![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the purpose of a block valve?
|
Block valve by definition is an on-off valve.
|
|
|
Most common type of Block Valve?
|
Most common type of block valve is the gate valve.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a control valve?
|
The purpose of control valves is to restrict flow, thus enabling the flow of fluid to be throttled.
|
|
|
Most common type of Control Valve?
|
Most common type of valve used to control flow is the globe valve.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a check valve?
|
Purpose of check valves is to allow for normal flow in one direction and stop any significant flow reversal
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a pressure relief valve?
|
Pressure safety valves are used to automatically release excessive pressures.
|
|
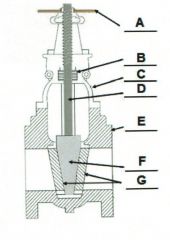
Identify the typical components of a valve.
A. |
A. Actuator (Hand Wheel)
|
|
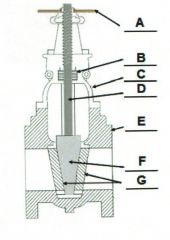
Identify the typical components of a valve.
B. |
B. Packing
|
|
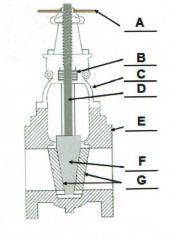
Identify the typical components of a valve.
C. |
C. Bonnet
|
|
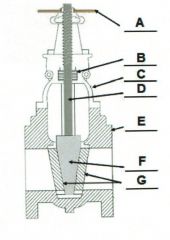
Identify the typical components of a valve.
D. |
D. Stem
|
|
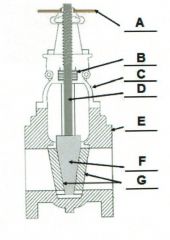
Identify the typical components of a valve.
E. |
E. Body
|
|
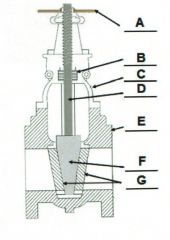
Identify the typical components of a valve.
F. |
F. Disk
|
|
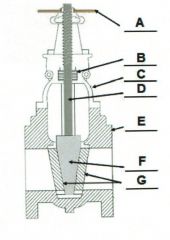
Identify the typical components of a valve.
G. |
G. Seat
|
|
|
What is valve trim?
|
Internal elements of valve collectively referred to as valve trim.
|
|
|
Valve Trim typically includes: (4)
|
Disk
Seat Stem and Sleeves to guide stem |
|
|
What is a rising stem?
|
Rising stem valve the stem rises above the hand wheel as the valve is opened.
|
|
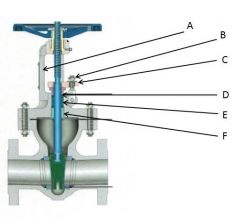
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
A. |
A. Yoke
|
|
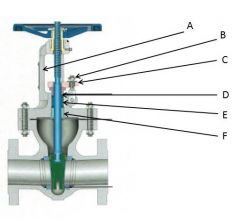
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
B. |
B. Gland Nuts
|
|
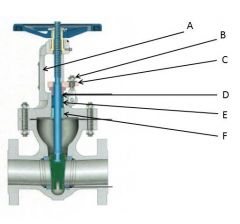
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
C. |
C. Gland Follower
|
|
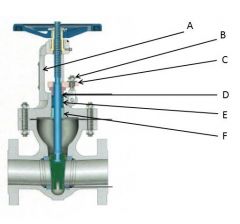
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
D. |
D. Packing Gland
|
|
|
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
E. |
E. Stuffing Box
|
|
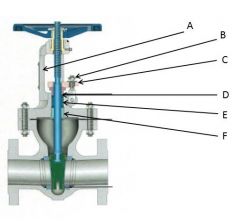
Identify the yoke, gland follower, packing gland, gland nuts, stuffing box, and packing:
F. |
F. Packing
|
|
|
Why are gate valves not used for throttling?
|
Most flow change occurs when valve more than 60% closed which causes:
Relatively high fluid velocity & results in disk and seat wear and eventual pass-through leakage For these reasons, gate valves normally not used to regulate or throttle flow. |
|
|
Why are Globe valves preferred for throttling?
|
The characteristic of moving gradually and evenly gives the globe valve good throttling ability.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a needle valve?
|
Needle valve is used to make relatively fine adjustments in the amount of fluid flow
|
|
|
Which types of valves are operated with a 90° motion of the stem?
|
Ball valves, Plug valves, & butterfly valves are all operated with a 90° motion of the stem.
|
|
|
How does a wedge plug valve operate?
|
A wedge plug valves operating mechanism lifts the plug off the seats, rotates the plug 90°, and then lowers the plug back onto the seats.
|
|
|
Where do we use wedge plug valves?
|
We use them in the Coker
|
|
|
Why does a butterfly valve have a locking handle
|
For throttling purposes, intermediate positions can be secured in place by handle-locking devices.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a sigh glass safety valve?
|
Used on gauge glasses to prevent leakage in the event of a gauge glass failure.
|
|
|
How does a sigh glass safety valve work?
|
When the valve is closed, the stem fits against the seat, preventing flow.
When the valve is partially open about ¼ of a turn (fill position), a pin on the bottom of the stem prevents the ball from seating as the fluid flows into the gauge glass. When the valve is open, a slow flow into the gauge glass can occur, but if the flow is too fast, as would occur with a gauge glass failure, the ball is forced against the seat, stopping the flow into the gauge glass. |
|
|
What is a sigh glass safety valve's normal position?
|
Normal position is 100% open
|
|
|
What are the three main classifications of valve actuators?
|
Pneumatic – air pressure.
Hydraulic – liquid pressure. Electric actuators – solenoids and motors. |
|
|
In what position will an air to open fail?
|
It will fail in the close position.
|
|
|
How does a diaphragm actuator work?
|
Diaphragm Actuators use air pressure to produce the mechanical motion required to position a valve.
|
|
|
How does a piston actuator work?
|
Piston actuators operate basically the same as diaphragm actuators.
Vertical piston actuators used in place of diaphragm actuators for Valves requiring: Significant force to operate, or large stem-travel distance. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a positioner?
|
Automatically adjusts actuator’s air output to diaphragm to maintain desired position in proportion to input signal.
|
|
|
How does a positioner work?
|
Positioner rapidly supplies a large volume of air to the actuator causing prompt movement to a new valve position.
|
|
|
How does a solenoid actuator work?
|
When current flows through coil a magnetic field is produced. As a result, coil becomes an electromagnet. Magnetic attraction pulls the plunger toward center of coil. When current flowing through coil stops the magnetic field is lost and Spring pushes iron core plunger and stem back to original positions which closes valve.
|
|
|
Draw a typical control valve station
|

|
|
|
What concerns must be addressed when bypassing a control valve?
CHECK THIS ONE NOT SURE |
Ensure that you understand what effect bypassing a control valve will have on process flow, pressure, or temperature.
|
|
|
When placing a control valve in automatic?
CHECK THIS ONE NOT SURE |
You must maintain communication with PTL
|
|
|
How does an electric motor valve actuator work?
|
The drive gear rotates the attached lug against the stem nut that then engages the threaded valve stem, which raises or lowers the stem and valve disk.
|
|
|
What are the safety concerns for using manual handwheel on a motor operated valve?
|
Forcing the actuator beyond the actuator’s designed torque/thrust limits.
Causing damage to the valve body which may cause loss of containment. |
|
|
How does a conventional PRV work?
|
Disk blocks the path between the inlet and the outlet when system pressure is normal.
Firm and even contact between the disk and the seat prevents fluid from leaking around the disk. The spring holds the disk in place against the seat to resist normal system pressure. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a thermal relief?
|
Thermal PRV’S release excess pressure that results from an increase in temperature.
|
|
|
What is the special purpose of a balanced bellows relief? ?
How does it do this? |
Balanced bellows PRVs are similar to conventional PRVs, but are designed to minimize the effect of outlet back pressure on valve performance.
With the balanced bellows valve, outlet back pressure has little effect on set pressure. The balanced bellows balances the valve disk by venting the interior of the bellows through the bonnet chamber to the atmosphere |
|
|
Safety concerns with bellows vent port?
|
Safety concerns are that process material from the discharge side to be released to the atmosphere
|
|
|
1.What is the special purpose of a pilot actuated relief valve?
2.How does it work? |
1. Pilot operated valves use process pressure instead of a spring to keep the valve closed to greatly minimize the backpressure
2.Pilot operated PRVs have a main valve combined with and controlled by a self-actuated auxiliary valve or pilot valve. Pilot operated valves use process pressure instead of a spring to keep the valve closed. The piston and seating arrangement in the main valve is designed so that the bottom surface area of the piston/disc, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the surface area of the top of the piston. Resultant downward force, therefore, holds the piston firmly on the piston’s seat. When inlet pressure reaches pilot set pressure, pilot valve opens to release fluid pressure above PRV piston to the discharge header. Inlet pressure exceeding pressure above the piston/disk causes main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to discharge. |
|
|
How does a rupture disk work?
|
As process pressure increases beyond allowable operating pressure, rupture disk starts to grow until the tensile strength of the material is reached and rupture occurs.
|
|
|
1.What is the purpose of a pressure vacuum vent?
2.How does it work? |
1.Located on tank roof, PV vent protects tank from overpressure and under-pressure (or vacuum) conditions. 2.When tank pressure increases, tank vapors lift pressure valve (called a pallet), allowing the vapors to flow out. When tank pressure decreases, atmospheric pressure lifts vacuum valve, allowing air to flow into the tank. |
|
|
What is the required position for the inlet and outlet block valves on a PRV?
|
Inlet and outlet block valves must be car sealed open (CSO) when the process is in service.
|
|
|
How should the block valves be installed?
|
PRV block and bypass valves are typically installed in a horizontal orientation
|
|
|
What is the purpose of snuffing steam on atmospheric PRVs?
|
Steam is used if the PRV has opened and released flammable material or is leaking and caught fire.
Unit personnel steam the vents to extinguish vent fires. Vents are also steamed during severe weather conditions, such as a thunderstorm, to prevent fires from leaking PRVs. |
|
|
How do you adjust valve packing?
|
One flat per turn, evenly across both gland nuts
|
|
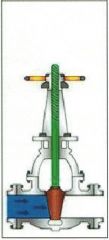
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Rising Stem Gate Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Gear Driven Knife Gate Valve
|
|
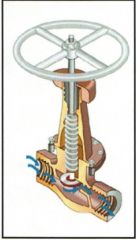
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Z-Body Globe Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Angle Body Globe Valve
|
|
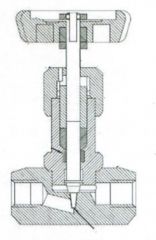
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Needle Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Plug Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Ball Valve
|
|
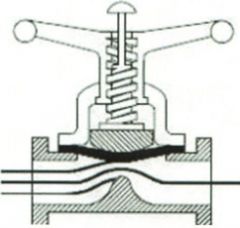
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Weir Type Diaphragm Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Split Disc/Wafer Check Valve
|
|
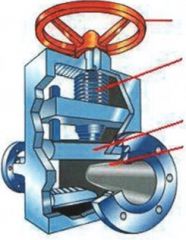
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Pinch Valve
|
|
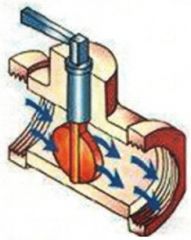
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Butterfly Valve
|
|
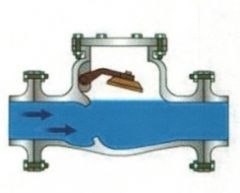
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Swing Type Check Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Float To Lift Type Check Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Spring Assisted Ball Check
|
|
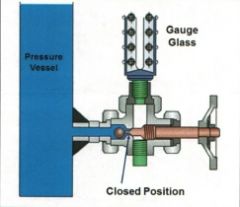
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Excess Flow Ball Check Valve / Sight Glass Safety Valve
|
|
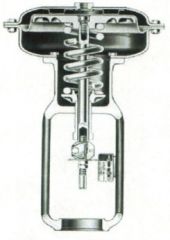
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Pneumatic Diaphragm Actuator
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Double Acting Piston Actuator
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Field Reversible Horizontal Pneumatic Piston Actuator
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Positioner
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Pneumatic Operated ¼ Turn Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Solenoid Actuator
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Motor Operated Valve
|
|
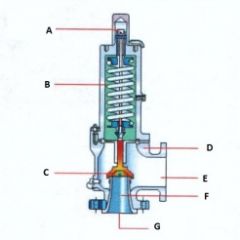
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Conventional Pressure Relief Valve
|
|
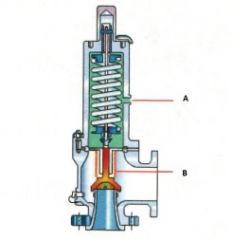
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Balanced Bellows Pressure Relief Valve
|
|
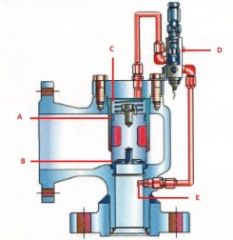
Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Pressure/Vacuum Vent Relief Valve
|
|

Identify the types of valves and valve actuators (including their components)
|
Rupture Disk
|
|
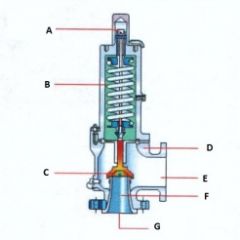
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
A. |
A. Adjusting Screw
|
|
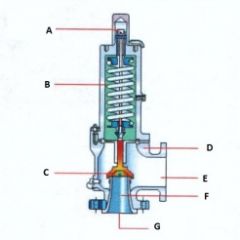
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
B. |
B. Spring
|
|
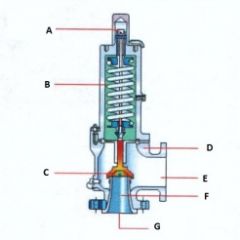
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
C. |
C. Disk
|
|
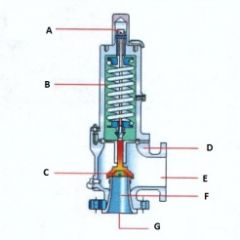
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
D. |
D. Body
|
|
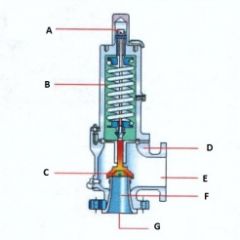
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
E. |
E. Outlet
|
|
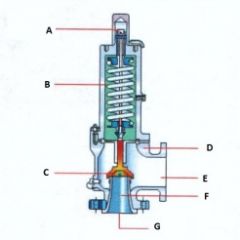
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
F. |
F. Seat
|
|
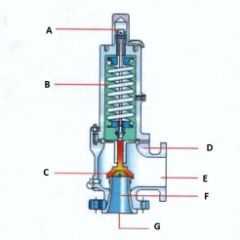
Name the components:(Conventional Pressure Relief Valve)
G. |
G. Inlet
|
|
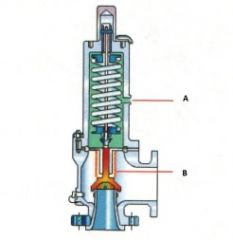
Name the components:(Balanced Bellows Pressure Relief Valve)
A. |
A. Bonnet Vent
|
|
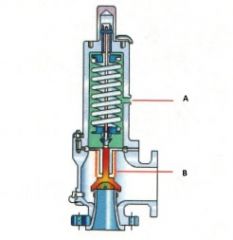
Name the components:(Balanced Bellows Pressure Relief Valve)
B. |
B. Bellow
|
|
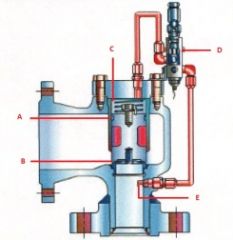
Name the components:(Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve)
A. |
A. Piston Seal
|
|
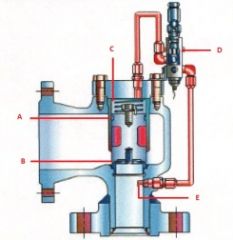
Name the components:(Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve)
B. |
B. Seat
|
|
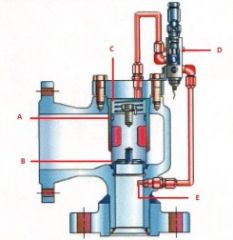
Name the components:(Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve)
C. |
C. Dome
|
|
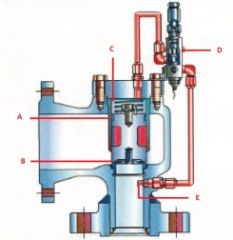
Name the components:(Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve)
D. |
D. Pilot Valve
|
|
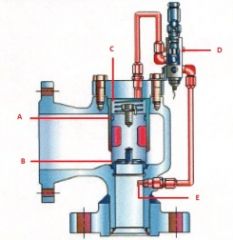
Name the components:(Pilot Operated Pressure Relief Valve)
E. |
E. Pressure Pick up
|

