![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the synthesis of estrogen by oocytes.
Begin with LH. |
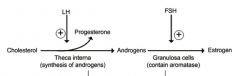
|
|
|
What is a normal lecithin to sphingomyelin ratio for a baby with mature lungs?
|
≥2.0
|
|
|
CGG repeats
|
Fragile X syndrome
|
|
|
Fragile X Syndrome:
Pathophys |
Familial MR Gene 1 on X chromosome has inc'd number of CGG repeats
Leads to hypermethylation and subsequent gene inactivation DOES NOT RESULT IN INC'D CHROMOSOMAL BREAKAGE/INSTABILITY |
|
|
Define polyploidy.
|
When more than 2 complete sets of homologous chromosomes exist within an organism or cell.
Ex: Hydatidiform moles have 69 chromosomes (a factor of 23) |
|
|
Define pleiotropy.
|
Occurrence of multiple phenotypic manifestations, often in different organ systems, as a result of a single genetic defect.
|
|
|
What is the Pygmalion effect?
|
Researcher's beliefs in efficacy of tx that can potentially affect outcome
|
|
|
What is Berkson's bias?
|
Selection bias created by selecting hospitalized patients as control group
|
|
|
Schizophrenia:
Presentation How does it differ from a Schizophreniform Disorder? |
Recurrent episodes of active psychosis and decline in functional capacity
Presentation includes hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thought, negative syx (blunted affect, social withdrawal, and anhedonia) When above syx are present for 1-6 months, diagnosis is schizophreniform disorder. |
|
|
Describe and explain the urinalysis findings of diabetic ketoacidosis.
|
Urine pH will decrease
HCO3- will be conserved in the body, and thus will be low in urine H2PO4- is used to transport H+ out of body, so will be inc'd in urine |
|
|
What are the 4 hypersensitivity reactions?
Describe and provide examples. |
I: Immediate allergy (IgE)--atopic dermatitis, anaphylaxis, asthma
II: Cytotoxic, Ab-dependent (IgM or IgG)--autoimmune hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, Erythroblastosis fetalis, Goodpasture's, Graves', Myasthenia gravis III: Immune complex (IgG)--Serum sickness, RA, SLE, Hypersensitivity IV: Delayed-type hypersensitivity, cell-mediated immune memory response, Ab-dependent (MEDIATED BY T CELLS)--CONTACT dermatitis, Mantoux Test (PPD), chronic transplant rejection, multiple sclerosis |
|
|
Transdermal candida extra injected into pediatric patient.
48 hours later, patient returns with firm nodule. What cell type responsible for this? |
T lymphocytes
|
|
|
Which hypersensitivity reactions rely on B-lymphocytes?
|
Type I--asthma, anaphylaxis (IgE mediated)
Type II--antibody mediated (ABO incompatibility hemolysis) Type III--immune complex (post-strep GN!!) |
|
|
Describe the fates of pyruvate in aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
List enzymes necessary. |
Pyruvate-->Acetyl-CoA in presence of Oxygen via PYRUVATE DH
Pyruvate-->lactate in lack of Oxygen vis LACTATE DH |
|
|
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency:
Dietary restrictions |
Patients should restrict themselves to a ketogenic diet (as opposed to glucogenic, i.e., aa's that contribute to formation of pyruvate and then lactate. Don't want pts in lactic acidosis!)
Such aa's are lysine and leucine. |
|
|
Glucogenic vs Ketogenic amino acids:
General |
Glucogenic--produce intermediates of citric acid cycle or pyruvate
Ketogenic--produce acetoacetate or precursors Ex: leucine, lysine are exclusively ketogenic and will not increase formation of lactic acid |
|
|
Valsalva maneuver:
Therapeutic utility |
Valsalva maneuver increases vagal tone and can be used to abolish paroxysmal SVT
|
|
|
DKA:
Treatment Protocol |
-Bolus of short-acting regular insulin
-Infusion of insulin adjusted to blood glucose levels -IV fluids and correct electrolyte imbalances |
|
|
Rapid-acting vs Regular insulin:
Peak time of effect Examples |
Rapid-acting: Peak effect within 30 minutes-1 hour; ex: Lispro
Regular: Peak effect around 3 hours, ex: regular insulin |
|
|
Intermediate insulin:
Peak time of effect Example |
Peak effect at 6-8 hours, lasts up to 16 hours
Ex: NPH, Lente |
|
|
This insulin lasts 18-24 hours and does not peak.
|
Glargine (Lantus)
|
|
|
Apoptosis:
Extrinsic vs Intrinsic Pathways |
Extrinsic: Death receptor, Fas, binds Fas-L-->produces protein called FADD-->activates caspases
Intrinsic: anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl2 and Bcl-x that reside in mitochondria replaced with Bak, Bax, Bim. Pro-apoptotic pathway allows for inc'd perm of mitochondria-->release of caspase-activating substances like cytochrome C. CYTOCHROME C! |
|
|
Vitamine E deficiency:
Effects Presentation Cause |
Degeneration of spinocerebellar tracts, dorsal column, peripheral nerves
Mimics Friedreich ataxia bc same areas of CNS affected Presentation: Ataxia, dysarthria, loss of position AND vibration sense |
|
|
Chronic fatigue
Mild weight gain Elevated creatine kinase |
Hypothyroidism
Elevated creatine kinase due to hypothyroid myopathy |
|
|
Hemiplegia
Aphasia Brain CT hypodensity |
Ischemic infarct
|
|
|
What cells are involved in repair of brain infarct?
|
Neutrophils followed by macrophages (MICROGLIA)
Macs phag debris, dead tissue CNS repair by astrocytes that migrate to area of necrosis within 2 weeks Will form cystic space surrounded by astrocytes (GLIOSIS) |
|
|
Formula for flow of incompressible fluid through a cylinder.
|
Total Flow = Flow Velocity x Cross Sectional Area = Constant
|
|
|
Lactase:
Reaction catalyzed |
Lactase:
Lactose ((galactosyl beta-1,4-glucose)-->Galactose + Glucose |
|
|
Neisseria meningitidis:
Route of infection |
Exposure to respiratory droplets or direct contact with respiratory secretions-->pilus-mediated adherence to, and penetration of mucosal epithelium-->circulation
Note: N. meningitidis produces an IgA protease that facilitates survival of organism in mucosa by destroying IgA ab's |
|
|
Cat scratch fever:
Cause Effects |
Bartonella
Can also present with bacillary angiomatosis, culture negative endocarditis |
|
|
How does HIV-1 become resistant to anti-retroviral drugs?
|
Pol gene mutations result in resistance fo HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors and HIV protease inhibitors
|
|
|
Cardiac AEs of TCAs
Treatment? |
TCAs have quinidine-like effect:
QRS and QT prolongation Due to inhibition of fast Na+ channels Tx: Sodium bicarb to correct QRS prolongation, reverse hypotn, tx ventricular dysrhythmias |
|
|
Treatment for benzodiazepine toxicity.
|
Flumazenil
|
|
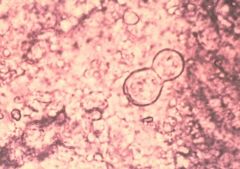
|
Blastomyces (broad based budding)
|
|
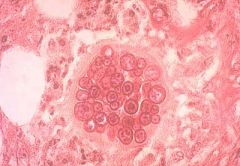
|
Coccidoides--large spherule filled w/endospores
|
|
|
Most common cause of sudden cardiac death in young, healthy individual.
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy resulting in ventricular tachycardia that deteriorates to ventricular fibrillation
|
|
|
Enoxaparin:
Drug Class MOA |
LMWH
Binds and activates anti-thrombin III, which binds to factor Xa and stops it from converting prothrombin to thrombin |
|
|
This structure supplies the ovary with nerves and vessels.
|
Suspensory ligament
|
|
|
Round ligament:
Locations |
Uterus (contains artery of Sampson; rarely source of major bleeding during surgery)
Liver |
|
|
This structure supplies contains the uterine artery.
|
Transverse cervical ligament
|
|
|
Fenoldopam:
MOA |
Dopamine-1 receptor agonist-->arteriolar dilation and natriuresis
Leading to dec'd systemic vasc resistance and bP reduction Also improves renal perfusion |
|
|
Which penicillins are resistant to peniciliinase?
Use? |
Nafcillin
Methicillin Oxacillin Use to tx Staph aureus (not not MRSA), ex: folliculitis, abscesses |
|

|
Dec'd compliance in LV (mitral in question stem)-->inc'd risk pulmonary edema
|
|
|
This molecule has 220 times more affinity for hemoglobin than does oxygen.
|
Carbon MONOxide
|
|
|
Treatment of CO poisoning.
|
100% or hyperbaric oxygen
|
|
|
Spontaneous hemarthroses
Easy bruising |
Hemophilia A
|
|
|
Hemophilia A:
Pathophys Presentation Treatment |
Factor VIII deficiency
(A--ATE--EIGHT) Presents with spontaneous hemarthroses, bleeding after dental procedures, easy bruising Tx: Desmopressin |
|
|
Desmopressin:
MOA in Hemophilia Other uses |
Stimulates release of Factor VIII and vWF from ENDOTHELIAL cells (temporarily increases plasma FVIII by 2-3 times)
Desmopressin is a synthetic analog of ADH, so used in tx of diabetes insipidus to inc reabsorption of water in collecting tubules |
|
|
Goodpasture Syndrome:
Pathophys Light vs Immunofluorescence findings |
Goodpasture: Anti-GBM Abs react with Collagen Type IV on GBM
Light findings: Glomerular crescent formation Immunofluorescence: Linear deposits of IgG and C3 along BM |
|
|
Functional Mitral Regurgitation:
What is it? Cause? |
Heart murmur in absence of valve lesion
Dilatation of LV in response to inc'd preload can result in fnal mitral regurgitation--eliminated by preload reduction and reduced by afterload reduction (diuresis!) |
|
|
Describe the breakdown of glucose to pyruvate.
RLS? |
Glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate **VIA PFK-1 (RLS)** F-1,6-Bisphosphate -->-->Pyruvate |
|
|
Describe the breakdown of galactose to pyruvate.
RLS? |
Galactose
Galactose 1P Glucose 1P Glucose 6P Fructose 6P **VIA PFK-1 (RLS)** F-1,6-bisphosphate -->-->Pyruvate |
|
|
Which monosaccharide does not require PFK1 for metabolism to pyruvate?
How does this affect rate of glycolysis? |
Fructose
Rapidly metabolized bc bypasses PFK-1--the RLS of glycolysis |
|
|
Filtration Fraction:
Equation, Subequations Normal Value |
FF = GFR/RPF
Normal = 0.2 or 20% GFR can be calculated by: creatinine OR inuline clearance, or Starling equation Cx = Ux * V/plasma [ ] Starling: GFR = Kf ((Pg - Pb) - (πg - πb)) Where P = hstatic P Where π = oncotic P Where G = Glomerular Capillaries Where B = Bowman's space RPF: Use clearance of PAH |
|

|
FF = [(200 x 1.0) /2] / [(100 x 1.0) / 0.2] = 100/500 = 0.2 = 20%
|
|
|
Leuprolide:
MOA Effects Use |
GnRH hormone administered in constant levels; used to dec both T and DHT levels
When GnRH administered constantly and not in pulsatile fashion: -Initial increase in release of FSH/LH-->initial increase in T and DHT But then results in suppression of pituitary release of gonadotropins, causing dec'd DHT and T |
|
|
This drug causes a discordant decrease in DHT compared to T.
|
Finasteride bc inhibits T-alpha reductase
|
|
|
Rickets:
Histologic hallmark |
Unmineralized osteoid matrix, widened osteoid seams
note: there is normal architecture unlike osteoporosis |
|
|
Osteoporosis:
Histologic hallmark |
Trabecular thinning with few interconnections (abnl architecture)
|
|
|
What determines whether a coronary artery plaque qill cause ischemic myocardial injury?
|
Rate at which occludes the involved artery
A slowly developing occlusion will allow for formation of collaterals that could prevent myocardial necrosis A thin fibrous |

