![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a hydrocarbon? |
A carbon bonded to a hydrogen. |
|
|
What are functional groups? |
Other atoms or molecules bound to the hydrocarbon skeleton. |
|
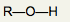
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Hydroxyl Occurrence: Alcohols |
|
|
What is the significance of the OH group in an alcohol? |
Hydrophilic and polar |
|
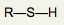
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Sulfhydryl Occurrence: Thiols |
|
|
What is the significance of the SH group in a thiol? |
Polar and hydrophilic
|
|
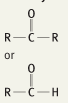
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Carbonyl Occurrence: Ketones and Aldehydes |
|
|
What is the significance of the carbonyl group in a ketone and aldehyde? |
Polar and hydrophilic |
|
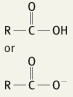
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Carboxyl Occurrence: Carboxylic acids |
|
|
What is the significance of the carboxyl group in a carboxylic acid? |
Hydrophilic |
|
|
What kind of acid always has the carboxyl group (COOH) at the end? |
Amino acids. |
|
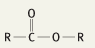
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Ester Occurrence: Esters |
|
|
Where do esters occur? |
In dietary fats and oils, and also in our body as triglycerides. |
|
|
What is a common medicinal ester? What is it an ester of? |
Aspirin, ester of salicylic acid. |
|
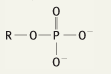
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Phosphate Occurrence: Phosphates |
|
|
What is the significance of the phosphate group in a phosphate? What is an important example in the body? |
Very hydrophilic. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). |
|
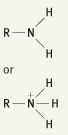
What is the functional group name for this structure? What does it occur in? |
Name: Amino Occurrence: Amines |
|
|
At the pH of body fluids, most amino groups have a charge of what? |
Charge of 1+. |
|
|
All _____ acids have an amino group at one end. |
All amino acids have an amino group at one end. |
|
|
What are macromolecules? |
Small organic molecules combined into very large molecules. Usually polymers |
|
|
What are polymers? |
Large molecules formed by the covalent bonding of many identical or similar small building-block molecules called monomers. |
|
|
What are isomers? |
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures. |
|
|
What are carbohydrates? |
Include sugars, glycogen, starches, and cellulose. Function mainly as a source of chemical energy for generating ATP. |
|
|
What elements are found in carbohydrates? |
C, H, O |
|
|
What are the three major groups of carbohydrates? |
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. |
|
|
What are monosaccharides? |
Simple sugars that contain from 3 to 7 carbon atoms. |
|
|
What are important examples of monosaccharides? |
Glucose (the main blood sugar). Fructose (found in fruits). Galactose (in milk sugar). Deoxyribose (in DNA). Ribose (in RNA). |
|
|
How are monosaccharides designated? |
They are designated by names ending in “-ose”. Ex. Trioses (3 carbon sugar) |
|
|
What are disaccharides? |
Simple sugars formed from the combination of two monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis. |
|
|
What are important examples of disaccharides? |
Sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose. Lactose (milk sugar) = glucose + galactose. Maltose = glucose + glucose. |
|
|
What are polysaccharides? |
From tens to hundreds of monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. |
|
|
What are important examples of polysaccharides? |
Glycogen Starch Cellulose |
|
|
Which body cells store glycogen? |
Cells in the liver and in skeletal muscle store glycogen. |
|
|
What are lipids? |
An organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that is usually insoluble in water, but soluble in alcohol, ether, and chloroform. |
|
|
What is a lipoprotein? |
One of several types of particles containing lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) and proteins that make it water soluble for transport in the blood.
|
|
|
What are the most important types of lipids in the body? |
Fatty acids Triglycerides Phospholipids Steroids Eicosanoids
|
|
|
What are the functions of fatty acids? |
Used to synthesize triglycerides and phospholipids or catabolized to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). |
|
|
What are the functions of triglycerides? |
Protection, insulation, energy storage. (fats and oils). |
|
|
What are the functions of phospholipids? |
Major lipid component of cell membranes. |
|
|
What are the five types of steroids? |
Cholesterol Bile Salts Vitamin D Adrenocortical hormones Sex hormones
|
|
|
What is the function of cholesterol? |
Minor component of all animal cell membranes; precursor of bile salts, vitamin D, and steroid hormones. |
|
|
What is the function of bile salts? |
Needed for digestion and absorption of dietary lipids. |
|
|
What are the functions of vitamin D? |
Helps regulate calcium level in body; needed for bone growth and repair. |
|
|
What are the functions of adrenocortical hormones? |
Help regulate metabolism, resistance to stress, and salt and water balance. |
|
|
What are the functions of sex hormones? |
Stimulate reproductive functions and sexual characteristics. |
|
|
What are the functions of eicosanoids? |
Have diverse effects on modifying responses to hormones, blood clotting, inflammation, immunity, stomach acid secretion, airway diameter, lipid breakdown, and smooth muscle contraction. |
|
|
What are four other important lipids? |
Carotenes Vitamin K Vitamin E Lipoproteins |
|
|
What are the functions of carotenes? |
Needed for synthesis of vitamin A (used to make visual pigments in eye); function as antioxidants. |
|
|
What are the functions of vitamin K? |
Required for synthesis of blood-clotting proteins. |
|
|
What are the functions of vitamin E? |
Promotes wound healing, prevents tissue scarring, contributes to normal structure and function of nervous system, and functions as antioxidant. |
|
|
What are the functions of lipoproteins? |
Transport lipids in blood, carry triglycerides and cholesterol to tissues, and remove excess cholesterol from blood. |
|
|
What are proteins? |
An organic compound consisting of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur and phosphorus; synthesized on ribosomes and made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. |
|
|
What are the six types of proteins? |
Structural Regulatory Contractile Immunological Transport Catalytic |
|
|
What are the functions of structural proteins? Examples? |
Form structural framework of various parts of body. Examples: collagen in bone and other connective tissues; keratin in skin, hair, and fingernails. |
|
|
What are the functions of regulatory proteins?Examples? |
Function as hormones that regulate various physiological processes; control growth and development; as neurotransmitters, mediate responses of nervous system. Examples: the hormone insulin (regulates blood glucose level); the neurotransmitter known as substance P (mediates sensation of pain in nervous system). |
|
|
What are the functions of contractile proteins? Examples? |
Allow shortening of muscle cells, which produces movement. Examples: myosin; actin. |
|
|
What are the functions of immunological proteins? Examples? |
Aid responses that protect body against foreign substances and invading pathogens. Examples: antibodies; interleukins. |
|
|
What are the functions of transport proteins? Examples? |
Carry vital substances throughout body. Example: hemoglobin (transports most oxygen and some carbon dioxide in blood). |
|
|
What are the functions of catalytic proteins? Examples? |
Act as enzymes that regulate biochemical reactions. Examples: salivary amylase; sucrase; ATPase. |
|
|
What are amino acids? |
Monomers of proteins. |
|
|
In an amino acid, what is the minimum number of carbon atoms? Of nitrogen atoms? |
An amino acid has a minimum of two carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. |
|
|
What is a peptide bond? |
The covalent bond joining each pair of amino acids. |
|
|
What type of reaction takes place during catabolism of proteins? |
Hydrolysis occurs during catabolism of proteins. |
|
|
What is a dipeptide? |
Combination of two amino acids. |
|
|
What is a tripeptide? |
Combination of three amino acids. |
|
|
What is a peptide? Polypeptide? |
Peptide: 4–9 amino acids Polypeptide: 10-2000 or more amino acids |
|
|
What is the primary structure? |
The unique sequence of amino acids that are linked by covalent peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. |
|
|
What is the secondary structure of a protein? |
The repeated twisting or folding of neighboring amino acids in the polypeptide chain. |
|
|
What is the tertiary structure? |
The three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide chain. |
|
|
What is the quaternary structure? |
The arrangement of the individual polypeptide chains relative to one another in proteins that contain more than one polypeptide chain (not all of them do). |
|
|
Proteins can be classified as what two things on the basis of overall shape? |
Fibrous or gobular. |
|
|
What distinguishes fibrous proteins? |
Insoluble in water and their polypeptide chains form long strands that are parallel to each other. |
|
|
What are some examples of fibrous protein? |
Collagen Elastin Keratin Dystrophin Fibrin Actin Myosin |
|
|
What distinguishes globular proteins? Function? |
More or less soluble in water and their polypeptide chains are spherical (globular) in shape. Metabolic function. |
|
|
What are some examples of gobular proteins? |
Enzymes Antibodies Complete proteins Hemoglobin Lipoprotein Albumins Membrane proteins Hormones (such as insulin) |
|
|
What is denaturation? |
Process that takes place if a protein encounters an altered environment, resulting in it unraveling and losing its characteristic shape. These proteins are no longer functional. |
|
|
What are enzymes? |
A substance that accelerates chemical reactions; an organic catalyst, usually a protein. |
|
|
Some enzymes consist of two parts. What are they? |
Apoenzyme: a protein portion Cofactor: a nonprotein portion |
|
|
What are the three important properties of enzymes? |
1. Highly specific 2. Efficient 3. Subject to a variety of cellular controls |
|
|
How do enzymes work? (3 steps) |
1. Enzyme and substrate come together at active site of enzyme, forming an enzyme-substrate complex 2. Enzyme catalyzes reaction and transforms substrate into product 3. When reaction is complete, enzyme is unchanged and free to catalyze same reaction again on a new substrate |
|
|
What is a nucleic acid? |
An organic compound that is a long polymer of nucleotides, with each nucleotide containing a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four possible nitrogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine or uracil). |
|
|
What are the two types of nucleic acids? What are their functions? |
DNA: forms the inherited genetic material inside each human cell. RNA: relays instructions from the genes to guide each cell's synthesis of proteins from amino acids. |
|
|
Each nucleotide of DNA consists of three parts. What are they? |
1. Nitrogenous base (A and G - purines, C and T - pyrimidines) 2. Pentose sugar (deoxyribose) 3. Phosphate group |
|
|
What are purines and pyrimidines? |
Purines: larger, double-ring bases Pyrimidines: smaller, single-ring bases |
|
|
Which bases always pair with each other? |
In DNA, thymine always pairs with adenine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in nitrogenous bases? |
DNA: A, C, G, T
RNA: A, C, G, U |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in sugar in nucleotides? |
DNA: deoxyribose
RNA: ribose |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in number of strands? |
DNA: Two (double-helix)
RNA: One |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in number of hydrogen bonds? |
DNA: A with T (2) and G with C (3)
RNA: A with U (2) and G with C (3) |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in how it is copied? |
DNA: self-replicating
RNA: Made by using DNA as a blueprint |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in function? |
DNA: Encodes information for making proteins
RNA: Carries the genetic code and assists in making proteins |
|
|
How do DNA and RNA differ in types? |
DNA: nuclear, mitochondrial
RNA: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA |
|
|
What are some cellular activities that depend on energy supplied by ATP? |
Cellular activities that depend on energy supplied by ATP include muscular contractions, movement of chromosomes, transport of substances across cell membranes, and synthesis (anabolic) reactions. |
|
|
What are the two phases of cellular respiration? |
Anaerobic phase Aerobic phase |

