![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Look at me while I am reading your mind...
You are thinking.... |
MAKE THIS CLASS END ALREADY D`^*IT!!!!!!!!!!!
& I totally agree with you. |
|
|
what 2 things make endocrine glands different than exocrine glands
|
secrete HORMONES directly into the blood stream
- well vascularized lack ducts |
|
|
define hormone
|
chemical substance, produced in the body, which has specific regulatory effects on the activity of other organs/ cells
|
|
|
name the 'endocrine organs' as defined by Dr. Newkirk in class (9 of them)
|
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Pineal Adrenal Cortex Adrenal Medulla Chemoreceptor Organs Thyroid Parathyroid Islets of Langerhans |
|
|
hypothalamus produces
|
antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)
- concentrates urine oxytocin - reproductive fxns |
|
|
hypothalamus releases
|
nothing
Hypothalamus produces ADH and oxytocin which is released by the posterior pituitary |
|
|
what hormones does the pituitary make
|
Pars distalis (anterior pituitary/ adenophypophysis)
- ACTH - GH - TSH - LTH - FSH - LH Pars Nervosa (posterior pituitary/ neurohypophysis) - ADH - Oxytocin Pars Intermedia - MSH |
|
|
describe the pars distalis
|
(aka adenohypophysis)
surrounded by CT corts or clusters of cells closely associated with vascular sinuses - chromophobic cells - chromophilic cells |
|
|
pars distalis makes and releases
|
ACTH
- tells adrenal to make cortisol TSH GH LTH LH FSH |
|
|
understand the basic anatomy of the pituitary gland
|
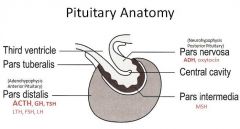
|
|
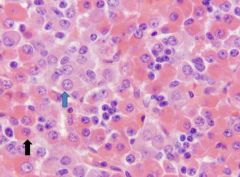
|
Pituitary (Pars Distalis)
chromophilic cells Acidophils - larger than chromophobic cells - granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (PAS negative granules) - make GH and PRL Basophils - larger than acidophils (PAS positive granules - less eosinophilic cytoplasm - make TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, MSH |
|
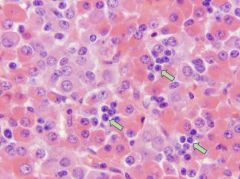
|
Pituitary (Pars Distalis)
chromophobes - AKA: chief cells, principle cells, reserve cells, gamma cells - small round cells with little cytoplasm (no cytoplasmic granules) - fxn unknown |
|
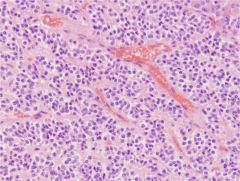
|
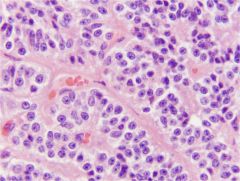
Pituitary (Pars Intermedia)
Cords or clusters of cells closely associated with vascular sinuses - Occasionally forms follicles - Basophilic cells Makes and releases: - Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) |
|
|
Pituitary (Pars Intermedia)
Cords or clusters of cells closely associated with vascular sinuses - Occasionally forms follicles - Basophilic cells Makes and releases: - Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) |
|
|
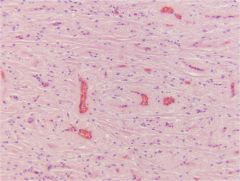
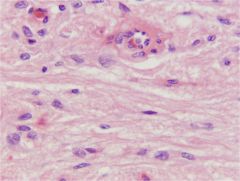
Pituitary - Pars Nervosa
AKA: Neurohypophysis Nervous tissue - Unmyelinated axons (cell bodies are in the hypothalamus) - ‘Pituicytes’ (neuroglial) Release - Oxytocin - Antidiuretic hormone |
|
|
Pituitary - Pars Nervosa
AKA: Neurohypophysis Nervous tissue - Unmyelinated axons (cell bodies are in the hypothalamus) - ‘Pituicytes’ (neuroglial) Release - Oxytocin - Antidiuretic hormone |
|
|
|
that is how I feel right about now
|
|

|
go on and try it, the slides make about the same sense both ways
|
|
|
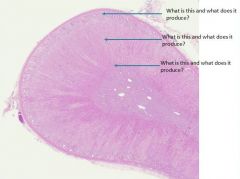
what is the pineal gland
describe it |
Dorsal evagination of the roof of the diecephalon
Photoreceptor organ in lower vertebrates - Receives light information from other parts of the brain - May function as biological clock - Sleeping, dreaming Covered by pia mater (meninges) Composed of Astrocytes - Between blood vessels and pinealocytes (interstitial cells) Pinealocytes (epitheliod) - Large cells with large, round nucleus Eosinophilic cytoplasm Makes: - Serotonin - Melatonin |
|
|
|
|
|
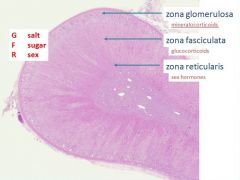
Adrenla Cortex - Zona glomerulosa
Subcapsular Clusters, arches of cells - Cuboidal to columnar - Eosinophilic cytoplasm - Small nuclei - Makes mineralocorticoids (salt!) - Aldosterone |
|
|
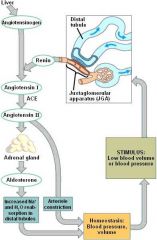
don't forget the RAAS
|
|
|
|
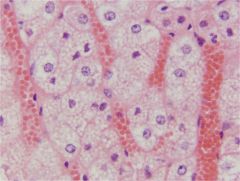
what is the widest zone of the adrenal cortex
|
zona fasiculata
|
|
|
Adrenal Cortex - Zona fasciculata
Widest zone Middle zone Cords 1-2 cells wide separated by vascular sinuses Sometimes: Very foamy cytoplasm due to lipid (spongiocytes) Makes glucocorticoids (sugar!) - Cortisol |
|
|
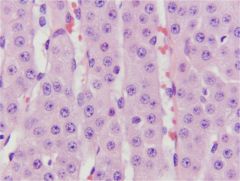
Adrenal Cortex - Zona fasciculata
Widest zone Middle zone Cords 1-2 cells wide separated by vascular sinuses Sometimes: Very foamy cytoplasm due to lipid (spongiocytes) Makes glucocorticoids (sugar!) - Cortisol |
|
|
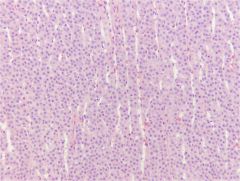
Adrenal Cortex - Zona fasciculata
Widest zone Middle zone Cords 1-2 cells wide separated by vascular sinuses Sometimes: Very foamy cytoplasm due to lipid (spongiocytes) Makes glucocorticoids (sugar!) - Cortisol |
|
|
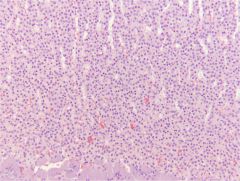
Adrenal Cortex - Zona Reticularis
top= zona glomerulosa middle = zona reticularis bottom left = medulla Anastomosing cords - Anastomosis: connection between parts of any branching system Similar to zona glomerulosa Makes sex hormones (sex!) - Testosterone etc |
|
|
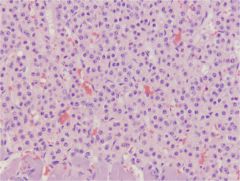
Adrenal Cortex - Zona Reticularis
Anastomosing cords - Anastomosis: connection between parts of any branching system Similar to zona glomerulosa Makes sex hormones (sex!) - Testosterone etc |
|
|
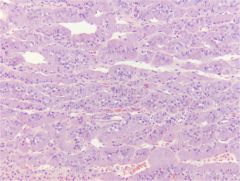
Adrenal Medulla
Ganglion cells Glandular cells - Cuboidal to columnar cells - Arranged around blood vessels - Basophilic cytoplasm with fine granules Makes catecholamines - Epinephrine (adrenalin) - Norepinephrine |
|
|
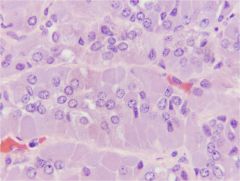
Adrenal Medulla
Ganglion cells Glandular cells - Cuboidal to columnar cells - Arranged around blood vessels - Basophilic cytoplasm with fine granules Makes catecholamines - Epinephrine (adrenalin) - Norepinephrine |
|
|
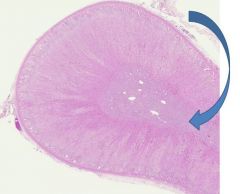
Adrenal Medulla
Ganglion cells Glandular cells - Cuboidal to columnar cells - Arranged around blood vessels - Basophilic cytoplasm with fine granules Makes catecholamines - Epinephrine (adrenalin) - Norepinephrine |
|
|
chemoreceptor organs
|
Aortic and carotid bodies
Sense blood oxygen, pH, carbon dioxide Stimulate respiration |
|
|
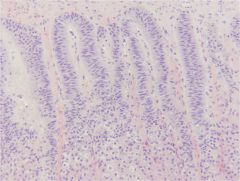
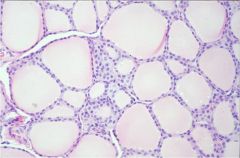
describe thyroid follicles
|
Multiple grapes
- Variable sized - Lined by cuboidal to columnar epithelium - Basal nucleus - Eosinophilic cytoplasm - Microvilli |
|
|
what does the thyroid release?
|
thyroid hormone (duh)
T3 & T4 which are released directly into the surrounding capillaries |
|
|
Thyroid follicles
In an active gland the follicles are smaller and the lining epithelium is taller - Because the colloid is secreted as soon as it’s made… |
|
|
what does thyroid hormone do?
|
regulates metabolism
|
|
|
a fat lazy dog is a diagnostic sign of
|
a fat lazy owner
or an owner in vet school who has not time for their own animals or hypothyroidism |
|
|
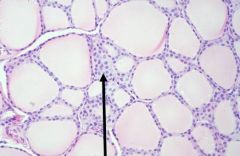
Thyroid - C cells
AKA: parafollicular cells, clear cells Present in interstitium Clear cytoplasm Make: - Calcitonin (CT) - Decreases calcium |
|
|
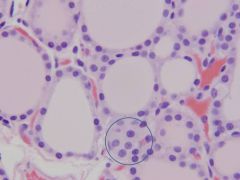
Thyroid - C cells
AKA: parafollicular cells, clear cells Present in interstitium Clear cytoplasm Make: - Calcitonin (CT) - Decreases calcium |
|
|
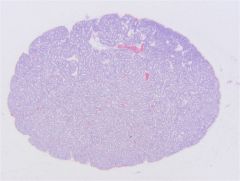
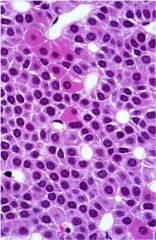
Parathyroid gland
Cords, clusters, strands, sheets, follicles or rosettes of secretory cells - Closely associated with blood vessels Chief (principle) cells - Light and dark chief cells - Eosinophilic cytoplasm (not granular) Makes Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) - increases serum calcium |
|
|
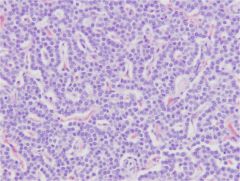
Parathyroid gland
Cords, clusters, strands, sheets, follicles or rosettes of secretory cells - Closely associated with blood vessels Chief (principle) cells - Light and dark chief cells - Eosinophilic cytoplasm (not granular) Makes Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) - increases serum calcium |
|
|
Parathyroid Gland
Oxyphil cells - Large cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm - Function unknown Only present in some species - Cattle - Horses = Humans |
|
|
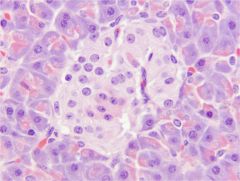
pancreas exocrine vs endocrine
|
Exocrine component
- Digestive enzymes Islets of Langerhans - Scattered throughout - Regulate glucose metabolism |
|
|
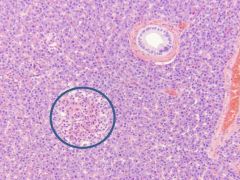
Pancreas - Islet of Langerhans
Pale-staining cells Alpha cells - Make glucagon (increases blood glucose) Beta cells - Make insulin (decreases blood glucose) C cells - Function unknown Delta cells - Make somatostatin (inhibits glucagon & insulin) These cell types CANNOT be differentiated with routine light microscopy |
|
|
Pancreas - Islet of Langerhans
Pale-staining cells Alpha cells - Make glucagon (increases blood glucose) Beta cells - Make insulin (decreases blood glucose) C cells - Function unknown Delta cells - Make somatostatin (inhibits glucagon & insulin) These cell types CANNOT be differentiated with routine light microscopy |
|

|
this is an example of a diabetes mellitus cat with low self esteem
Due to lack of insulin production - Destruction of the islets or due to ‘insulin resistance’ Hyperglycemia |
|
|
what makes calcitonin & what does it do
|
made by thyroid C cells
decreases calcium levels |
|
|
what can increase serum calcium levels and where is it produced
|
parathyroid hormone
i'm not answering the second half of that question b/c if you can't figure it out, you're screwed... |
|
|
where is ACTH produced
what does it do |
pituitary - pars distalis
tells adrenal cortex to make cortisol |
|
|
where is MSH produced
|
in pars intermedia (by chromophilic basophils)
|
|
|
where is serotonin produced
|
pineal gland
|
|
|
where is aldosterone secreted
|
adrenal cortex
zona glomerulosa |
|
|
where are mineralocorticoids secreted
|
adrenal cortex
zona glomerulosa |
|
|
where are sex hormones secreted
|
adrenal cortex
zona reticularis |
|
|
where are glucocorticoids secreted
|
adrenal cortex
zona fasciculata |
|
|
where is epinephrine secreted
|
adrenal medulla
|
|
|
what is colloid
|
storage form of thyroid hormone
|
|
|
what are the 4 cell types of the islets of langerhans & what do they do
|
Alpha cells
- make glucagon - increase blood glucose Beta cells - make insulin - decrease blood glucose C cells - function unknown Delta cells - make somatostatin - inhibits glucagon and insulin |
|
|
what is produced by the pars distalis
|
ACTH
TSH LTH GH FSH LH |
|
|
where is growth hormone secreted
|
pituitary - pars distalis
|
|
|
where is LTH secreted
|
pituitary - pars distalis
|
|
|
what do pituitary acidophils secrete?
basophils? |
acidophils
- GH - PRL Basophil - FSH - LH - TSH - ACTH - MSH |

