![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
species
|
a species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
|
|
|
biodiversity
|
is the range of different types of species present in an ecosystem. it's important for medicine, food sources, habitats and building materials e.g llamas, cacti, seals
|
|
|
biome
|
a biome is a geographical region of the planet that contains distinctive communities of plants and animals, and is made up of connected ecosystems i.e forests, deserts, grasslands and freshwater. These have different animals and plants living there and different climates.
|
|
|
flora
|
the characteristic types of plants in the biome
|
|
|
fauna
|
the characteristic types of animals found in the biome
|
|
|
what distinguishes a biome?
|
their flora, fauna and climate
|
|
|
what determines the distribution of biomes?
|
the non living factors (abiotic) such as temperature and rainfall
|
|
|
ecosystem
|
is made up of many habitats and all the organisms and the abiotic factors in one particular area
|
|
|
habitat
|
is the place where an organism lives
|
|
|
community
|
is two or more different types of organisms living together.
|
|
|
population
|
is all the organisms of one type living together
|
|
|
biotic factor
|
a living factor which affects population numbers e.g food, predation, grazing, competition
|
|
|
biotic factors' affect on biodiversity
|
▪if food increases, biodiversity may increase
▪if predators increase, biodiversity may decrease |
|
|
competition
|
occurs when organisms require the same recourses e.g
▪plants - light, water, space, soil nutrients ▪animals - food, water, space, mates |
|
|
intra specific competition
|
competition between one species
|
|
|
interspecific competition
|
competition between two different species
|
|
|
competition intenseness
|
intra specific competition is more intense than interspecific competition because the organisms require the EXACT same recources. Intense competition can result in organisms being forced to leave the ecosystem or the death of the organism
|
|
|
predation
|
is when one organism eats another
high levels - decreases biodiversity as more organisms are eaten moderate - maintains biodiversity as it keeps the dominant organisms in check low levels - decreases biodiversity as more dominant organisms survive |
|
|
parasitism
|
is when one organism (a parasite) feeds from another organism (the host) and it causes harm, but rarely kills it e.g headlice, fleas.
They rarelu kill their host as this would cut off their food supply. |
|
|
grazing
|
is when animals feed on parts of plants i.e cows, sheep, ladybirds.
high levels - decreases biodiversity as more plants species are eaten moderate - maintains biodiversity as it allows the less dominant plants to survive low levels - decreases biodiversity as it allows better competitors to succeed |
|
|
abiotic factors
|
a non living factor which affects populations. e.g light intensity, carbon dioxide levels and oxygen levels
|
|
|
affect of light intensity
|
plants need light to photosynthesise.
high light intensity = more photosynthesis = more plants |
|
|
affect of temperature
|
the closer the temperature is to the optimum the more enzyme controlled reactions there will be which results in more plants
|
|
|
affect of carbon dioxide
|
The more carbon dioxide, the more photosynthesis and therefore more plants
|
|
|
acid rain
|
is formed when sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are released when fossil fuels are burned
|
|
|
acid rains affect on biodiversity
|
▪decreases plant biodiversity as the acid destroys the leaves so it can't photosynthesise
▪decreases fish biodiversity as it lowers the pH levels of freshwater which leads to the death of the fish |
|
|
global warming
|
is when fossil fuels are burned and carbon dioxide, nitrogenoxide and water vapour are released and form a blanket around the earth's atmosphere. These gases trap heat and cause global warming
▪An increase in temperature decreases fish biodiversity |
|
|
exploitation
|
is when something is used in order to gain benefit
E.g overfishing, overhunting, overgrazing, habitat destruction and pollution |
|
|
ecosystem affected by pollution
|
air, land, freshwater and seawater
|
|
|
indicator species
|
species whose presence or absense reflects the state of the environment e.g lichens are sensitive to sulphur dioxide
|
|
|
samples (ecosystems)
|
It's impossible to count all the animals/plants in an ecosystem as it'd take too long and the habitat may get damaged so sampling must be used
|
|
|
sampling reliability
|
several samples must be taken to ensure a reliable representation of the area
|
|
|
quadrats
|
▪plants and relatively static organisms are counted using quadrats e.g daisies, lichens
▪Quadrats should be randomly thrown several times ▪to prevent errors: use a key to identify organisms, throw quadrat randomly and take more samples |
|
|
pitfall trap
|
▪woodlice and beetles are counted using a pitfall trap
▪a pitfall trap isba sampling technique used to measure the population of organisms. ▪to decrease errors: have a camouflage top to prevent the organisms escaping, make hole deep enough so the pot in level with the surface and empty frequently so organisms don't eat each other |
|
|
pooter
|
is a sampling technique used to measure the population number of insects found in tree barks e.g spiders
▪to decreaae errors: empty frequently so organisms don't eat each other ▪make needles holes so organisms don't die due to lack of oxygen |
|
|
kick
|
kick nets is a sampling technique used to measure the population number of organisms found in rivers e.g mayfly larvae
▪To decrease errors : kick the gravel on the floor of the river, point the kick net upstream and have sampling bottles ready. |
|
|
biological keys
|
organisms can be identified using biological keys. e.g branching keys or paired statement keys
|
|
|
light intensity (abiotic factor)
|
light meters - an error when using a light meter may be that the scientists is shading the light sensor
|
|
|
soil moisture (abiotic factor )
|
soil thermometer - an error when using the soil thermometer could be the scientists not putting the thermometer deep enough into the soil.
|
|
|
pH ( abiotic factor )
|
pH meter - may have left soil / moisture on the probe and probe wasn't wiped betweem samples
|
|
|
niche
|
an organism's niche is the role it plays within the community
|
|
|
niche of Scottish wild cat
|
-rare Scottish mammal
-found in woodland and mountains -it's a predator and active at night -humans have decreased their numbers |
|
|
producers
|
organisms that make their own food by photosynthesis
|
|
|
primary consumer
|
organisms that eat plants only (herbivores)
|
|
|
secondary consumers
|
eat primary consumers (carnivores)
|
|
|
omnivore
|
eats both plants and animals
|
|
|
food chain
|
▪food chains are diagrams that show the direction of energy flow whem one organism eats another
▪ grass > vole > barn owl ▪the arrows represent the flow of energy ▪food chains are unstable because if one organism dies off the food chain collapses |
|
|
food webs
|
▪are stable because if one organism dies off there are still other connected food webs available
▪mice would decrease if woodlice died off due to disease because there'd be less food sources or it would stay the same because they'd still have the grassy woodlands |
|
|
energy loss in food webs
|
▪heat, movement and undigested faeces
▪10% energy is passed on to the next stage |
|
|
pyramid of numbers
|
the number if organisms at each stage in a food chain, as you go up the pyramid the number of organisms decrease and organism size increases
The pyramid of numbers is unusually shaped because one oak tree can be very large and support many many caterpillars |
|
|
pyramid of biomass
|
the mass of organisms at each stage in a food chain
|
|
|
pyramid of energy
|
the energy levels at each stage in a food chain
|
|
|
nitrogen cycle
|
- carbon ,hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen are found in all organisms -Nitrogen is needed to make protein by plants and animals
- plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate - animals eat plants/animals containing protein to get their supply of nitrogen |
|
|
nitrogen cycle diagram
|
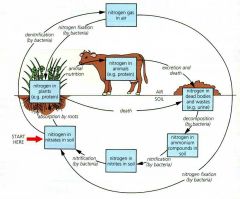
|
|
|
decomposition
|
bacteria and fungi (decompose)
proteins + nitrogenous wastes = ammonium compounds |
|
|
nitrification
|
nitrifying bacteria
ammonium compounds = nitrites = nitrates |
|
|
nitrogen fixation - free living soil bacteria
|
atmospheric nitrogen = nitrate
|
|
|
nitrogen fixation - bacteria in roots nodules
|
atmospheric nitrogen = nitrate
|
|
|
denitrification
|
denitrifying bacteria
nitrate = nitrogen gas (in atmosphere) |
|
|
summarised nitrogen cycle
|
ammonium = nitrites = nitrates
|
|
|
demand for food
|
▪is increasing as human population increases
▪starvation occurs due to distribution problems, political disputes and adverse weather conditions ▪food production is increased using intensive farming ,fertilisers, pesticides. biological control and GM crops |
|
|
monoculture
|
is when farmers grow a single crop on a large scale , to create large fields farmers remove hedgerows between small fields
|
|
|
problems with intensive farming
|
▪when hedgerows are removed habitats are destroyed i.e voles
▪pests thrive because of the rich food supply of one crop ▪they constantly remove the same nutrients from the soil which means they need to used fertilisers |
|
|
pesticides
|
are chemicals sprayed onto crops to kill pests
|
|
|
insecticides
|
insect pests
|
|
|
fungicides
|
fungal pests
|
|
|
herbicides
|
weeds
|
|
|
problems with pesticides
|
▪some pesticides aren't specific, therefore they kill other organisms aswell
▪sometimes when organisms eat pests (insects) the pesticide is persistent and builds up inside their body causing death |
|
|
fertilisers
|
▪planting and harvesting crops continually removes nutrient and when crops are harvested these nutrients aren't replaced by the natural process of death and decay.
▪fertilisers are used to add nitrites to the soil, so in turn farmers get an increase in crop production |
|
|
elements in fertilisers
|
▪nitrogen to make protein, ATP , nucleic acids and DNA
▪Phosphorus for root growth ▪potassium for fruit and flowers ▪magnesium to make chlorophyll |
|
|
problems with fertilisers
|
1. fertilisers can leach from the soil in the fields into fresh water systems due to heavy rainfall
2. the fertilisers in the water systems increase growth of algae in the water 3. algae grow and reproduce and form an algal bloom on top of the water 4. algal blooms block out the light to the underwater plants so they die due to lack of photosynthesis 5. bacteria feed on dead plants, reproduce and use up oxygempn in the water 6. the decrease in oxygen concentration results in the death of fish |
|
|
biological control
|
biological control involves using organisms as natural predators or parasites to control pest numbers
▪the Australia cotton cushion was accidently introduced to California so the Australian ladybird beetles had to be introduced |
|
|
GM crops
|
are crops that have had their genes altered by adding in genes from other organisms
▪Golden rice has been developed to contain beta - carotene, which helps childreb produce vitamin A |
|
|
Adaption
|
adaption is an inherited characteristic that helps an organism survive. some adaptions are formed within a species due to random advantageous mutations. It's spontaneous and allows species to adapt to a changing environment
|
|
|
physiological adaptions
|
Are structural /body adaptions. In the kangaroo rat , for example, these are: no sweat glands , produce very dry faeces and high levels of ADH to reabsorb water from kidneys
|
|
|
behavioural adaptions
|
Are what the organisms do. The kangaroo rat lives in the deserts, is active at night and inactive in the day
|
|
|
avoidance
|
avoidance behaviour occurs when an organism retreats to avoid danger
|
|
|
habituation
|
is when an organism stops retreating to a harmless stimulus in order to save energy. It is a short term change in behaviour
|
|
|
natural selection
|
1. organisms always produce more offspring than the environment can support
2. variation exists within the species due to different mutations 3. organisms struggle for survival and compete for space, food and mates 4. Those organisms best suited for the environment survive as they have selective advantage. those less suited die off and this is called survival of the fittest 5. the surviving organisms mate, reproduce and pass on favourable genes. |
|
|
peppered moths
|
There are two different types of moths: light and dark. The dark for, occured naturally by mutation. The light moths had a selective advantage because it could camouflage against white lichens growing on trees in non polluted areas, therefore the birds could not see them. However, aftet the industrial revolution the lichens died off so light moths could no longer camouflage which gave the dark moths the selective advantage as they could now camouflage with the dark trees. The dark moths mated and reproduced.
|
|
|
antibiotics
|
over prescribing antibiotics has increased the number of resistant bacteria and has lead to some infections being very hard to treat like MRSA in hospitals
|
|
|
speciation
|
is the formation of a new species.
Speciation occurs when a barrier splits a population and it becomes isolated. The barrier prevents interbreeding and gene exchange between the sub - populations. Mutations occur randomly in the subpopulations giving a rise to variation (some mutations are advantageous). Different selection pressures occur in each subpopulation. Natural selection occurs in each subpopulation in a different way. Each subpopulation evolves so much that they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring with the othet population. They are now different species |

