![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gram-Negative Cocci
|
Neisseria spp.
Gram-Negative Rods (everything else) |
|
|
Bordetella pertussis Disease Features
|
Whooping cough, dry hacking cough
Incubation - asymptomatic Catarrhal - cold symptoms (best culture) Paroxysmal - clinical whoops (less culture) Convalescent - getting better, secondary infection (damaged cilia) |
|
|
Bordetella pertussis Identification
|
1. Oxidase positive coccobacillus with capsule.
2. Grows on Regan-Lowe. 3. Clinical "whoop" |
|
|
Bordetella pertussis Pathogenic Factors
|
1. A-B toxin; Increases cAMP
2. Hemagglutinin (attachment to ciliated endothelial cells -> further complications) 3. Tracheal cytotoxin |
|
|
Escherichia coli Disease Features
|
1. ETEC traveler's diarrhea (watery)
2. EPEC pediatric diarrhea 3. EIEC (invasive) watery/bloody diarrhea (bacterial dysentery) 4. EHEC (non-invasive) watery/blood diarrhea O157:H7, hemolytic uremic syndrome in children |
|
|
Escherichia coli Identification
|
1. Oxidase (-)
2. Lactose (+) -> Appearing purple on MacConkey Agar |
|
|
Escherichia coli Pathogenic Factors
|
1. ETEC - two enterotoxins increasing cAMP,
2. Endotoxin (LPS) 3. Adhesions |
|
|
Haemophilus ducreyi Disease Features
|
Painful genital ulcer
|
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae Disease Features
|
1. Infantile meningitis
2. Pediatric epiglottitis 3. Otitis media (children and adults) 4. Bronchitis/Pneumonia (elderly, those with chronic pulmonary disease |
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae Identification
|
1. Coccobacillus
2. Catalase (+) 3. Factor X (heme) and factor V (NAD) needed for growth |
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Endotoxin (LPS)
2. Capsule (Hib vaccine) |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae Disease Features
|
Pneumonia (especially in alcoholics and those with poor lung function) CURRENT JELLY sputum
|
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae Identification
|
1. Lactose fermenter
2. Mucoid-appearing colonies in culture |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae Pathogenic Factors
|
Large antiphagocytic capsule
|
|
|
Legionella pneumophila Disease Features
|
1. Legionnaire's disease: atypical pneumonia (smoking history) caused by inhalation of water
2. Pontiac fever: self-limited, febrile illness |
|
|
Legionella pneumophila Identification
|
1. Coccobacillus 2. Facultative intracellular 3. BYCE agar (need cysteine and iron)
|
|
|
Legionella pneumophila Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Growth in macrophages 2. Degradative enzymes kill parasitized cells
|
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Disease Features
|
Male (more likely to present) - urethritis, pus
Female - PID, endocervitis Infants - opthalmia - leads to blindness if untreated |
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Identification
|
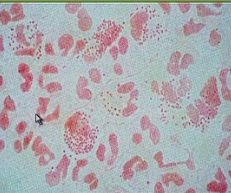
1. Diplococcus
2. Ferments glucose (NOT maltose) 3. Growth on Thayer-Martin or chocolate agar |
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Pili
2. Endotoxin (LPS) |
|
|
Neisseire meningitidis Disease Features
|
1. Meningitis - fever, stiff neck, vomitting
2. Meningococcemia - petechial/purpura rash, septicemia, and WATERHOUSE-FRIDERICHSEN SYNDROME - hemorrhagic destruction of the adrenal glands (rapid) |
|
|
Neisseire meningitidis Identification
|
1. Diplococcus
2. Capsule 3. Ferments glucose AND maltose 4. Growth on Thayer-Martin or chocolate agar |
|
|
Neisseire meningitidis Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Capsule 2. Endotoxin (LPS) 3. Individuals deficit in C5-C8
|
|
|
Proteus mirabilis Disease Features
|
UTI
|
|
|
Proteus mirabilis Identification
|
1. Swarming growth on agar
2. Motile 3. H2S producer |
|
|
Pseudomona aeruginosa Disease Features
|
1. Pulmonary infection (ventilator)
2. Hot tub folliculitis 3. Burn wounds - very susceptible 3. UTI 4. Ear (swimmer's ear) eye (corneal ulcers from contact lens) 5. Endocarditis |
|
|
Pseudomona aeruginosa Identification
|
1. Motile
2. Oxidase (+) Lactose (-) 3. Aerobic 4. Fruity odor and Blue-green pigment |
|
|
Pseudomona aeruginosa Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Exotoxin A - inhibit elongation factor EF2
2. Endotoxin (LPS) 3. Capsule 4. Tissue hydrolases |
|
|
Salmonella spp. Identification
|
1. Motile
2. Oxidase (-) 3. Lactose (-) 4. H2S |
|
|
Salmonella enteritidis Disease Features
|
Gastroenteritis with vomiting, watery/bloody diarrhea
Sepsis in sickle cell |
|
|
Salmonella enteritidis Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Capsule 2. Exotoxin 3. Intracellular growth
|
|
|
Salmonella typhi Disease Features
|
Typhoid fever: 1. Increasing fever 2. Constipation 3. Septicemia 4. Gallbladder/Liver involvement
|
|
|
Salmonella typhi Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Capsule 2. Invasion of M cells of Peyer patches
|
|
|
Shigella spp. Disease Features
|
Shigellosis (bacterial dysentery): Watery/bloody stools, pus, fever and abdominal pain
Hemolytic uremic syndrome in children |
|
|
Shigella spp. Identification
|
1. Non-motile
2. No H2S 3. Lactose (-) colorless on MacConkey |
|
|
Shigella spp. Pathogenic Factors
|
1. Invades immune cells in Peyer's patches
2. A-B exotoxin (Shiga toxin) that inhibits protein synthesis |

