![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define "Model" or "Paradigm". How do the models of abnormality in psychology influence clinicians? |
Perspective used to explain an event. A way to try to make sense of what you are seeing. Influences: What clinicians ask, what they focus on while observing clients, how they interpret information, and what treatments they choose. |
A F II T |
|
|
Explain the main idea behind the biological model. |
Mental illness/ abnormal behavior is due to abnormalities in brain structure or function (chemistry.) |
|
|
|
Explain the main idea behind psychodynamic model. |
A person's behavior is determined largely by underlying psychological forces of which he/she is not consciously aware. • all behaviors are determined by past experiences |
Sigmund Freud Id, Ego, Superego |
|
|
Explain the main idea behind the behavioral model. |
Behavioral model is based on the idea that responses/ behaviors (external or internal) an individual makes are determined by our prior experiences (learned.) |
"Learned behaviors" can be adaptive or maladaptive |
|
|
How is the nervous system divided? |
Into the central nervous system & the peripheral nervous system. |
|
|
|
What makes up the central nervous system CNS. |
The brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
What makes up the peripheral nervous system? |
The somatic nervous system & autonomic nervous system which is made up by the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. |
|
|
|
What is the somatic nervous system & what is the autonomic nervous system. |
SNS- voluntary muscles ANS- involuntary muscles and organs/glands |
|
|
|
Are neurotransmitters excitatory, inhibitory, or either? |
Either |
|
|
|
1) What is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS? 2) What is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter? |
1) Glutamate 2) gamma - amino - butyric acid, GABA |
|
|
|
Explain the main idea behind the cognitive model. |
Development of new, more functional ways of thinking *** therapists help clients *** |
|
|
|
Explain the three basic steps of Cognitive therapy |
1. Recognize their biased negative interpretations, 2. Challenge the dysfunctional thought, 3. Try new interpretations and apply new ways of thinking. |
|
|
|
What division of the nervous system takes over if you are being chased by a bear? If you are resting in bed? |
Bear: somatic nervous system (voluntary muscles) Resting: autonomic nervous system (involuntary muscles) |
|
|
|
Neuron and the synapse, locate and describe dendrites, cell body, axon, presynaptic terminal, receptors, post-synaptic cell, reuptake protein. |
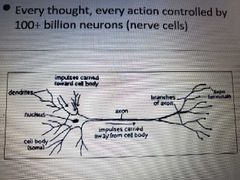
|
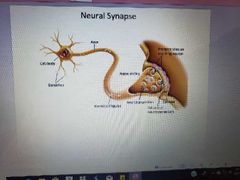
|
|
|
About what % of your personality traits and cognitive abilities were inherited from your parents? |
Best guess about 50% About 60% of your cognitive ability as shown through IQ testing is inherited. |
|
|
|
How can environmental factors affect gene expression? |
These changes in gene function lead to changes at the synapse - e.g., increased number of receptors, dendrite branches, neurotransmitters. This is how learning occurs. |
May be dormant genes becoming active or active genes becoming dormant. |
|
|
Define diathesis |
An inherited tendency/vulnerability |

|
|
|
Explain the diathesis - stress model |
People inherit genetic vulnerabilities to certain psychological disorders or behaviors which may be activated under conditions of stress. |
The smaller the genetic vulnerability, the greater the life stress required to produce the disorder and vice versa. |
|
|
We looked at a 2003 New Zealand study that showed an interaction between genetics and environmental stressors and how these factors contribute to the development of mental illness. Understand this study and the significance. |
• 847 people studied between ages 3-26 • age 26 reported if individual had been depressed during the past year. 17% had major depression during the proceeding year. • researchers looked at a gene that produces a protein involved in the transport of serotonin (5HT.) • there are 2 versions of this gene, a short (s) version and a long (l) version. |
|
|
|
2003 New Zealand study continued |
• if the person had 2 copies of the long gene, (one from each parent) they were found to be resistant (ll) to depression with similar life stressors compared to people with 2 copies of the short gene (ss) who were found to be more susceptible to depression. • people with ss where twice as likely to experience depression with 4 life stressors compared to ll |
|
|
|
2003 New Zealand Findings |
• in people with ss, severe maltreatment doubled the risk of depression compared to those who carried the ss genes but did not experience severe maltreatment. • for people with ll, severe maltreatment did not appear to significantly affect the incidence of depression. • genes and life experiences appear to contribute to the likelihood of developing the disorder . |

|
|
|
What are some factors that we know contribute to the biology of the development of mental illness. |
Genetics, viruses, trauma-mental or physical, toxins, drugs. |
|
|
|
Describe the ID |
Instinctual needs, drives, impulses - said to be always seeking gratification. Freud believed all id instincts were related to sex and libido fueled the id. |
|
|
|
Describe the superego |
We unconsciously adopt our parents values and judge ourselves by their standards. We develop a conscious and unconcious view of "right" and "wrong." • we are said to have developed a conscience |
|
|
|
Describe the ego |
The ego also unconsciously seeks gratification but it employs reason, that was gained through experiences, to control unacceptable id impulses and reduce the anxiety they arouse. |
|
|
|
Describe "Object Relations Theory" |
Propose that people are motivated by the need for relationships and that problems in relationships between children and caregivers leads to abnormal psychological development. "Object" refers to the important people in the child's early development. |
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of conditioning or learning models described in class. |
Classical Operant Modeling |
|
|
|
Describe "Pavlov's Dogs" as an example of classical conditioning. |
1. Before conditioning Unconditioned stimulus: food Unconditioned response: salivation 2. Before conditioning Neutral stimulus: bell No conditioned response: no salivation 3. During conditioning Bell + food > response Unconditioned response salivation 4. After conditioning Conditioned stimulus: bell Conditioned response: salivation |
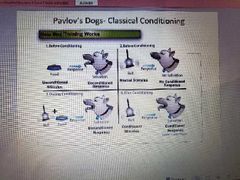
|
|
|
Define "classical conditioning" |
Type of learning in which a neutral stimulus is paired with a response until it elicits that response. An important concept in many emotional disorders. • initially studied by Ivan Pavlov (1849- 1936) |
|
|
|
Define "operant conditioning" |
•B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) •a type of learning in which behavior changes as a function of what follows the behavior. Operant conditioning is different from classical conditioning because it connects the behavior with reinforcement or punishment. |
|
|
|
Negative reinforcement |
Involves the removal of a negative condition in order to strengthen a behavior A behavior is strengthened by stopping or removing or avoiding a negative outcome/averse stimulus Behaviors that allow one to escape an adverse stimuli are said to be negatively reinforced |
Think of subtracting something from a situation. If you remove something to increase a behavior its negative reinforcement |
|
|
Cortisol |
Secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress. Associated with anxiety and mood disorders. |
|
|
|
Estrogen and progesterone |
Associated with premenstrual dysphoria, postpartum depression. |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus 2 important systems |
1. The autonomic nervous system 2. The endocrine system |
|
|
|
What would you need to happen to runaway from a tiger? |
SNS, direct stimulation of organs that is consistent with needs to fight or flight. |
|
|
|
Examples of negative reinforcement |
Sunscreen Leaving for work early to avoid traffic A child misbehaving at dinner to avoid eating vegetables. Parent removes vegetables = negative reinforcement of child's behavior. Elevator phobia |
By eliminating undesirable outcomes, these behaviors become more likely to occur. |
|
|
Positive reinforcement |
Presenting a reinforcer in order to strengthen a behavior. Most effective when presented immediately after the behavior. This is the most effective way to strengthen a behavior. |
|
|
|
Punishment |
Involves either presenting a negative stimulus (e.g. the roommate yelling about the dirty bathroom, child having to sit on the stairs, doing extra chores) or taking away a positive stimulus (taking the game boy away, removing TV time) in order to weaken a behavior. |
|
|
|
Which of these methods of operant conditioning is most effective? |
Positive reinforcement |
|
|
|
Describe "modeling" |
Individuals learn behaviors simply by observing others and repeating their behaviors. 1963 - only children exposed to an adult beating the clown doll also beat the clown doll. |
|
|
|
Behavior therapy |
Therapy based on the principles of conditioning/learning as applied to clinical problems. Example systematic desensitization |
|
|
|
Describe the cognitive model of abnormal psychology |
Albert Ellis * Aaron Beck 1960's - Ellis and Beck proposed that cognitive processes are at the center of behaviors, thoughts and emotions. • people make assumptions and adopt attitudes that are disturbing and inaccurate. • illogical thinking processes lead to abnormal functioning. Example - overgeneralization - in depression this may look like the drawing of a broad negative conclusion on the basis of a single insignificant event. |
|
|
|
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) |
Help clients accept their problem cognitions as "just thoughts" - recognize these thoughts without judging them or trying to change them and just let them pass. Employs mindfulness-based techniques. |
|
|
|
What % of people will qualify for a DSM diagnosis in their lifetimes? |
About 50% |
|

