![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bacteria |
Most diverse and well known group of single celled organisms that lack nucleus |
|
|
|
Prokaryote |
Organisms with no nucleus |
|
|
|
Archaea |
Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus but are more closely related to eukaryotes than to bacteria - found in extreme locations |
|
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Organisms whose dna is contained with in the nucleus, some are unicellular, others multicellular, typically larger and more complex than bacteria or archaea |
|
|
|
Protists |
Simplest eukaryotes as a group they vary a great deal, single celled consumers to giant, multicelled producers |
|
|
|
Prostists |
A eukaryote that is not a plant, animal or fungus |
|
|
|
Fungi |
Multicelled eukaryotes (mushrooms) many are decomposers, all are consumers that secrete substances that break down food outside the body and absorb released nutrients |
|
|
|
Plants |
Multicellular eukaryotes that live on land or freshwater environments - most are photosynthetic producers, also serve as food for most other organisms in the biosphere |
|
|
|
Animals |
Multicelled consumers that ingest tissues or juices of other organisms |
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
The science of naming and classifying species |
|
|
|
Species |
Each type of organism is given a unique name - defined and grouped based on shared traits |
|
|
|
Genus |
Group of species that share unique traits |
|
|
|
Two part scientific name |
genus and species |
|
|
|
Taxon |
Rank - a group of organisms that share a unique set of features |
|
|
|
Classification System Order |
domain - kingdom - phylum - class - order - family - genus - species |
D - k - p - c - o - f - g - s |
|
|
Three Domain System |
bacteria, archaea, eukarya |
|
|
|
Eukarya |
Protists, plants, animals, fungus |
|
|
|
Prokaryote |
Bacteria, archaea |
|
|
|
Atoms |
Building blocks, make up all living things and all non living |
|
|
|
Molecules |
Two or more atoms |
|
|
|
Cell |
Smallest unit of life |
|
|
|
Tissue |
Specialized cells organized to perform a collective function |
|
|
|
Organ |
Structural unit of interacting tissues |
|
|
|
Organ system |
A set of interacting organs |
|
|
|
Multicelled organism |
Individual consisting of more than one cell |
|
|
|
Sir Francis Bacon |
Came up with scientific method |
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
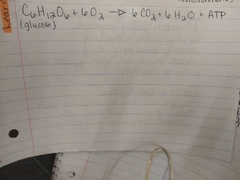
|
|
|
|
Photosynthesis |
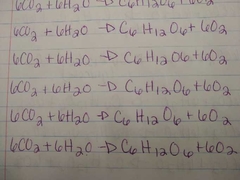
|
|
|
|
Endergonic |
Energy in from environment |
|
|
|
Exergonic |
Energy out to environment |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
A sac with two membranes that encloses and protects cell DNA |
|

