![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is pH?
|
It is a scale representing relative concentrations of hydrogen ions in a solution.
|
|
|
Hydrogen ions (H+) are?
|
Acidic!
|
|
|
What is the number range on the pH chart? Which is acidic and which is basic?
|
0 is the most acidic, and 14 is the most basic.
|
|
|
The lower the pH the more?
|
H+ (Acidic - Lower on Chart)
|
|
|
What is the Normal mammalian pH?
|
Approximately 7.4, slightly basic.
|
|
|
What is a substance which helps keep the pH at the correct level?
|
Buffers
Example: Bicarbonate Carbonic acid -> Bicarbonate -> Carbonate |
|
|
What the outermost shell of electrons in an atom has too many or too few electrons the atom is called a?
|
Ion!
Negative ion - too many electrons. Positive ion - too few electrons |
|
|
A full electron shell equals?
|
Stability
|
|
|
Ions are attracted to their opposite and like to make the outermost?
|
electron shell full.
|
|
|
Multiple atoms bonded together are?
|
Molecules
|
|
|
The electron shells of the individual atoms in a molecule contribute to the molecules?
|
Polarity
Think of a magnet, one end is positive and the other negative. |
|
|
Carbon has how many electrons in out shell?
|
Four!
Wants to have 8. |
|
|
Carbon molecules form?
|
chains, rings and branches.
|
|
|
What is the most important monosaccharide in the body?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
Words of sugars always end in?
|
"ose"
Glucose Fructose |
|
|
Glycogen and Cellulose are a form of fuel storage. What is the big word term for this?
|
Carbohydrates
|
|
|
A fat that cannot be synthesized by the cell and must be provided in the diet is?
|
Essential Fatty Acids
|
|
|
What are the four main groups of lipid - fats, that are important for living organisms>?
|
Triglyceride
Phospholipids Steroids Eicosanoids |
|
|
Triglyceroides provide?
|
Energy use and Storage
Insulation and protection |
|
|
What do phospholipids do?
|
Have two ends one is hydrophilic and the other is hydrophobic. They create the "Lipid Bilayer"
|
|
|
Steroids are?
|
Hydrophobic, non-polar.
They can be used to make another. |
|
|
What do Eicosanoid lipids do?
|
They mediate complex chemical processes.
They have a hairpin formation. |
|
|
The building blocks of Proteins are?
|
Amino acids
|
|
|
Enzymes always end in?
|
"ase"
Lipase Dehdrogenase |
|
|
This acid is located in the nucleus or mitochondria?
|
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
|
|
|
What are the three types of Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)?
|
Transfer
Messenger Ribosomal |
|
|
What is a single cell organism without a nuclei?
|
A Prokaryote
|
|
|
What is a cell with a nucleas and found in all multicellular organisms?
|
Eukaryotes
|
|
|
What is a semi-permeable membrane which acts as a barrier between the cytoplasm and the enviornment called?
|
Cell Membrane
|
|
|
What is the inner substance of the cell, ecluding the nucleus called?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
What are the organelle within the cytoplasm that are the powerhouse of the cell? They produce and store ATP!
|
Mitochondrion
Mitochondria |
|
|
What is part of the cell responsible for protein synthesis?
|
Ribosomes
|
|
|
What part of the cell packages and alters substance for secretion or internal use?
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
What part of the cell transports and store materials in the cell? It also synthesis lips, carbs, and scretory proteins?
|
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
|
|
|
What part of the cell acts as garbage disposal?
|
Lysosome
|
|
|
What part of the cell separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm? It also controls movement in/out of the nucleus.
|
Nuclear Envelope
|
|
|
What part of the cell contains the DNA of the cell. Also controls cell metabolism and protein synthesis.
|
Nucleus
|
|
|
What acts as a cellular skeleton providing microtubules and strength?
|
Cytoskeleton
|
|
|
What are small hair like structures that are responsible for movement of a cell or movement of material over a cell?
|
Cilia and Flagella
|
|
|
Active Membrance Processes require?
Processes: Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis |
ATP! Requires Energy!
|
|
|
What is a Resting Membrane Potential?
|
A result from charged ions within the intracellular and extracellular enviornments.
|
|
|
What is the time period between cell division called?
|
Interphase
|
|
|
What is cell dividision and replication of somatic cells called?
|
Mitosis
|
|
|
What is cell division of ovocytes and sperm called?
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
What are the two categories of cancer and their meaning?
|
Benign - Rarely dangerous and doesn't spread.
Malignant - Invasive, Aggressive, and Metastasis |
|
|
A plane that runs the length of the body and divides it into left and right parts.
|
Sagittal Plane
|
|
|
A sagittal plane that divides into equal symmetrical halves?
|
Median Plane
(Midsagittal) |
|
|
This plane divides the body into cranial and caudal parts.
|
Transverse Plane
|
|
|
This plane divides the body into dorsal and ventral parts.
|
Dorsal Plane
|
|
|
Towards the back
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
Toward the belly
|
Ventral
|
|
|
Toward the head.
|
Cranial
|
|
|
Toward the tail
|
Caudal
|
|
|
Toward the tip of the nose.
|
Rostral
|
|
|
The pad. Back aspect of the forelimb.
|
Palmar
|
|
|
The pad. Back aspect of the hindlimb.
|
Plantar
|
|
|
Towards the median plane.
|
Medial
|
|
|
Away from the median plane.
|
Lateral
|
|
|
Toward the body or a point of attachment.
|
Proximal
|
|
|
Away from the body or a point of attachment.
|
Distal
|
|
|
Toward the center of the body or body part.
|
Deep / Internal
|
|
|
Away from the center of the body or part.
|
Superficial / External
|
|
|
Towards the center on a limb. (Deep)
|
Axial
|
|
|
Away from the center of a limb. (Superficial)
|
Abaxial
|
|
|
Types of Recombancy
|
Dorsal
Ventral Sternal Lateral |
|
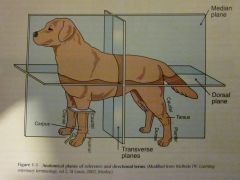
Planes
|
Know These!
|
|

Second Figure of Planes
|
Know all of these!
|

