![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Artifacts
|
- not real
- not seen on image -incorrect shape or size, position, and/or brightness |
|
|
Causes of Artifacts
|
- violation of assumptions
- equipment malfunction or poor design - the physics of ultrasound -operator error |
|
|
Hyperechoic
|

Portions of an image that are brighter than surrounding tissues
|
|
|
Hypoechoic
|
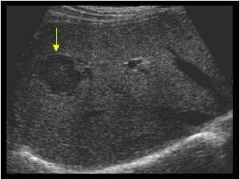
Portions of an image that are not as bright as the surrounding tissue
|
|
|
Anechoic
|
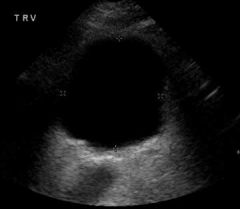
An extreme form of hypoechoic, echo free, fluid filled structure
|
|
|
Isoechoic
|
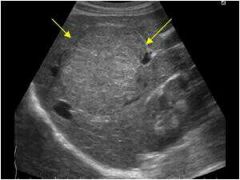
Structures with equal echo brightness
|
|
|
Homogeneous
|
A portion of tissue or an image that has similar characteristics throughout
|
|
|
Heterogenous
|
A portion of tissue or an image that has differing echo characteristics throughout
|
|
|
Six Assumptions of Imaging Systems
|

|
|
|
Reverberation
|
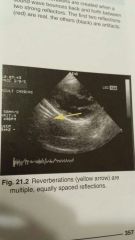
-locational artifact
- located parallel to sound beams main axis, at ever increasing depths -resemble venetian blinds |
|
|
Comet tail
|
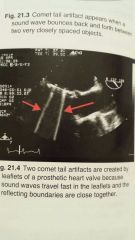
-Locational artifact
- appears as a single long hyperechoic echo - located parallel to the sound beams main axis - appears mostly due to metallic objects or calcifications |
|
|
Ring down artifact
|
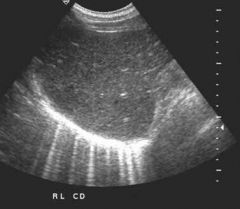
-Locational artifact
- appears as a single long hyperechoic echo - located parallel to the sound beams main axis -appears due to gas bubbles |
|
|
Shadowing
|
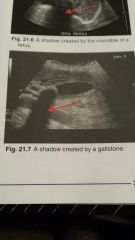
-appears as hypoechoic or anechoic region extending downward
- result of too much attenuation -shadows may provide valuable diagnostic info that helps characterize the tissue |
|
|
Edge shadow
|
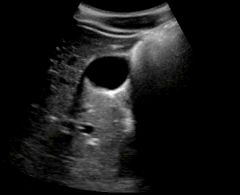
- hypoechoic or anechoic
- results when beam spreads after striking a curved reflector -extends downward from curved reflector edge - prevents visualization of true anatomy on the scan |
|
|
Enhancement
|
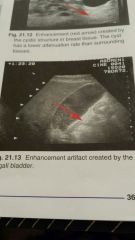
- occurs when the sound beam travels through a region of lower attenuation than surrounding tissue
- is the opposite of shadowing - clinically useful in diagnosing - Hyperechoic |
|
|
Focal enhancement
|
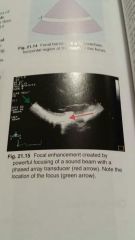
- Hyperechoic side to side region (appears the same as the foreground color)
- results from an increased intensity at the focus |
|
|
Mirror image
|
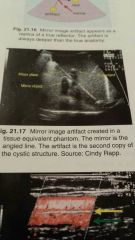
-second copy of a true reflector
- artifact appears deeper than true reflector - the mirror lies on a straight line between the artifact and the transducer - true reflector and artifact are equal distances from the mirror |

