![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autonomic physiological effects on the heart |
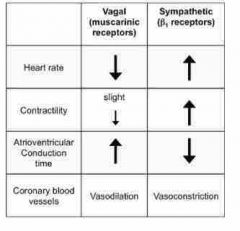
|
|
|
Receptors allowing SNS function at the heart ? |
Beta 1 |
|
|
Components of the autonomic NS? |
PSNS SNS Enteric NS |
|
|
Coronary filling occurs during? |
Diastole |
|
|
SNS effect on coronary blood flow? |
Decrease but usually increases due to the main control being via metabolites which increase with increasing cardiac contractility / work |
|
|
Effect of SNS on SA node pacemaker function? |
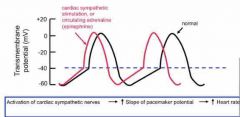
|
|
|
Location of preganglionic cell bodies? |
IML intermediolateral column of the spinal cord and motor nuclei of the brainstem |
|
|
Type of nerve fibers? 1. Motor 2. Preganglionic - autonomic 3. Postganlionic - autonomic |
1. Motor /Somatic - alpha - large + fast 2. Preganglionic - B fibers, small, myelinated, slow 3. Postganglionic - Unmyelinated C fibers |
|
|
Path of a SNS preganglionic fiber from the IML? |
Exits with one of the thoracolumbar via the VENTRAL root --> WHITE rami communicans --> paravertebral ganglion and either synapse here or move up or down the chain to synapse (or move to the prevertebral ganglia --> prior to moving towards the target organ. Toward the limbs etc --> grey communicans and travels with the spinal nerve or goes directly there if to an organ |
|
|
With the SNS - the coeliac ganglion feeds forward via postganglionic nerve to which organs? |
Stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen |
|
|
With the SNS - the superior mesenteric ganglion feeds forward via postganglionic nerve to which organs? |
Small intestine and colon |
|
|
With the SNS - the inferior mesenteric ganglion feeds forward via postganglionic nerve to which organs? |
colon, kidney, bladder, sex organs |
|
|
What are the names of the SNS ganglia? |
Cervical Coeliac Superior mesenteric Inferior mesenteric Sacral |
|
|
Which CN nuclei are involved in parasympathetic outflow? |
CN - III, VII, IX, X III - Edinger Westphal --> ciliary ganglion VII - Superior salivatory nucleus --> Sphenopalatine ganglia (lacrimal gland + nasal mucosa) + submandibular ganglia (submanddibular gland) IX - Glossopharyngeal - Inferior salivatory nucleus --> otic ganglion (parotid) X - VAGUS - Nucleus Ambiguus (SA + AV nodes) + Dorsal motor vagal nucleus (viscera) |
|
|
What is the effect of activating a nicotininc ACh receptor ? |
Depolarisation Opening of Na+ + K+ channels Initially EPSP - fast excitatory post synaptic potential (depolarisation) then slow-EPSP - modulates transmission through sympathetic ganglia Note Late, Slow EPSP due to peptide (minutes) |
|
|
Atropine blocks which receptors? |
mACh |
|
|
What are the main types of Muscarinic receptors? Where are they found? |
M1-5 M2 --> Heart M3 --> Smooth muscle and glands |
|
|
How do the main 2 types of muscarinic receptors signal intracellularlly? |
M2 (HEART) - Opens K channels and inhibits Adenylyl cyclase - ie reduced cAMP M3 (SMOOTH MUSCLE + GLANDS) - Formation of IP3 + DAG and increase intracellular Ca2+ |
|
|
Control of lacrimal glands is via? |
PSNS --> CNVII |
|
|
Adrenergic receptor in bronchical smooth muscle? Heart? |
Bronchial - Beta 2 Heart - mainly Beta 1 |
|
|
What causes organophosphate poisoning? |
Pesticides + Sarin gas MOA: Inhibit acetylcholinesterase --> increase ACh effects Signs + Symptoms: miosis, salivation, sweating, bronchial constriction, vomiting, diarrhoea, cognitive disturbance, seizures, coma Rx: ATROPINE |
|
|
Signs of anticholinergic poisoning |
"Blind as a bat (cyclopegia, myadriasis), mad as a hatter (delirum), red as a beet (flushed), hot as hare (hyperthermia), dry as a bone (no sweating), bowel and bladder lose their tone and the heart runs alone" Ie with mushroom poisoning - mycetism --> Inocybe |
|
|
Describe the symptoms of Horner's Syndrome |
Anhidrosis Ptosis Miosis Enophthalmos (sunken eye) Due to disruption of sympathetic outflow to the face |
|
|
Give examples of nonadrenergic noncholinergic transmitters. |
NA - related ATP Neuropeptide Y - NPY ACh - related VIP - Vasoactive intestinal peptide Calcitonin gene-related peptide Substance P Also Nitric oxide
|
|
|
In which organ do the PSNS and SNS work together? |
Salivary glands PSNS - watery saliva SNS - thick saliva Male ejaculation |
|
|
Which organs have sole SNS or PSNS innvervation? |
SNS - blood vessels, pilomotor muscles in the skin, adrenal gland, sweat glands PSNS - lacrimal, ciliary (accommodation for near vision), sublingual |
|
|
Descending inputs to the AUTONOMIC NS? |
Hypothalamic parventricular Nucleus Pontine A5 cell group Rostral ventrolateral medulla Medullar raphe nucleus All these send signals to the IML |
|
|
Name the layers of the GIT |
Mucosa (epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa) Submucosa - Miessner's plexus Muscularis propria ( circular muscle, auerbach's plexus, longitudinal muscle) Serosa/adventitia |
|
|
Multisystem atrophy is a neurodegenerative disorder associated with loss of which type of neurons? |
Preganglionic autonomic neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord |
|
|
In addition to classic neurotransmitters, some autonomic fibres also release neuropeptides. In postganglionic noradrenergic neurons, what (in addition to noradrenaline) is in the large granulated vesicles? |
Neuropeptide Y ATP in small vesicles |
|
|
Receptors on the liver ? |
α1β2 adrenergic only |
|
|
How does Resperine work? |
Blocks Neurotransmitter storage in vesicles |
|
|
How does cocaine work? |
Blocks reuptake of NA Same at tricyclic antidepressants |
|
|
What drug prevents inactivation of neurotransmitter - ACh? |
Edrophonium Neostigmine Physostigmine Inhibits acetylcholinesterase increased PSNS effects Reversal of non depolarising muscle relaxants |
|
|
Beta2 agonists? |
albuterol salbutamol |
|
|
Beta 1 agonist? |
Dobutamine |
|
|
Alpha 2 agonist? |
Clonidine |
|
|
Alpha 1 antagonist? |
prazosin |
|
|
Muscarinic antagonist? |
atropine ipratropium tropicamide |
|
|
Receptors on the Liver? |
Adrenergic Alpha 1 Beta 2 SNS only |
|
|
Receptors on the gallbladder |
Beta 2 relaxation SNS |
|
|
Receptors on adipose tissue? |
Beta 3 adrenergic |
|
|
M2 receptor location? |
Heart |
|
|
M3 receptor location? |
Smooth muscle and glands |
|
|
SNS receptors on the eye? |
alpha 1 - constriction of radial iris muscle |
|
|
Location of of the cell bodies of preganglionic neurons? |
IML - intermediolateral column of the spinal cord and some cranial nuclei |
|
|
Which of the following are incorrect: 1. alpha neurons examples of myelinated MOTOR neurons 2. Preganglionic autonomic neurons are small, myelinated slow conducting B fibers 3. 1 preganglionic neuron diverges multiple postganglionic neurons 4. All preganglionic neurons use ACh as their neurotransmitter 5. Postganglionic neurons are mostly myelinated c fibers |
5. Postganglionic neurons are mostly myelinated c fibers - incorrect - C fibers are UNMYELINATED |
|
|
Postganglionc nerves used which neurotransmitter? |
Noradrenaline ACh - sweat glands + some blood vessels to produce vasodilation (skeletal muscle) Dopamine - Renal nerves |
|
|
Describe the path of preganglionic SNS neurons. |
Leave the IML --> via ventral root with motor neurons --> leave via WHITE rami communicans --> sympathetic paravertebral ganglion Here some synapse, others leave and move up or down the chain or synapse at paravertebral ganglia (including coeliac, SM, IM ganglia) |
|
|
Which nerves traverse the gray rami communicans? |
Postganglionic neurons leave the chain and re-enter spinal nerves via the GREY rami |
|
|
Name the cranial PSNS ganglia and the end effector organs. |
Ciliary ganglion - pupillary constrictor, ciliary muscle Sphenopalatine - Lacrimal and nasal glands Submaxillary - Submaxillay, sublingual glands Otic - Parotid |
|
|
Name the CRANIAL NUCLEI associated with PSNS and the associated CN |
Edinger-Westphal N. --> III --> Ciliary --> pupil Superior salivatory nucleus - VII --> Glands Inferior salivatory N. - IX - - Otic G. --> Parotid Dorsal Motor N. of Vagus - X --> heart, lungs, GIT Nucleus Ambiguus - X --> heart |
|
|
Parts of the GIT served by the COELIAC Ganglion (SNS) |
Stomach Liver Pancreas Spleen |
|
|
Parts of the GIT served by the Superior mesenteric ganglion - SNS ? |
Small intestine + Colon |
|
|
Parts of the GIT served by the Inferior mesenteric ganglion SNS ? |
Colon Kidney Bladder Sex organs |
|
|
Which of the following are incorrect - 1. The sex organs, kidneys, bladder and colon receive SNS innervation via the inferior mesenteric ganglia 2. The superior mesenteric ganglia provide PSNS input for only the small intestine 3. Nucleus Ambiguus provides PSNS output to the heart via the vagus nerve 4. Vagal supply to organs is from the dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (except the heart) 5. CNVII serves the lacrimal and nasal glands |
2. The superior mesenteric ganglia provide PSNS input for only the small intestine - incorrect - provide SYMPATHETIC input to the SI + colon |
|
|
PSNS input to the sex organs? |
Via S2/3/4 --> to the bladder, colon and sex organs via the pelvic nerves |
|
|
Nicotinic receptors opens ? |
Na and K channels |
|
|
How are slow EPSP produced? |
Fast EPSP --> ACh - nAChR - milliseconds Slow EPSP --> ACh acting on mAChR (Seconds) Modulate and regulate transmission NOTE: SLOW, LATE EPSP due to peptides (minutes) |
|
|
Which of the following are incorrect: 1. M2 are located on the heart and open K channels and inhibit adenylyl cyclase 2. M3 receptors are located on smooth muscle and glands --> IP3 + DAG --> Ca2+ 3. Activation of alpha 1 results in contraction of the radial muscle of the iris and miosis 4. The ciliary muscle is controlled by the PSNS 5. PSNS results in erection but not ejaculation |
3. Activation of alpha 1 results in contraction of the radial muscle of the iris and miosis - incorrect - results in mydriasis - Contraction |
|
|
Which of the following are incorrect: 1. PSNS activation results in lacrimal secretion 2. B3 adrenergic receptors result in lipolysis 3. Both SNS and PSNS increase salivary secretion (viscous vs watery) 4. SNS has no effect on insulin production 5. B2 receptor activation results in relaxation of the detrusor |
4. SNS has no effect on insulin production - incorrect - Alpha decreases secretion but B2 increases secretion |
|
|
SNS effects on the bladder - which receptors? |
B2 - relaxation detrusor (Gs - increases cAMP) Alpha 1 - contraction sphincter (IP3, DAG) |
|
|
PSNS effects on the bladder |
Contraction of the detrusor and relaxation of the sphincter |
|
|
Most vasoconstriction via the SNS is via which receptor? Intracellular signalling? |
Alpha 1 - constriction ---> IP3 + DAG = Ca influx |
|
|
Effects of PSNS/SNS on lungs? |
SNS - B2 - relaxation PSNS - constriction |
|
|
Examples of mAChR antagonist? |
atropine ipratropium scopolamine tropicamide |
|
|
Main target of dobutamine |
Beta 1 |
|
|
MOA of alpha 2 signalling? |
Gi inhibits adenylyl cyclase reduced cAMP |
|
|
MOA of pralidoxime ? MOA Pyridostigmine? |
Pralidoxime - Breaks the covalent bond between organophosphates and AChE --> must be given early Pyridostigmine - Preventatively binds AChE and prevents binding of organophosphates (given to soldiers) with atropine and carbamate |
|
|
Function of the ciliary muscle ? |
accommodation for near vision under PSNS control |
|
|
Sweat glands contain what type of receptor? |
Muscarinic but responding to SNS - ACh resulting in sweating |

