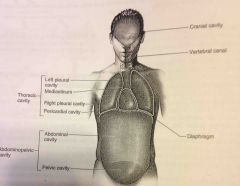
Pelvic cavity |
Enclosed by the hip bones is portion of the abdominopelvic cavity. Contains the terminal portion of the large intestine, urinary bladder as internal reproductive organs. |
|
|
|
Oral cavity |
The teeth and tongue |
|
|
|
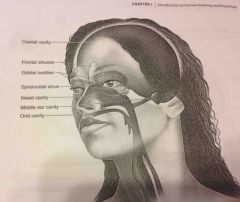
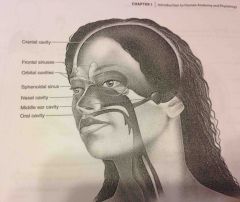
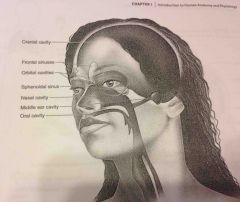
Nasal cavity |
Within the nose and divided into right and left portions by a nasal septum. Air fled sinuses connect to it |
|
|
|
Orbital cavities |
Contains eyes and skeletal muscles and nerves |
|
|
|
Middle ear cavities |
Containing the middle ear bones |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Reproductive system |
|
|
|
Bilateral |
Paired structures (one of which is on each side) |
The lungs are bilateral. |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
Refers to the structure on the same side |
The right lung and the right kidney are ipsilateral. |
|
|
Contralateral |
Refers to structure on the opposite side |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Describes a body part that is closer to a point of attachment to the trunk of another body part |
The elbow is proximal to the wrist. |
|
|
Meta |
[change] |
Metabolism: chemical changes in the body |
|
|
Pariet |
[wall] |
Parietal membrane: membrane that lines the wall of a cavity |
|
|
Pelv |
[basin] |
Pelvic cavity: enclosed by the pelvic bones |
|
|
Peri |
[around] |
Pericardial membrane: membrane that surrounds that heart |
|
|
Pleur |
[rib] |
Pleural membrane: membrane that encloses the lungs and lines the thoracic cavity |
|
|
-stasis |
[standing still] |
Homeostasis: maintenance of a stable internal environment |
|
|
Cran |
[helmet] |
Cranial: pertaining to the portion of the skull that surrounds the brain |
|
|
-tomy |
[cutting] |
Anatomy: study of a structure, which often in ok ex. Urging or removing body parts |
|
|
Atoms |
Microscopic particles that make up chemicals |
|
|
|
Macromolecules |
Small molecules combine in complex ways to form larger _______ |
|
|
|
Cell |
The basic unit of structure and function |
|
|
|
Organelles |
All cells of humans and other complex organisms contain ______ |
|
|
|
Movement |
Change in position of the body or of a body part; motion of an internal organ |
|
|
|
Responsiveness |
Reaction to a change inside or outside the body |
|
|
|
Growth |
Increase in body size without change in shape |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Production of new organisms and new cells |
|
|
|
Respiration |
Obtaining oxygen, removing Cain dioxide and releasing energy from foods |
(Some forms of life so not use oxygen in respiration) |
|
|
Dors |
[back] |
Dorsal: position towards the back |
|
|
Digestion |
Breakdown of foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used |
|
|
|
Circulation |
Movement of su estancia in body fluids |
|
|
|
Assimilation |
Changing absorbed substances into chemist different forms |
|
|
|
Excretion |
Removal of wastes production by metabolic reactions |
|
|
|
Receptors |
Provide info about specific conditions in the internal environment (stimuli) |
|
|
|
Set point |
Tells what a particular value should be (Example: such as a body temperature at 98.6 Fahrenheit or 37 Celsius) |
|
|
|
Effectors |
Bringing about responses that can alter conditions in the internal environment |
|
|
|
Respiration |
Obtaining oxygen, removing Cain dioxide and releasing energy from foods |
(Some forms of life so not use oxygen in respiration) |
|
|
Appendicular portion |
Upper and lower limbs |
|
|
|
Circulation |
Movement of su estancia in body fluids |
|
|
|
Homeo |
[same] |
Homeostasis: maintenance of a stable internal environment |
|
|
Vertebral canal |
Spinal cord and sections of the backbone |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic and Thoracic cavity |
Viscera |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
Thin skeletal voluntary muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Effectors |
Bringing about responses that can alter conditions in the internal environment |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Enclosed by the hip bones is portion of the abdominopelvic cavity. Contains the terminal portion of the large intestine, urinary bladder as internal reproductive organs. |
|
|
|
Oral cavity |
The teeth and tongue |
|
|
|
Cranial cavity |
(Within axial portion) houses the brain |
|
|
|
Vertebral canal |
Spinal cord and sections of the backbone |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic and Thoracic cavity |
Viscera |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
Thin skeletal voluntary muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
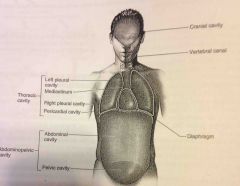
|
|
|
-logy |
[study of] |
Physiology: study of the body functions |
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Enclosed by the hip bones is portion of the abdominopelvic cavity. Contains the terminal portion of the large intestine, urinary bladder as internal reproductive organs. |
|
|
|
Oral cavity |
The teeth and tongue |
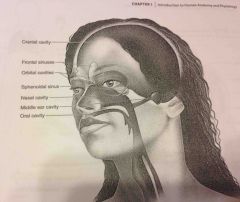
|
|
|
Nasal cavity |
Within the nose and divided into right ad lest portions by a nasal septum. Air fled sinuses connect to it |
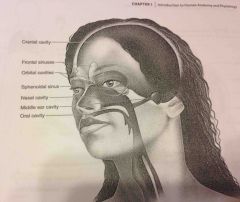
|
|
|
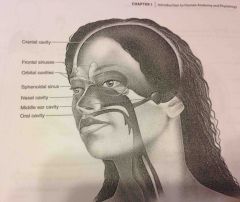
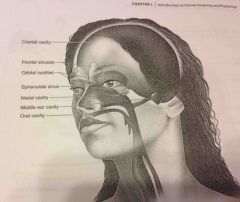
Orbital cavities |
Contains eyes and skeletal muscles and nerves |
|
|
|
Middle ear cavities |
Containing the middle ear bones |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Reproductive system |
|
|
|
Bilateral |
Paired structures (one of which is on each side) |
The lungs are bilateral. |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
Refers to the structure on the same side |
The right lung and the right kidney are ipsilateral. |
|
|
Contralateral |
Refers to structure on the opposite side |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Describes a body part that is closer to a point of attachment to the trunk of another body part |
The elbow is proximal to the wrist. |
|
|
Meta |
[change] |
Metabolism: chemical changes in the body |
|
|
Distal |
The opposite of proximal. A particular body part is father from a point of attachment to the trunk than another body part is |
The fibers are distal to the wrist. |
|
|
Pariet |
[wall] |
Parietal membrane: membrane that lines the wall of a cavity |
|
|
Pelv |
[basin] |
Pelvic cavity: enclosed by the pelvic bones |
|
|
Peri |
[around] |
Pericardial membrane: membrane that surrounds that heart |
|
|
Pleur |
[rib] |
Pleural membrane: membrane that encloses the lungs and lines the thoracic cavity |
|
|
-stasis |
[standing still] |
Homeostasis: maintenance of a stable internal environment |
|
|
Superior |
Above another body part |
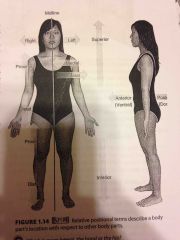
The thoracic cavity is superior to the abdominopelvic |
|
|
Inferior |
Below another body part |
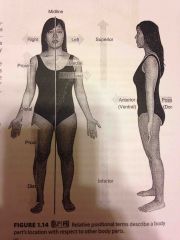
The neck is inferior to the head |
|
|
Anterior |
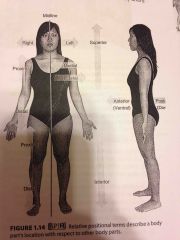
Towards the front |
The eyes are anterior to the brain. |
|
|
Posterior |
Means towards the back |
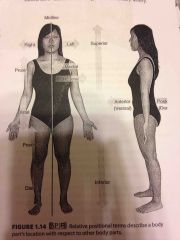
The pharynx is posterior to the oral cavity |
|
|
Medial |
Refers to an imaginary midline dividing the body into equal right and left halves |
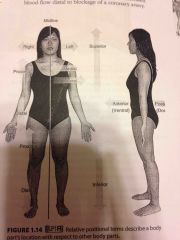
The nose is medial to the eyes |
|
|
Lateral |
Towards the side, away from the midline |
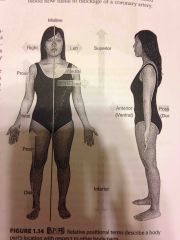
The ears are lateral to the eyes |
|
|
Superficial |
Means situated near the surface |
The epidermis is the superficial layer of skin |
|
|
Sagittal |
Refers to a lengthwise plane that divides the body into right and left portions |
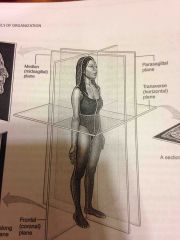
Much like the midline |
|
|
Transverse |
Refers to a plane that divides the body into superior and inferior portions |
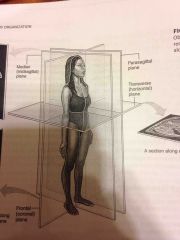
|
|
|
Frontal |
refers to a plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions |
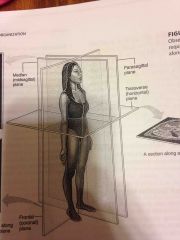
|
|
|
Epigraphic region |
The upper middle portion |
|
|
|
Right/left hypochondriac regions |
Each side of the epigastric region |
|
|
|
Right/left lateral regions |
on each side of the umbilical region |
|
|
|
Umbilical region |
The middle portion |
|
|
|
Pubic region |
The lower middle portion |
|
|
|
Right/left inguinal iliac regions |
Each side of the hypogastric region |
|

