![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Uric acid crystals appearance |
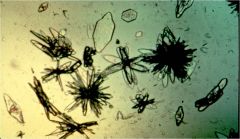
yellow-brown; pleomorphic; birefringent |
|
|
Crystals soluble in alkaline and heat |
uric acid, and urates (amorphous, acid, sodium), tyrosine |
|
|
Macroscopic appearance of acid urates |
Macroscopically resemble brick dust |
|
|
Acid urates description |
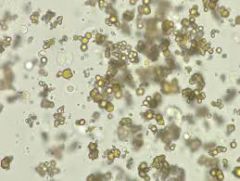
Small brown spheres; may cluster in pairs and triplets |
|
|
Sodium urates are usually found in? |
Synovial fluid |
|
|
Sodium urates appearance |
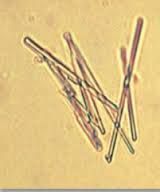
Colorless birefringent needles |
|
|
Commonly seen after refrigeration |
Amorphous urates, and amorphous phosphates |
|
|
CCalcium oxalate dihydrate appearance |
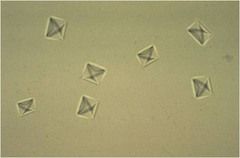
octahedral envelope |
|
|
Calcium oxalate is soluble in? |
Diluted Hydrochloric acid |
|
|
Monohydrate calcium oxalate appearance |
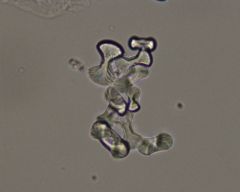
oval or dumbbell shaped |
|
|
Causes of increased uric acid crystals |
in gout, leukemia, and Lesch-Nyhan |
|
|
Crystal associated with renal calculi |
Calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate |
|
|
Calcium sulfate appearance |
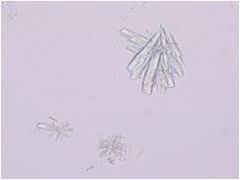
long, thin colorless needles or prisms identical to calcium phosphate |
|
|
Appearance of amorphous urates microscopically |
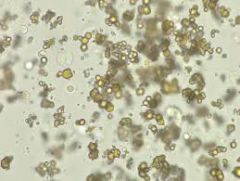
appear as granular |
|
|
Hippuric acid appearance
|
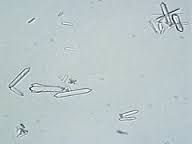
yellow-brown or colorless, needles, rhombic plates, and four-sided prisms |
|
|
Crystals soluble in diluted acetic acid |
Calcium sulfate, amorphous phosphates, calcium phosphate, and triple phosphate |
|
|
Hippuric acid is soluble to? |
Hot water and alkali |
|
|
Hippuric acid crystals are associated with? |
Foods containing benzoic acid |
|
|
Radiographic dye appearance |

flat, colorless, notched, rhombic plates |
|
|
Radiographic dyes are soluble in? |
10% Sodium hypochlorite |
|
|
Sulfonamide appearance |
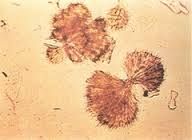
colorless to yellow-brown needles, sheaves of wheat, and rosettes |
|
|
Ampicillin appearance |
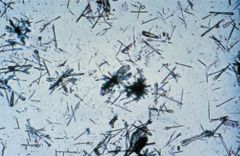
colorless needles that tend to form bundles following refrigeration |
|
|
Sulfonamide and ampicillin indication |
inadequate hydration among patients being treated for UTI |
|
|
These crystals may cause tubular damage if formed in the nephron |
sulfonamide and ampicillin |
|
|
Normal and iatrogenic crystals in acidic urine |
Uric acid, Urates, calcium oxalate, calcium sulfate, hippuric acid, radiographic dye, sulfonamide, ampicillin |
|
|
Normal Crystals in Alkaline Urine |
Amorphous phosphate, calcium phosphate, triple phosphate, ammonium biurate, calcium carbonate |
|
|
Other name for Triple Phosphate |
Ammonium Magnesium Phosphate |
|
|
Amorphous Phosphate macroscopic appearance |
milky white |
|
|
Amorphous phosphate microscopic appearance |
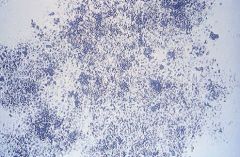
granular in appearance (alkaline) |
|
|
Calcium phosphate appearance |

colorless, flat rectangular plates or thin prisms in rosette formations |
|
|
Triple phosphate appearance |
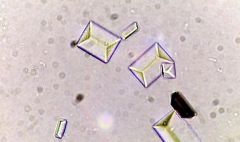
Prism resembling coffin-lid |
|
|
Ammonium biurate appearance |
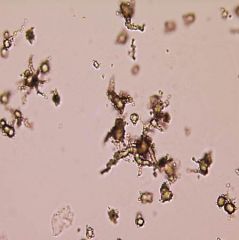
yellow-brown spicule-covered spheres described as thorny apple |
|
|
Calcium carbonate appearance |
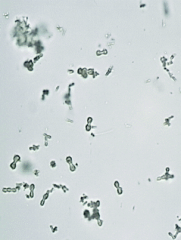
Small, colorless, dumbbell or spherical crystals that may occur in clumps |
|
|
Abnormal crystals
|
Cystine, cholesterol, leucine, tyrosine, bilirubin |
|
|
Ammonium biurate is soluble in? |
Acetic acid and heat |
|
|
Sulfonamides are soluble in? |
Acetone |
|
|
Calcium carbonate solubility characteristics |
Soluble in acetic acid with evolution of gas |
|
|
Indicates presence of urea splitting bacteria |
Triple phosphate, and ammonium biurate |
|
|
Cystine appearance |
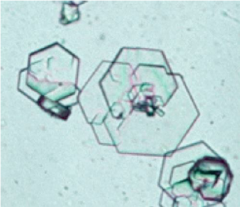
colorless, hexagonal which may be confused with uric acid |
|
|
Cystine is soluble in? |
dilute hydrochloric acid and ammonia |
|
|
Rare cause of calculi formation |
cystine |
|
|
Confirmatory test for cystine crystals |
Cyanide nitropruside test
|
|
|
Cyanide nitropruside test result if positive for cystine |
red-purple |
|
|
Appearance of cholesterol |

Rectangular plates with a notch in one or more corners |
|
|
Cholesterol is soluble in? |
Chloroform |
|
|
Cholesterol diagnostic significance |
Present in lipiduria e.g. in nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
Appearance of leucine crystal |
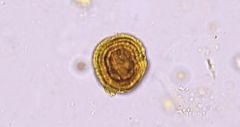
yellow-brown spheres that demonstrate concentric circles and radial striations |
|
|
Bilirubin appearance |
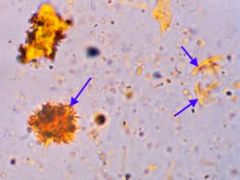
Clumped needles or granules with characteristic yellow color |
|
|
Leucine is soluble in? |
Hot alcohol and alkali |
|
|
It has an oily-looking sphere appearance |
leucine |
|
|
Bilirubin is soluble in? |
HAc, HCl, NaOH, ether, Chloroform |
|
|
Birefringent crystals |
uric acid, radiographic dye, triple phosphate, cholesterol |
|
|
Appearance of tyrosine crystals |
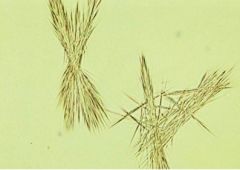
fine colorless to yellow needles that frequently form clumps or rosettes |
|
|
Most common artifact |
Starch granules |
|
|
Starch granules appearance |
produces maltese cross pattern |
|
|
Source of starch granules |
Gloves |
|
|
Air bubbles, and oil droplets characteristics |
can be mistaken as RBC; oil has high refractive index |
|
|
Differentiates RBC from air bubbles |
Lysis with acetic acid |
|
|
Pollen grains characteristics |
seasonal contaminant; large spheres that cause microscopist to lose focus |
|
|
Hair, fibers sources |
diapers and applicator sticks |
|
|
Hairs and fibers characterstics |
mistaken for casts but they are longer, and refractile |
|
|
Fecal elements contaminated urine characteristics |
may be from recto-vesicle fistula, and urine may contain vegetable cells and muscle fibers |
|
|
Cigarette butt looking crystals |
Calcium sulfate |
|
|
Can still be present in neutral or slightly alkaline urine |
Calcium oxalates |
|
|
Iatrogenic crystals |
radiographic dye, sulfonamides, and ampicillin |
|
|
Substance added to convert ammonium biurate to uric acid |
glacial acetic acid |
|
|
Appearance of AMP in old specimens |
fern-like |
|
|
Semi automated chemistry analyzers tests detected |
urine chemistry (9) and specific gravity (1) |
|
|
Principle used in urine chemistry analysis |
Reflectance photometry |
|
|
Fully automated chemistry analyzers tests detected |
color, clarity, urine chemistry, specific gravity |
|
|
Automated clarity principle used |
turbidimetry or nephelometry |
|
|
SG measurement in semiautomated chemistry principle |
Reflectance photometry |
|
|
SG measurement in automated chemistry principle |
Refractometry |
|
|
Urine sediment analysis test principle |
flow cytometry |
|
|
Refractive index in old yellow IRIS models used? |
harmonic oscillation densitometry |
|
|
Workstations or fully automated urinalysis systems or workstations principle for urine sediment analysis |
Flow cytometry or intelligent microscopy system |
|
|
Tests measured in workstations |
color, clarity, urine chemistry, SG, urine sediment analysis |
|
|
Automated microscopy analyzers measure? |
urine sediment analysis |
|
|
Reflectance photometry is based on principle that? |
light reflection from test pads decreases in proportion to the intensity of color |
|
|
Normal number of nephrons per kidney |
1-1.5 million |
|
|
Cortical region of the nephron composes how much of it? |
85% |
|
|
Juxtaglomerular cell of the nephron composes how much of it? |
15% |
|
|
Normal renal blood flow |
1200mL/min |
|
|
normal glomerular filtration rate |
120mL/min |
|
|
SG of the glomerular filtrate |
1.010 |
|
|
Factors affecting glomerular filtration |
cellular layers, hydrostatic pressure, and RAAS |
|
|
Substance/s absorbed actively in PCT |
Glucose, Amino acids, salts |
|
|
Substance/s absorbed passively in PCT |
water, and urea (40-50%) |
|
|
Substance/s passively absorbed in DLoH |
Water |
|
|
Substance/s actively absorbed in ALoH |
Chloride |
|
|
Substance/s passively absorbed in ALoH |
Urea, Sodium |
|
|
Substance/s that are actively reabsorbed in the DCT |
Sodium |
|
|
substance/s that are passively reabsorbed in the collecting ducts |
Water |
|
|
ADH acts upon what part of the nephron? |
DCT, and Collecting ducts |
|
|
Liver disease casts |
leucine, tyrosine, bilirubin |
|
|
Cigarette butt looking crystals |
Calcium Sulfate |
|
|
Appears fern-like in old specimens |
Triple phosphate |

