![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
phenol red
|

What is the pH indicator in a TSI?
|
|
|
Ferrous sulfate
|

What is the indicator of H2S in a TSI?
|
|
|
Glucose
|

What carbohydrate has been fermented in this TSI?
|
|
|
Sucrose and lactose have not been fermented
|

What does the slant of this TSI tell you about the fermentation of carbohydrate?
|
|
|
Sucrose and/or lactose have been fermented
|

What does the slant of this TSI tell you about the fermentation of carbohydrate?
|
|
|
Acid
Ferrous sulfate will not turn black in the presence of H2S unless both H2S and acid are present, so the black color can be read as H2S positive and acidic. |

What is the pH of the butt of this TSI? How do you know?
|
|
|
In some organisms, glucose fermentation produces gas (CO2)
|

Why is gas produced in TSI by some organisms?
|
|
|
Alkaline
|

What is the pH of this TSI slant?
|
|
|
Ammonia
Deamination of the amino acids of protein in the media |

What is produced to turn this TSI slant this color? How is this product made?
|
|
|
Pseudomonas is an aerobe and thus can not ferment any carbohydrates. The slant turns red/pink because of protein utilization (deamination)
|

Why does Pseudomonas not turn a TSI yellow?
|
|
|
K slant
A butt Gas negative Sulfur positive |

What are the results of this TSI?
|
|
|
K slant
A butt Gas positive (small bubble on side) Sulfur negative |

What are the results of this TSI?
|
|
|
A slant
A butt Gas negative Sulfur positive |

What are the results of this TSI?
|
|
|
A slant
A butt Gas positive Sulfur negative |

What are the results of this TSI?
|
|
|
phenol red
|

What is the pH indicator in a carbohydrate fermentation broth?
|
|
|
Acidic (A)
|

What is the pH of this carbohydrate fermentation broth?
|
|
|
Alkaline (K)
|

What is the pH of this carbohydrate fermentation broth?
|
|
|
Neutral (N)
|

What is the pH of this carbohydrate fermentation broth?
|
|
|
Acidic with gas (AG)
|

What is the pH of this carbohydrate fermentation broth?
|
|
|
Ammonia
Deamination of the amino acids of protein in the media |

What is produced to turn this carbohydrate fermentation broth red/pink? How is this product made?
|
|
|
Citrate
|

What is the sole carbon source in this media?
|
|
|
Bromothymol blue
|

What is the pH indicator in a citrate?
|
|
|
alkaline
|

What is the pH of this citrate slant?
|
|
|
Ammonia
|

What product of metabolism turned this citrate blue?
|
|
|
Ammonium phosphate was utilized and ammonia is produced.
This only occurs if citrate can be used as a carbon source |

What was metabolized to turn this citrate slant blue? How does this mean that citrate was metabolized?
|
|
|
positive
|

What are the results of this citrate?
|
|
|
negative
|

What are the results of this citrate?
|
|
|
phenol red
|

What is the pH indicator in a urea broth?
|
|
|
Alkaline
|

What is the pH of this positive urea broth?
|
|
|
Ammonia
|

What is produced when urea is utilized?
|
|
|
positive
|

What are the results of this urea broth?
|
|
|
negative
|

What are the results of this urea broth?
|
|
|
positive
|

What are the results of this methyl red broth?
|
|
|
negative
|

What are the results of this methyl red broth?
|
|
|
Mixed acid
|

What is produced from the utilization of glucose in this methyl red?
|
|
|
Glucose
|
What is the carbon source in a MR/VP broth?
|
|
|
positive
|

What are the results of this Voges-Proskauer broth?
|
|
|
negative
|

What are the results of this Voges-Proskauer broth?
|
|
|
Acetoin
|

What is produced from the utilization of glucose in this Voges-Proskauer?
|
|
|
Diacetyl
|

Acetoin is converted to _____ when KOH and O2 are added to the Voges-Proskauer test?
|
|
|
alpha naphthol
|

What is the indicator of diacetyl in the Voges-Proskauer test?
|
|
|
peptonized iron
|

What is the indicator of H2S in the SIM?
|
|
|
Tryptophan
|

What is the carbon source in the SIM?
|
|
|
ammonia
indole pyruvate |

What compounds are produced when tryptophan is utilized in the SIM?
|
|
|
Kovac's reagent
|

What is the indicator of indole in the SIM?
|
|
|
Indole
|

Kovac's reagent turns pink in the presence of _____.
|
|
|
positive
|

Is this SIM sulfur positive or negative?
|
|
|
negative
|

Is this SIM sulfur positive or negative?
|
|
|
positive
|

Is this SIM indole positive or negative?
|
|
|
negative
|

Is this SIM indole positive or negative?
|
|
|
positive
|

Is this SIM motility positive or negative?
|
|
|
negative
|

Is this SIM motility positive or negative?
|
|
|
positive
|

Is this SIM motility positive or negative?
|
|
|
Lactose
|
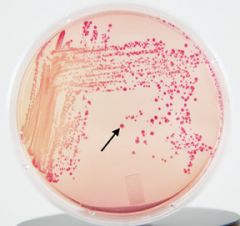
What is the carbohydrate in a MacConkey plate?
|
|
|
Neutral red
|
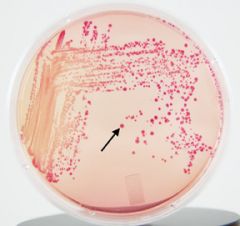
What is the pH indicator in a MacConkey plate?
|
|
|
Bile salts and crystal violet
|
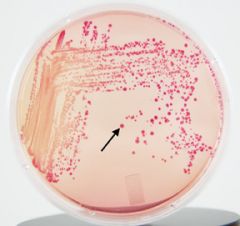
What are the inhibitors in a MacConkey plate?
|
|
|
Acid
|

What is produced when lactose is fermented in a MacConkey plate?
|
|
|
acid
lactose |
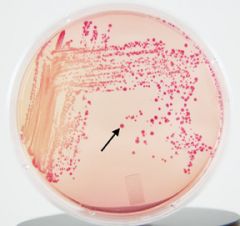
The bright pink colonies on this MacConkey plate indicate that ____ is produced when _____ is fermented.
|
|
|
lactose
protein |
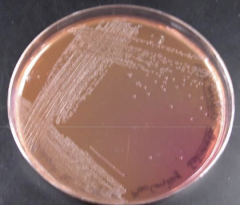
These translucent pale pink colonies on this MAC indicate that ____ was not fermented but ____ was used as a carbon source instead.
|
|
|
positive
|
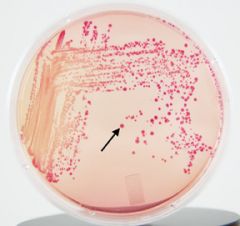
This MacConkey plate is lactose ______.
|
|
|
negative
|
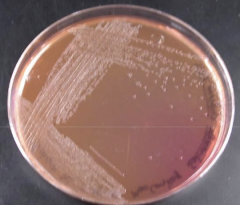
This MacConkey plate is lactose ______.
|
|
|
bile salts
|

The pink fuzzy halo around these colonies growing on a MacConkey plate is the result of lactose fermentation and the precipitation of ________ because of the very low pH.
|
|
|
Reversion
The organism uses lactose first and the pH drops but later begins to use the protein. The breakdown of protein produces ammonia from deamination and the pH goes up. |
What causes the results of lactose positive organism on MacConkey's or EMB to appear to change to negative? Why?
|
|
|
Gram positives
|
MAC is selective because bile salts and crystal violet inhibit the growth of _____.
|
|
|
Serratia
|
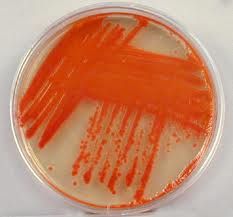
This red pigment indicates that this organism is _____
|
|
|
Pseudomonas
|
Which organism smells like grapes?
|
|
|
Proteus
|
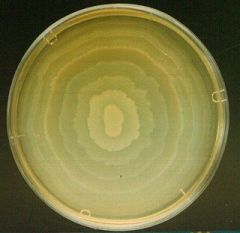
The spreading growth on this TSA indicates growth of ______
|
|
|
Swarming
|
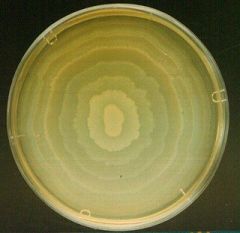
The spreading growth on this TSA is called ______.
|
|
|
Enterobacteriaceae
|
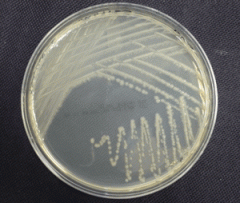
The family that enterics belong to is the _____
|
|
|
Facultative aerobes
|
All enterics are _____ (O2 utilization)
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Which carbohydrate can all enterics utilize?
|
|
|
Mannitol
|
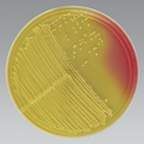
What is the carbohydrate in MSA?
|
|
|
Phenol red
|
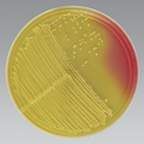
What is the pH indicator in MSA?
|
|
|
7.5% NaCl
|
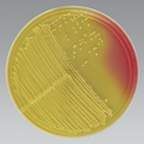
What is the inhibitor in MSA?
|
|
|
Acid
|
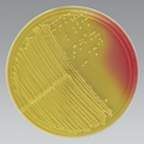
What is produced when mannitol is fermented in MSA?
|
|
|
acid
mannitol |
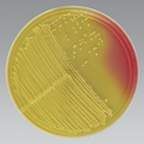
The bright colonies with a yellow halo on this MSA plate indicate that ____ is produced when _____ is fermented.
|
|
|
mannitol
protein |

These white colonies with a bright pink halo on this MSA indicate that ____ was NOT fermented but ____ was used as a carbon source instead.
|
|
|
positive
|
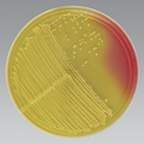
This MSA plate is mannitol ______.
|
|
|
negative
|

This MSA plate is mannitol ______.
|
|
|
Non-halophiles
|
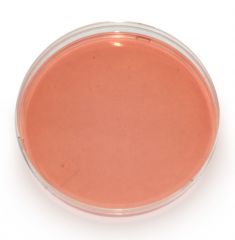
MSA is selective because the high salt inhibits the growth of _____
|
|
|
Staphylococcus
|
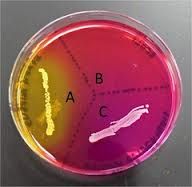
The organism in our lab that grows on MSA because it is a halophile is _____
|
|
|
Ammonia
Deamination of the amino acids of protein in the media |

What is produced to turn this MSA bright pink? How is this product made?
|
|
|
positive
|

This MacConkey plate is lactose ______.
|
|
|
Sodium thiosulfate
|

What is the sulfur source in a TSI?
|
|
|
Sodium thiosulfate
|

What is the sulfur source in a SIM?
|
|
|
Acid
|

What is the pH of the butt of this TSI?
|

