![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the range equation?
|
Equation used to determine the depth at which an echo signal is formed (D) related to the time delay between the pulse emission and the echo reception (t)
D= ct/2 c= speed of sound propagation (average of 1540 in soft tissues) the 2 is because it takes into account the time it takes to get to the reflector and return back to the transducer by crossing the same distance twice |
|
|
If the sound propagation speed of the imaged tissue is slower than 1540 m/s, the calculated distance will be erroneously (long/short)?
|
long
|
|
|
What is A-mode?
|
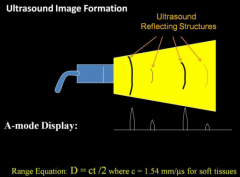
amplitude mode- basically shoots a pulse and gives a display of sequence of amplitude vs distance (not generally used)
|
|
|
What is M-mode?
|
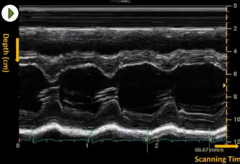
Motion mode- echo signal amplitude for a single line segment is displayed as a function of time. Best used to evaluate moving structures (heart valves)
|
|
|
What is B-mode?
|
Brightness mode- The basic 2D greyscale mode we use everyday.
|
|
|
What is pulse duration?
What is pulse repetition period? What two factors determine the minimum pulse repetition period? |
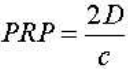
pulse duration: The time it takes for an ultrasound pulse to be emitted and the echo to return to the transducer (1ms)
This is done along the length of the transducer at different angles, the time it takes before the next sequence of pulses are emitted is the pulse repetitoin period. (50-200 ms) Limiting factors: speed of sound propagation (c) Maximum depth of the field of view (D) |
|
|
What is the pulse repetition FREQUENCY?
|
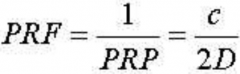
The time needed for the emitted pulse to reach te maximum depth of field of view; the reciprocal of pulse repetiton PERIOD called the pulse repetition fequency (kHz)
|
|
|
What is the benefit of an array transducer over a single element transducer?
|
An array allows you to electronically focus the sound beam to multiple focal zones. A single element transducer has a fixed focal zone.
Downside: Longer time is needed to form the image frame The segment of the beam before the focal zone is the near field (fresnel zone) The segment of the beam beyond the focal zone is the far field (Fraunhofer zone) |
|
|
What is framerate?
|

The time it takes to generate a single image frame. This is directly proportional to temporal resolution, therefor the higher the framerate, the more precisely you can watch something move.
The limiting factors are identical to those of the pule repetition frequency. (speed of sound, depth of field) Additonal factors: total number of scan lines/frame, total number of focal zones |
|
|
What is the effect of the following on framerate?
1) Depth 2) Multiple focal zones 3) Line density |
Depth = slower framerate
Multiple focal zones = slower framerate (with newer parallel processing technology, the delay is reduced but is susceptible to range ambiguity artifacts) Line density: more lines = slower framerate |
|
|
Match the type of resolution to it's determining factor
Axial Resolution Slice thickness Lateral Resolution Pulse length Elevational Resolution Beam width |
Axial Resolution: Pulse length
Lateral Resolution: Beam width Elevational Resolution: Slice thickness |
|
|
What is transmit power?
|
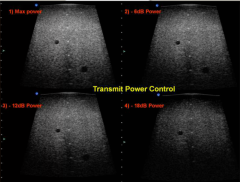
Affects the amplitude of the pulse emitted.
Strong pulse = better signal to noise ratio and better penetration. Increased potential of bioeffect from ultrasound exposure use ALARA |
|
|
What is overall gain?
|
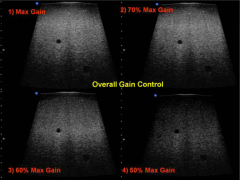
Like the volume knob on a radio.
Just increases brightness has no effect on signal to noise ratio or depth of penetration (unlike transmit power) |
|
|
What is time gain compensation?
|
Series of knobs which amplify or dampen signal relative to distance from transducer. Since sound is attenuated as a function of time and frequency used, TGC allows for amplification of the far field to produce a uniform image.
|
|
|
What is dynamic range?
How is it related to contrast? |
Range of signal used to generate an image. If the signal is too low, it is rejected as noise. if the signal is too high, it is considered saturated and is reassigned a maximum predefined value.
The range is wide and therefore logarithmic Low range = better contrast but noisier (fewer grey values to define image) high range= less contrast but smoother image |
|
|
How is transducer frequency related to spatial resolution and penetration?
|
high frequency = better spatial resolution, poor penetration
low frequency = poor spatial resolution, better penetration |
|
|
What's the difference between write zoom and read zoom?
|
write zoom is done by rescanning the region of interest and writing only the echo signal withn the ROI (benefit: better resolution but requires a rescan of patient)
read zoom uses already stored image data and just zooms in on the already written image (poorer resolution but can be done on a frozen image |
|
|
What is preprocessing?
What is persistence? What is postprocessing? |
any manipulation of the raw transducer data (live data) before it is written to memory.
persistence: frame averaging which is used to minimize noise at the expense of temporal resolution. Any image manipulation done after the image is stored. |
|
|
What is compound imaging?
|
averaging of multiple frames at multiple angles to reduce ultrasound artifacts such as speckles, clutter and shadowing.
|
|
|
What is panoramic Imaging?
|
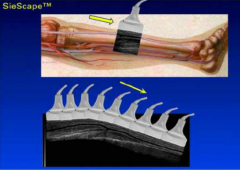
stitching together of multiple slices of a large segment of anatomy
|
|
|
What is a scan converter?
|
The physical device which converts ultrasound echo signals into a display image
|
|
|
What is the pixel depth of a B-mode or M-mode ultrasound image?
Color Doppler? |
8 bits (256 gray levels)
24 bit for color doppler 8 bits/ 1 byte. Therefor a B-mode/M-mode US pixel is 1 byte in size. 3 bytes for color doppler. 1 MB = 2^20 Bytes |
|
|
What's the difference between hard copy and soft copy?
|
hard copy = print out, video tape recorder
soft copy = unprinted digital file |
|
|
QC: Use phatoms (2 types) water and rubber
water- more accurate but prone to dehydration rubber- less accurate more stable Check for visual/physical defects Check for Sensitivity/Penetrance capability- if changes >1 cm: replace Check for Image uniformity |
Check workstation and hard copy fidelity
Check anechoic void perception (ability to detect cystic objects) Low-Contrast Object Detectability Horizontal and Vertical Distance Accuracy Check axial and lateral spatial resolution Check Ring down and dead zone (distance from surface where image becomes clear (should be less than 3mm for a 7 MHz transducer This can be done using the system display or dedicated transducer testing device (better) |
|
|
What is the average attenuation coefficient for soft tissue?
|
0.5 - 1.0 dB/cm/MHz
|

