![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Glycolysis |
Occurs in cytoplasm of cells 1. Glucose is phosphorylated using ATP forming hexose phosphate +ADP and its phosphorylated it again to form hexose bisphosphate. This splits into 2 triose phosphates 2. Triose phosphate is oxidised to form pyruvate. NAD accepts the h+ and becomes reduced and 4 ATP is produced so net production of 2 ATP |
|
|
|
The link reacton |
Pyruvate is actively transported into matrix of mitochondria 1.pyruvate is decarboxylated by removing co2 2. NAD is reduced by collecting hydrogen from the pyruvate and changing it into acetate 3.acetate is combined coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A No ATP is need for this Products: 2 acetyl coenzyme a 2 co2 2 reduced NAD |
|
|
|
The kreb cycle |
Occurs in matrix 1. Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate. Catalysed by citrate synthase. CoA goes back to link reaction 2.citrate is converted to 5C compound. Decarboxylation occurs where CO2 is removed. Dehydrogenation occurs too, h+ is used to reduce NAD 3 5C is converted to 4C (oxaloacetate) by Decarboxylation and Dehydrogenation. Reduced FAD, 2 reduced NAD and ATP is produced by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate.
Substare level phosphorylation where phosphate group is transfered dirxtkey from one molecule to another |

|
|
|
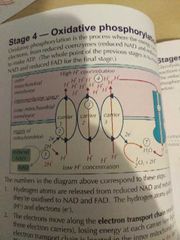
Oxidative phosphorylation |
1.hydrogen atoms are released from the reduced NAD and FAD forming h+ and e- 2.e- move along the electron transport chain losing energy at rack carrier. The chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane which is folded into cristae for increased SA 3. The energy is used to pump h+ from the matrix into the intermembrane space creating a electrochemical gradient 4. H+ moves back down the conc gradient into the matric through ATP synthase 5. This movement synthesis ATP and in the matrix e-, h+ and O2 combine to form h2o
This process can be known as chemiosmosis |
|

