![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
133 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe where foregut, midgut, and hindgut structures produce pain respectively
|
foregut (stomach, duodenum, liver, pancreas, etc): upper (epigastric) abd pain
midgut (small bowel, appendix, prox colon): periumbilical pain hindgut (distal colon, genitourinary): lower abd pain |
|
|
what is responsible for the periumbilical and then later RLQ pain in appendicitis respectively?
|
periumbilical: visceral
RLQ: parietal (as inflammation extends to peritoneum) |
|
|
pain radiates to right infrascapular region:
pain radiates to the midback: pain radiates to flank/genitals: |
pain radiates to right infrascapular region: biliary colic
pain radiates to the midback: pancreatitis pain radiates to flank/genitals: stone/AAA |
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
pain out of proportion to exam |
Mesenteric ischemia
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
female of child bearing years |
ectopic
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
pain with walking or hitting bumps in the road on car ride |
appy, peritonitis
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
syncope |
ectopic or AAA
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
tearing pain, hx of vascular dz |
AAA, aortic dissection
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain history give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
abdominal surgery |
SBO
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
hypotension |
AAA, ectopic
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
abdominal distention or bilious emesis |
SBO, volvulus, malrotation
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
fever, RUQ pain, jaundice |
cholangitis
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
pulsatile mass |
AAA
|
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
ascities |
SBP
remember need >250 neutrophils in fluid |
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
blood in stool |
colitis
intussusception IBD cancer |
|
|
given the following abdominal pain exam finding give the concerning diagnosis (could be more than one):
benign abd exam but severe pain |
mesenteric ischemia
MI |
|
|
give at least 3 causes for pain in the RUQ
|
Acute cholecystitis and biliary colic
Acute hepatitis Acute pancreatitis Appendicitis Hepatic abscess Hepatomegaly/CHF Herpes zoster MI Perforated duodenal ulcer RLL pneumonia |
|
|
give at least 3 causes for pain in the diffuse abdominal pain
|
pancreatitis
Aortic dissection or ruptured AAA SBO early appy gastroenteritis mesenteric ischemia perforated bowel peritonitis sickle cell crisis |
|
|
give at least 3 causes for pain in the LUQ
|
acute pancreatitis
Gastric ulcer Gastritis LLL pneumonia MI Splenic pathology |
|
|
give at least 3 causes for pain in the RLQ
|
Appy
cecal diverticulitis endometriosis incarcerate/strangulated inguinal hernia meckels'diverticulitis mesenteric adenitis mittelschmerz PID Psoas abscess Regional enteritis AAA ruptured ectopic seminal vesiculitis Crohns dz Ovarian torsion Ureteral calculi |
|
|
give at least 3 causes for pain in the LLQ
|
Endometriosis
Incarcerated or stangulated inguinal hernia Mittelschmerz PID Psoas abscess Regional enteritis Ruptured AAA ruptured ectopic seminal vesiculitis sigmoid diverticulitis ovarian tosion ureteral calculi |
|
|
what is Mittelschmerz
|
lower abdominal pain that occurs in women at or around the time of an egg is released from the ovaries (ovulation)
|
|
|
child with bilious vomiting raises concern for
|
acute bowel obstruction
|
|
|
blood and mucus in stool indicates
|
intussusception
this is currant jelly (yummy) |
|
|
sore throat + abd pain
|
Strep pharyngitis
more often in kids |
|
|
tachycardia with abd pain can signify what?
|
occult blood loss
sepsis volume contraction pain |
|
|
What are the 2 signs associated with retropeeritoneal hemorrhage (esp in hemorrhagic pancreatitis)
|
Cullen's (bluish umbilicus)
Grey Turners sign (discoloration of the flank) |
|
|
high pitched or tinkling sounds can be associated with ____ especially in the presence of abdominal distention
|
SBO
|
|
|
describe murphy's sign
|
when a pt abruptly ends deep inspiration during palpation of the RUQ
sensitive for acute cholecysitits |
|
|
What is the psoas sign?
|
pt flex the thigh against resistance
appy |
|
|
what is obturator sign
|
have the pt internally and externally rotate their flexed hip
appy |
|
|
what is rovsings sign
|
pain in the RLQ precipitated by palpation of the LLQ
suggests appy |
|
|
What is Carnett's sign?
|
increased tenderness to palpation when the abdominal muscles are contracted, as when the pt lifts his or her head or legs off the bed
may be useful to distinguish abdominal wall from visceral pain |
|
|
woman with discharge from her vag along with RUQ pain
|
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
|
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
vague periumbillical pain, migrates to RLQ |
Appendicitis
CT US in preg/kids |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
rovsin,psoas, or obturator signs |
Appy
CT US |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
acute crampy colicky RUQ pain, radiate to subscapular area |
Biliary colic, cholecystitis, cholangitis
US Liver function tests Amylase, lipase |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
Crampy diffuse abd pain, n/v, no flatus or stool, hx of previous surgery |
Bowel obstruction
abdominal plain films CT |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
LLQ pain, fever, change in stool pattern, rectal bleed |
Diverticulitis
CT US Barium contrast enema |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, dizziness |
Ectopic
urine/serum pregnancy Quant hCG Rh type Hematocrit |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
intermittent crampy abdominal pain, poorly localized, nonspecific abdominal pain, absence of peritoneal signs |
Gastroenteritis
|
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
episodic colicky abd pain, n/v, bloody stool, diarrhea, episodes of crying and drawing legs up, poor feeding |
Intussusception
abdominal plain films barium/air contrast enema (gold standard, sometimes therapeutic) US Abdominal CT |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
Palpable abdominal mass, occult blood in stool, dehydration and lethargy between episodes, abdominal pain |
Inutssusception
|
|
|
What is the gold standard for diagnosing intussusception?
|
Barium or air contrast enema
sometimes is therapeutic |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
poorly localized unrelenting abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, may develop hypovolemia nad sepsis |
Mesenteric ischemia
serum lactate Abdmoinal plain films: may show pnumatosis intestinalis, portal vein gas or thumbprinting CT MRA Angiography |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
abrupt onset, severe unilateral abdominal or pelvic pain, n/v. tender adenexal mass |
Ovarian torsion
Transvag US with doppler exclude pregnancy |
|
|
Abdmoinal plain films: may show pnumatosis intestinalis, portal vein gas or thumbprinting in this problem
|
Mesenteric ischemia
|
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
severe dull epigastric or LUQ pain, radiate to back |
Pancreatitis
Amylase Lipase Abdominal CT (with contrast) |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
lower abd pin, dull constant, vaginal discharge/bleed, dypareunia |
PID
Culture for GC, Chlamydia Preg test Pelvic US to exclude tubo-ovarian abscess |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
sudden severe abd pain, may radiate to back, rigid abdomen, volume depletion |
Perforated peptic ulcer
Abdominal plain films: may show fee air Abdominal CT |
|
|
abdominal plain films may show free air in what problem?
|
perforation
|
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
severe abd pain, radiation to groin, pulsatile abd mass, abd bruit, decreased pulses |
Ruptured or leaking aortic aneurysm
Straight to OR Abd plain films ED US Abd CT |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
sudden onset severe pain may be felt in the lower abdomen scrotum or inguinal area. Previous episodes resolving spontaneously |
Testicular torsion
Straight to OR Color doppler remember you have loss of cremasteric reflex |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
abrupt onset of severe pain in the flank, radiates to the groin, n/v, writhing in pain |
Ureteral colic
UA may show mehaturia CT US + KUB |
|
|
given the following sx/signs give the diagnosis and workup:
sudden severe colicky abd pain, abd distension, n/v, constipation, tympany on exam |
Volvulus
abd plain films: extremely distended colon Barium Enema Sigmoidscopy |
|
|
what has the higher sensitivity and specificity for pancreatitis
|
Lipase
|
|
|
in cases of bowel ischemia, what are 2 important labs to order?
|
Phosphate
Lactate |
|
|
when should a plain film abdomen be ordered (what dz processes)
|
SBO
Perforated viscus Foreign bodies note: CT is still better ( more specific/sensitive) |
|
|
preferred image of choice for RUQ pain
|
US
for acute cholecystitis, gallstones, gb wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, sonographic murphy's sign |
|
|
the primary sonographic criterion of appendicitis is demonstration of a swollen, noncompressible appendix >__mm in diameter with a target configuration
|
>7mm
|
|
|
what shoudl be done for a pt with confirmed bowel obstruction or vomiting refractory to antiemetic administration?
|
G-tube
|
|
|
of pts more than 65 years of age presenting to the ED with abd pain, nearly half are admitted and about 1/3 require surgery...so you should consider getting what on them
|
Abd CT
|
|
|
entrocolitits with profuse diarrhea and dehydration
large bowel perforation associated with CMV bowel obstruction from _____ all seen in what problem |
SBO from Kaposi's sarcoma
HIV |
|
|
you have a suspected AAA, what is the very first thing to do
|
Call surgery
|
|
|
T/F
Presence of fever can distinguish btw surgical and medical causes of abd pain |
FALSE
|
|
|
T/F
Pain medications alter the ability to accurately diagnose abd pain |
FALSE
|
|
|
___ should be obtained in all oder pts and those with cardiac risk factors presenting with abd pain
|
ECG
|
|
|
an amount of blood loss greater than what is considered excessive?
|
80mL
|
|
|
menorrhagia=
metrorrhagia= oligomenorrhea= |
menorrhagia=excessive mentrual blood flow
metrorrhagia=heavy, asynchronous bleeding oligomenorrhea=decreased frequency of menstrual periods |
|
|
the corpus luteum secretes what hormone that maintains the endometrium?
|
estradiol and progesterone
in the absence of pregnancy the CL involutes resulting in withdrawal of the effects of estradiol and progesterone on the endometrium-->menstruation |
|
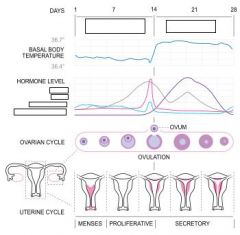
what prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum?
|
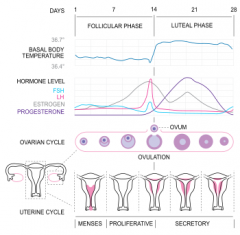
hCG
|
|
|
Greater than 95% of ectopic pregnancies occur where?
|
Fallopian tube
80% of these happen in the AMPULLA |
|
|
what is an interstitial ectopic pregnancy?
|
one that occurs at the junction of the fallopian tube and the uterus
RARE and DANGEROUS (mortality rate more than twice that of other ubal pregnancies) |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB + Fever and/or foul discharge |
septic miscarriage
PID |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB + Sycope |
ectopic pregnancy
severe anemia |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis: VB + abdominal pain |
Ectopic
Miscarriage Appy Endometritis Pyelonephritis |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB + ovulation induction (fertility) agents |
Heterotopic pregnancy
|
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB + cervical motion tenderness |
Ectopic
PID Appy |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB+ asymmetric adnexal tenderness |
Ectopic
Tubo-ovarian abscess Adnexal torsion |
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB+open internal cervical os |
miscarriage in progress (inevitable miscarriage)
|
|
|
given the following history/exam finding give the concerning diagnosis:
VB+enlarge tender uterus and/or foul discharge |
Septic miscarriage
PID Salpingitis endometritis retained products of conception in recently postpartum |
|
|
pregnancy despite the presence of an IUD is what until proven otherwise?
|
ectopic
|
|
|
pt with VB + dizziness/lightheadedness should be treated how
|
with fluid resuscitation
|
|
|
how would you list a woman with 3 live births, and one miscarriage, and one therapeutic abortion
|
G#P#Ab#
so G5P3Ab1,1 |
|
|
most common cause of ectopic pregnancy is? so what should be in your history
|
damage to the mucosa of the fallopian tube
most often a result of tubal infection/scarring so you should ask about previous PID, ectopic, tubal surg, smoking, douching |
|
|
why is there an increased risk of ectopic pregnancies in pts on fertility agents?
|
supraphysiologic lvls of estradiol or progesterone have been shown to inhibit tubal migration
|
|
|
at what fetal age should an examiner be concerned if they don't hear fetal heart sounds
|
12 weeks EGA
note they can be heard around 10 weeks normal rate is 120-160 |
|
|
given the following symptoms and signs, give the likely diagnosis of a pt with vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
benign exam, internal cervical os closed, abdominal pain |
completed miscarriage or threatened
|
|
|
given the following symptoms and signs, give the likely diagnosis of a pt with vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
vaginal spotting or bleedin, abdominal pain, near syncope, tachycardia |
ectopic
|
|
|
given the following symptoms and signs, give the likely diagnosis of a pt with vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
b-hCG greater than expected for EGA, US shows snowstorm appearance |
gestational trophoblastic dz
(molar pregnancy) |
|
|
given the following symptoms and signs, give the likely diagnosis of a pt with vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
interanl cervical os open |
Inevitable miscarriage
|
|
|
pt with menometrorrhagia, benign exam, symptomatic anemia...consider what?
|
uterine leiomyoma (fibroid)
|
|
|
compare the b-hCG lvls in a pt with an ectopic versus IUP
|
extopic will have lower quantitative hCG than IUP
|
|
|
an increase in b-hCG < __ % over 48 hours is 75% sensitive and 93% specific for abnormal gestation of some variety
|
<66%
|
|
|
T/F
it is standard of care to give Rh immune prophylaxis to Rh-negative pregnant women with vaginal bleeding in the ED |
TRUE
RhoGAM provides protection if given within 72hrs of bleeding |
|
|
what is the double ring sign?
|
the two layers of the decidua of the endometrium (decidua cdapsularis and parietalis)
this is where the gestational sac lies. if the 2 layrs are seen (the double ring), it is diagnsotic of an interuterine gestational sac |
|
|
an endometrial stripe thickness in a postmenopausal woman of what size reliably excludes endometrial neoplasm as the etiology of bleeding (thus eliminating the need for biopsy)?
|
<4mm
|
|
|
what is the medication that can be used in a stable pt with ectopic pregnancy?
|
Methotrexate
this is a folic acid antagonist that prevents synthesis of aas, RNA and DNA main complication is tubal rupture (occurs in about 4% of pts) |
|
|
first line therapeutic option for vaginal bleeding in non-pregnant pt
|
Gonadal steriods
|
|
|
pt with first trimester bleeding, b-hCG < 1,500 and indeterminate EVUS... what may be done?
|
Send home from Ed with dg of "possible ectopic pregnancy" if they are hemodynamically stable
these pts require close follow-up and repeat b-hCG in 48hrs by OB/GYN (this sounds aggressive...) |
|
|
every pt with first trimester bleeding without a document IUP must have ectopic pregnancy ruled out. This includes what 2 tests
|
Quant hcg
transvaginal US |
|
|
what is the tx for a pt diagnosed with intrauterine fetal demise (also known as missed miscarriage)
|
Manage pts expectantly
do not require emergent D&C |
|
|
pts dg with incomplete miscarriage by exam and/or EVUS are excellent candidates for medical management with what drug?
|
misoprostol
|
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
Elderly |
cardiac dysrhythmia
ACS |
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
associated with severe headache |
SAH
ICH |
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
associaed with abdominal or back pain |
Ruptured AAA
ectopic preg |
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
associated with dyspnea |
PE
|
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
documented hypotension |
ruptured AAA/ectopic
ACS Dysrhythmia aortic dissection sepsis GI bleed other blood loss |
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
diaphoresis |
cardiac or vascular etiology
|
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
cardiac murmur |
aortic stenosis
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
|
|
given the following history or exam finding, give the red flag concerning diagnosis for a pt with syncope:
rales, JVD |
CHF
|
|
|
given the following events leading to syncope, give the reason:
from supine to standing |
orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
given the following events leading to syncope, give the reason:
during exertion |
cardiac outflow obstruction (Hypertrophic CM/AS)
|
|
|
given the following events leading to syncope, give the reason:
sudden head turning, tight neck colloar |
carotid sinus hypersensitivity
|
|
|
given the following events leading to syncope, give the reason:
shortly after exposure to pain or emotions |
vasovagal
|
|
|
absence of any prodromal symptoms prior to true syncope suggests what cause
|
dysrthymia
|
|
|
prodrome of lightheadedness, nausea, diaphroesis and tremulousness should be evaluated for what cause of syncope
|
hypoglycemia
|
|
|
describe orthostatic vital sign changes
|
HR increase of more than 30 beats per minute
or systolic BP fall of more than 20mmHg |
|
|
where is the murmur of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy loudest? is it systolic or diastolic? what makes it louder?
|
Loudest at the lower sternal obrder or apex
systolic louder with valsalva (decreases with squatting) |
|
|
given the following symptoms and sign, give the cause of syncope and some of the work-up
sudden onset of ripping/tearing CP radiation to back |
Aortic dissecion
CXR (says it is not sensitive or specific...pretty sure that isn't true) CT |
|
|
given the following symptoms and sign, give the cause of syncope and some of the work-up
occurs with exertion, pt usually young, athelete, systolic murmur |
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
echocardiography |
|
|
given the following symptoms and sign, give the cause of syncope and some of the work-up
tachycardia and hypotension. lungs clear, JVD, dyspnea. |
Pericardial tamponade
ECG shows electrical alternans CXR shows cardiomegaly definitive diagnosis is made with emergent echocardiograpy(diastolic collapse of the RA and RV) |
|
|
2 most important quick tests to get in a pt with syncope
|
ECG
Glucose |
|
|
what are the EKG findings in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
|
Large amplitude QRS
Tall R waves in right precordial leads Deep narrow Q waves in the inferior or lateral leads |
|
|
what are the EKG findings of Brugada syndrome
|
complete or incomplete RBBB
with ST segment elevation in the right precordial leads |
|
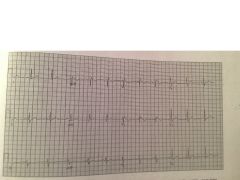
|
Brugada
coved ST segment elevaion in V1 and 2 and RBBB |
|
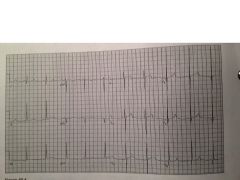
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
high QRS voltage, LVH, speudo infarct pattern (Q waves in V4-6) |
|
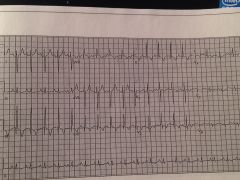
|
PE
classic S1Q3T3 |
|
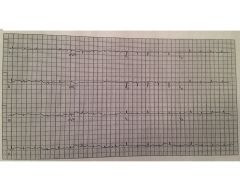
|
tamponade
electrical alternans |
|
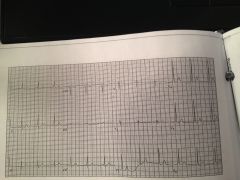
|
WPW
short PR and delta waves |
|
|
what is the FED 30 90 rule?
|
Syncope rules to predict short-term serious outcomes
F: failure (CHF) E: ecg abnormalities D: dyspnea 30: Hematocrit<30% 90: SBP<90 |
|
|
up to ___% of cardiac related syncope cases have positive orthostatic vital sign changes
|
30%
|
|
|
T/F
orthostatic vital sign abnormalities are highly specific for dehydration and rule out cardiac causes of syncope |
FALSE
|

