![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Trapezius |
N: accessory n. A: elevator & retractor of scapula |
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi |
N: thoracodorsal n. A: adduct, medially rotate and extend arm |
|
|
|
Rhomboids |
N: dorsal scapular n. Retract scapula |
|
|
|
Levator scapulae |
Elevate scapula N: dorsal scapular n. |
|
|
|
Serratus posterior |
N: ventral rami of spinal n Proprioceptive |
Connects adjacent lamina forming posterior wall of vertebral canal |
|
|
Ligamentum flava |
Pierced during lumbar puncture |
Splenius capitis & cervicis |
|
|
Extrinsic back muscles |
Attach to either ribs scapula or humerus N: ventral rami of spinal n |
|
|
|
Intrinsic back muscles |
Extend spine/head N: dorsal rami of spinal n. |
|
|
|
Splenius m. |
Unilateral: flexes and rotates head to same side |
|
|
|
Erector spinae |
Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis Unilateral a: ipsilateral flexion |
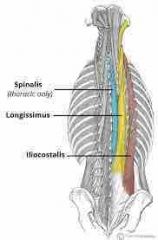
|
|
|
Transversospinalis m. |
Rotatores Multifidus Semispinalis Unilateral a: contralateral rotation |
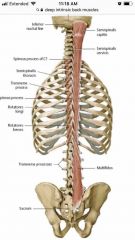
|
|
|
Deep (minor) intrinsic back muscles |
Interspinales Levator costarum N: dorsal rami Intertransversarii N: dorsal & ventral rami |
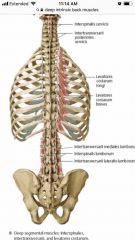
|
|
|
Suboccipital muscles |
N: suboccipital n A: rectus capitis posterior (major & minor) & obliquus capitis inferior - ipsilateral rotation A: obliquus capitis superior - contralateral rotation |
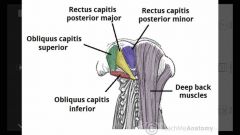
|
|
|
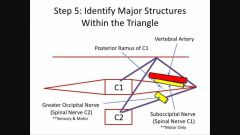
Contents of suboccipital triangle |
Vertebral a. Suboccipital n.
Greater occipital n. originated inferior to obliquus capitis inferior |
|
|
|
Conus medullaris Filum terminalae Cauda equina Denticulate ligaments |
End of the spinal cord at L1 Pial prolongation anchoring to coccyx Bundle of lumbar and sacral n. roots Lateral extensions of pia mater that attach to dura mater |
|
|
|
Cervical spinal n. exit: Remaining nerves exit: |
Above the correspondingly number vertebrae Starting at T1 they exit bellow the correspondingly numbered vertebrae |
|
|
|
Dorsal roots Ventral roots Rami |
Dorsal roots - sensory Ventral roots - motor Rami - both motor & sensory |
|
|
|
Ventral/dorsal rami supply |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Glenohumeral joint dislocation |
Anterior dislocation is most common Possibly damaging: axillary n. & posterior humeral circumflex vessels |
|
|
|
Deltoid |
A: abducts, adducts, flexes, extends, and rotates the shoulder N: axillary n. |
|
|
|
Rotator cuff |
Formed by tendons of Supraspinatus (initiates abduction) Infraspinatus (lateral rotator) - N: suprascapular n. Teres minor (laterally rotates & weakly adducts) - N: axillary n. Subscapularis (medially rotates) - N: upper & lower supscapular n.
Supraspinatus tendon is commonly damaged in rotator cuff tears pt will have trouble with first 15* of abduction. |
SITS |
|
|
Teres major |
A: internally rotates, adducts, & extends the arm N: lower subscapular n. |
|
|
|
Serratus anterior |
N: long thoracic n. A: protracts and rotates scapula upward during arm elevation |
Paralysis causes winging of the scapula |
|
|
1. Quadrangular space, 2. Triangular space, 3. Triangular interval Boundaries |
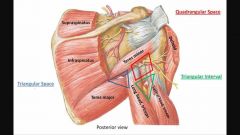
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
1. Quadrangular space, 2. Triangular space, 3. Triangular interval contents
& Fractures would affect: |
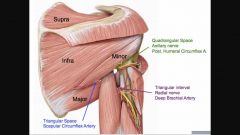
Fracture of the surgical neck: axillary n. & posterior circumflex humeral a. Fracture of shaft of humerus: radial n. & deep brachial a. |
|
|
|
Pectoralis major |
N: lateral & medial pectoral n. A: flexes, adducts & medially rotates Vascular: pectoral branch of thoracoacromial trunk |
|
|
|
Pectoralis minor |
N: medial pectoral n. Helps with inspiration and stabilizes scapula |
|
|
|
Coracobrachialis |
N: musculocutaneous n. Flexes arm |
|
|
|
Cutaneous innervation of the upper limb |
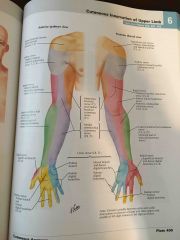
|
|
|
|
Biceps brachii |
Flexor of all and forearm N: musculocutaneous n. |
|
|
|
Biceps brachii |
Flexor of arm and forearm, supinator of forearm N: musculocutaneous n. |
|
|
|
Coracobrachialis |
Flexes arm N: musculocutaneous n. |
|
|
|
Brachialis |
Prime flexor of forearm N: musculocutaneous n. |
|
|
|
Triceps |
Extend the elbow N: radial n. |
|
|
|
Anconeus |
Extends the elbow N: radial n. |
|
|
|
Contents of the carpal tunnel |
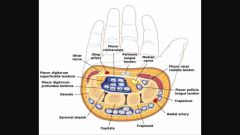
4FDS 4FDP FPL Median n. |
|
|
|
Anatomical snuff box |
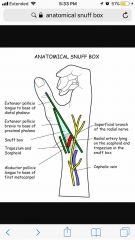
Back (Definition) |
2 things in the roof 1 on the floor |
|
|
Movement at the Metacarpophalangeal joint |
PAD & DAB Flexion - lumbricals & interossei Extension - extensor digitorum |
|
|
|
Movement at the interphalangeal joints PIP & DIP |
Flexion - PIP - flexor digitorum superficialis DIP - flexor digitorum profundus
Extension - lumbricals & interossei; extensor digitorum |
|
|
|
Palmar arches primary contribution |
Superficial - ulnar a.
Deep - Radial a. |
|
|
|
Brachioradialis |
Radial n. Flexes forearm |
|
|
|
Extensors - Muscles of Posterior Forearm (superficial) |
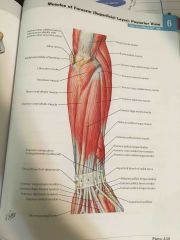
Abductor pollicis longus is an extensor |
|
|
|
Extensors - muscles of the posterior forearm (deep) |
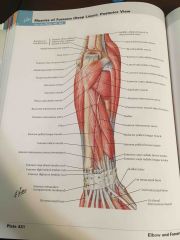
N: Radial n. |
|
|
|
Flexors - muscles of anterior forearm (superficial) |
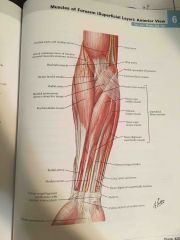
N: Median n.
except - flexor carpi ulnaris & medial half of flexor digitorum profundus - ulnar n. |
|
|
|
Flexors - Anterior forearm (intermediate) |
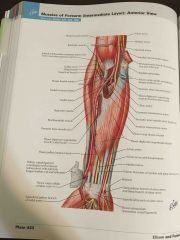
|
|
|
|
Flexors - Anterior forearm (deep) |
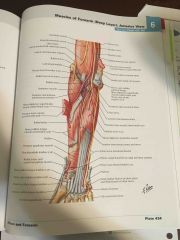
|
|
|
|
Flexors - muscles of anterior forearm (superficial) |
N: Median n.
except - flexor carpi ulnaris & medial half of flexor digitorum profundus - ulnar n. |
|
|
|
Flexors - Anterior forearm (intermediate) |
|
|
|
|
Flexors - Anterior forearm (deep) |
|
|
|
|
Greater sciatic foramen |
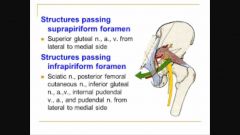
Additional infrapiriformic contents m: n. to quadratus femoris & obturator internus |
Formed by sacrotuberous ligament |
|
|
Movements of the hip joint - muscle actions |

|
|
|
|
Femoral triangle |
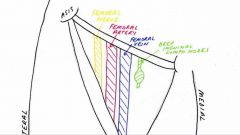
NAVL |
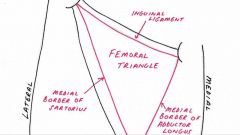
|
|
|
Thenar muscles
|
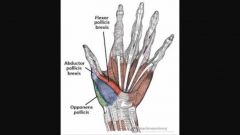
N: median n. |
|
|
|
Popliteal fossa |
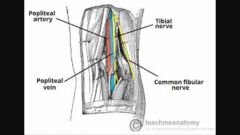
|
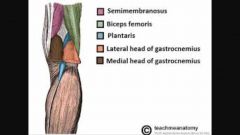
|
|
|
Hypothenar m. |
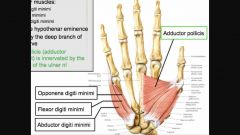
N: Ulnar n. Also innervates adductor pollicis |
|
|
|
Cruciate ligaments |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Cruciate ligaments |

|
Excessive lateral rotation of a flexes knee will tear ACL, TCL & medial meniscus |
|
|
Talocrural joint |
Talus, tibia, fibula
Inversion injury (common) tearing of lateral collateral log.
Eversion injury - medial collateral lig. = deltoid lig. |
|
|
|
Quadriceps group |
Vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris (also hip flexion)
N: femoral n. Knee extension |
|
|
|
Quadriceps group |
Vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris (also hip flexion)
N: femoral n. Knee extension |
|
|
|
Sartorius |
N: femoral n. Hip: flexion, abduction, lateral rotation Knee: flexion & medial rotation - attaches on pes anserinus |
|
|
|
Medial thigh muscles (Superficial) |
Abductor longus & brevis Pectineus Gracilis (also flexes and internally rotates knee)
A: hip adduction & flexion N: obturator n. |
|
|
|
Medial thigh muscles (deep) |
Obturator externus (lateral hip rotation) Adductor magnus
N: Obturator n. - except hamstring part of adductor magnus - tibial n.
A: adducts the thigh
Hamstring portion - extends the thigh Adductor portion - flex the thigh |
|
|
|
Gluteus maximus |
Extends & laterally rotates thigh N: inferior gluteal n. |
|
|
|
Gluteus medius, minimus, tensor fascia latae |
Abduct & medially rotate thigh N: superior gluteal n. |
|
|
|
Gluteus medius, minimus, tensor fascia latae |
Abduct & medially rotate thigh N: superior gluteal n. |
|
|
|
Piriformis, gamelli, obturator internus, quadratus femoris |
Laterally rotate thigh
N. to piriformis, n. to obturator internus, n. to quadratus femoris |
|
|
|
Hamstring muscles |
A: hip extension & knee flexion
Semimembranosus Semitendinosus (pes anserinus) Medial knee rotation
Biceps femoris Lateral knee rotation
N: tibial n. - except short head of biceps femoris - common fibular n. |
|

