![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are three aspects of blood?
|
Transportation System
Regulatory System Defense System |
|
|
Blood is a Transport Ion System and carries?
|
O2, Nutrients and Essential Compounds
|
|
|
What part of blood carries the O2?
|
Hemoglobin
|
|
|
What part of blood carries components other than O2?
|
Plasma
|
|
|
What does blood transport?
|
Hormones, White Blood Cells and Platelets.
It also carries waste products like carbon dioxide away from cells. |
|
|
Heat wise blood regulates?
|
Body Temperature
|
|
|
Blood aids in tissue fluid content! Also called?
|
Homeostasis
|
|
|
Blood aids in the regulation of chemical?
|
Blood pH!
Remains slightly alkaline! |
|
|
White blood cells use phagocytosis to ingest foreign bodies or taxic invaders. So blood is also a?
|
Defense System
|
|
|
What is the liquid portion of blood called?
|
Plasma
|
|
|
What are red blood cells called?
|
Erythrocytes
|
|
|
What are white blood cells called?
|
Leukocytes
|
|
|
What are platelets called?
|
Thrombocytes
|
|
|
What is a sample that contains plasma and all other components?
|
Whole Blood
|
|
|
What is plasma composed of?
|
45 to 78% of blood volume and it is 93% water.
Proteins - albumins, globulins, fibrinogen Gases - O2, CO2, Nitrogen Lipids, Amino Acids, Electrolytes (Ions) |
|
|
What carries O2 from lungs to tissue / cells?
|
RBC - Red Blood Cell
(Erythrocytes) |
|
|
What prevent leaks from blood vessels; clotting?
|
Platelets
(Thrombocytes) |
|
|
There are five types but they act as immune system protection?
|
WBC - White Blood Cells
(Leukocytes) |
|
|
From top to bottom label the HCT Tube
|
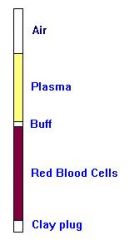
HCT Tube
|
|
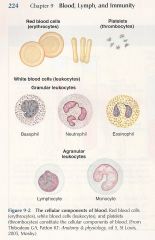
Take A Look
|
Can you remember them all?
|
|
|
What is Hematopoiesis?
|
Production of all blood cells!
Takes place within bone marrow (red) Stem cells (Pluripotent) are stimulated to produce each type as needed. Infection or special circumstances can stimulate massive production of specific cells. |
|
|
What is the process of RBC (Red Blood Cell) production called?
|
Erythropoiesis
|
|
|
When levels of O2 are low in the blood (Hypoxia) what hormone is produced to signal the red marrow to produce RBC?
|
EPO - Erythropoietin
(Hormone) |
|
|
What is the composition of the red blood cell?
|
65% water, 35% solids
Hemoglobin makes up 95% of the solids! |
|
|
What is the shape of RBC - Erythrocytes? And Why?
|
Round, non-nucleated, biconcave disks.
More membrane surface for diffusion of O2 and CO2. Shorter diffusion distance in and out. Allows to take in water without rupturing. |
|
|
Hemoglobin is composed of 2 components. What are they?
|
Heme - Pigment portion produced in the mitochondria
Globin - Protein portion produced by ribosomes |
|
|
How many molecules of O2 can a heme group carry?
|
One
|
|
|
How many heme groups attach to a globin?
|
4 heme groups attach to a globin. This means each hemoglobin can carry 4 molecules of O2.
|
|
|
What are some factors that affect the ability for hemoglobin to carry oxygen?
|
pH
Temperature Oxygen Level CO2 Level |
|
|
What does most of the destruction of old or damaged cells?
|
Macrophages
|
|
|
What is the color of blood?
|
Normal hemoglobin is red in color.
|
|
|
What is the color of plasma?
|
Plasma is normally yellow.
|
|
|
What is the destruction of RBCs within the vascular system called?
|
Intravascular Hemolysis
Occurs from insult or strees and tends to release hemoglobin into system which is picked up by plasma protein. |
|
|
What is a low number of circulating red blood cells called?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
What is an above normal increase in RBC concentration within blood called?
|
Polycythemia
|
|
|
Platelets (Thrombocytes) do what exactly?
|
Maintain and nurture endothelial cells in vascular system (prevent leaking)
Plug holes in the lining of blood vessesl and prevent hemorrhage. Stabilizes the initial plug formed when the clotting process begins (pile on top of each other). |
|
|
What is the word used for the production of platelets?
|
Thrombopoiesis
|
|
|
Any nucleated cell normally found in blood is a?
|
WBC (White Blood Cell)
Leukocyte |
|
|
What are the two main subtypes of white blood cells (leukocytes)?
|
Granulocytes
-Neutrophils -Eosinophils -Basophils Agranulocytes -Monocytes -Lymphocytes |
|
|
What is the most common WBC in dogs, horses and cats?
|
Neutrophils
|
|
|
What white blood cell type uses phagocytosis to engul and digest bacteria and viruses that they come in contact with?
|
Neutrophils
|
|
|
This white blood cells are less than 5% of total WBC count. They can inhibit local allergic reactions and also are somewhat effective against large pathogens like protozoa and parasitic worms.
|
Eosinophils
|
|
|
Least often seen and least understood WBC is the?
|
Basophils
They do contain histamine and heparin so seem related to allergic reaction and inflamation. |
|
|
What are the largest in size of WBC and are a major phagocytic cell?
|
Monocytes
|
|
|
What do monocytes do?
|
Clean up cellular debris that remain after infection.
Process antigens and present them to lymphocytes for destruction. Ingest foreign substances (Fungi, protozoa, viruses) |
|
|
What is the one WBC that has no phagocytic capabilities?
|
Lymphocytes
|
|
|
There are three types of lymphocytes, what are they?
|
T Lymphocytes
B Lymphocytes Natural Killer Cells |
|
|
What do T Lymphocytes do?
|
They are responsible for cell-mediated immunity and for activiating B cells.
|
|
|
What do Killer T Cells (T Lymphocytes) do?
|
Killers destroy cells during cell mediated immunity.
|
|
|
What do B Lymphocytes do?
|
They help produce antibodies.
Each is developed to respond to a specific antigens and produce antibodies. |
|
|
What is another word for antibodies?
|
Immunoglobulins
|
|
|
What do Natural Killer Cells do?
|
They don't have to be activated by T or B cells and have the ability to kill tumor cells and cells infected with various viruses on contact!
|
|
|
Different terms:
-cytosis -philia -penia |
-cytosis - increased number of cell type.
-philia - increased number of cell type. -penia - decreased number of cell type. |
|
|
A system that carries excess fluid from tissues to blood vessels near the heart where it is put back into the bloodstream is?
|
Lymphatic System
The fluid is called Lymph |
|
|
These ducts drump fluid back into blood vessels to be used again. Part of the lymphatic system...
|
Thoracic Ducts
|
|
|
What is a clear fluid made up of sugar, water, electrolytes and lymphocytes?
|
Lymph
|
|
|
What is the term for lymphatic fluid absorbed from the intestines - appears white or pale yellow and cloudy?
|
Chyle
|
|
|
What are the three compartment to the lymphatic system?
|
1. Bone Marrow
2. Central Lymphoid Organs 3. Peripheral Tissues |
|
|
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
|
Removal of excess tissue fluid.
Waste material transport Filtration of lymph Protein transport |
|
|
What are lymph nodes?
|
Small structures located along a lymph vessels.
Lymph from each area always passes through the same node. Contain lymphocytes that filter the lymph as it passes through. |
|
|
What is a large lymphoid organ with a capsule in the body?
|
Spleen
|
|
|
The spleen contains?
|
White pulp tissue containing lymphocytes.
Red pulp has blood vessels and blood storage spaces. |
|
|
The Thymus and Tonsils are part of the?
|
Lymphatic System
|
|
|
Over 25% of the mucosa of the intestinal tract is lymph tissue making it the?
|
largest lymphoid organ in the body.
|
|
|
The term for an inappropriately exaggerated allergic response that is life-threating is?
|
Anaphylaxis
|
|
|
The term for a disease process where an individuals immune system is sensitized to respond against certain protein that would actually be unlikely to cause disease or damage.
|
Allergy
|
|
|
The term for a disease wher the body reacts to "self" as if it is "non-self".
|
Auto-immune Diseases
|
|
|
Using vaccinations to stimulate the immune system to produce memory cells that will respond to an active threat is called?
|
Active Immunity
|
|
|
The use of antibodies not produced by the body to boost immunity. Like colostrum is?
|
Passive Immunity
|

