![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a chemical reaction? |
The formation of new chemical bonds or the breaking of old chemical bonds between atoms. |
|
|
What is potential energy? |
Energy stored by matter due to its position. |
|
|
What is kinetic energy? |
The energy associated with matter in motion. |
|
|
What is chemical energy? |
A form of potential energy that is stored in the bonds of compounds and molecules. |
|
|
What is the law of conservation of energy? |
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. It may be converted from one form to another. |
|
|
What is an exergonic reaction? |
Release of more energy than is absorbed. |
|
|
What is an endergonic reaction? |
Absorbing of more energy than is released. |
|
|
What is activation energy? |
The minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. |
|
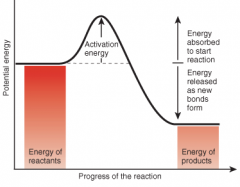
Is this reaction exergonic or endergonic? |
This reaction is exergonic because the reactants have more potential energy than the products. |
|
|
What two factors influence the chance that a collision will occur and cause a chemical reaction? |
Concentration: The greater the concentration, the greater the chance a reaction will occur
Temperature: The higher the temperature, the more likely a reaction will occur |
|
|
What are catalysts? |
Chemical compounds that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur. |
|
|
Does a catalyst change the potential energies of the products and reactants? |
No. A catalyst does not change the potential energies of the products and reactants; it only lowers the activation energy needed to get the reaction going. |
|
|
What are synthesis reactions? |
The process when two or more atoms, ions, or molecules combine to form new and larger molecules. |
|
|
What is anabolism? |
All of the synthesis reactions that occur in your body, collectively. |
|
|
What are decomposition reactions? |
A reaction that splits up large molecules into smaller atoms, ions, or molecules. |
|
|
What is catabolism? |
The decomposition reactions that occur in your body, collectively. |
|
|
What are exchange reactions? |
Reactions that consist of both synthesis and decomposition reactions. |
|
|
What are reversible reactions? |
Reactions in which the products can revert to the original reactants. |
|
|
What is oxidation? |
Refers to the loss of electrons; in the process the oxidized substance releases energy. |
|
|
What is reduction? |
Refers to the gain of electrons; in the process the reduced substance gains energy. |

