![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
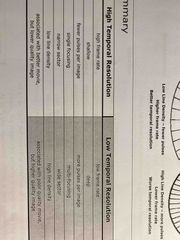
High vs low temporal resolution -focusing -sector size -line density -depth |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Acoustic parameters |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Direction of Sounds waves |
Longitudinal Compression and rarefaction |
|
|
Speed of sound affected by |
Density and stiffness More stiff, faster propagation (More compressible, slower propagation) I.e Gas < liquid < solid More dense, slower propagation Density does not affect attenuation |
|
|
At what frequency is imaging performed |
1-30 MHz |
|
|
Formula for velocity |
Velocity = frequency x wavelength |
|
|
Ultrasound |
Frequency > 20 kHz |
|
|
Audible sound |
20Hz to 20,000Hz |
|
|
As sound travels deeper in the body amplitude |
Decreases Amplitude is the strength of a sound beam |
|
|
As sound propagate through body, power and intensity (power/beam area) |
Decreases |
|
|
Safety of ultrasound determined by |
Intensity |
|
|
What is the relationship between period and frequency |

Period = time required to complete one cycle Period and frequency are reciprocals of each other |
|
|
Pulse repetition frequency -definition -formula -relation to depth |

Back (Definition) High PRF means less depth |
|
|
Pulse |
Stream of cycles emitted by the ultrasound that’s inherent to the property of the ultrasound. It cannot be changed. Usually lasts for 2-4 cycles |
|
|
Pulse duration |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
PRP x PRF = ? |
1 Reciprocals |
|
|
Duty factor |

Machine spends most time listening and less time transmitting pulse Normal .001 to .01 |
|
|
Attenuation |
Directly Related to distance and frequency Ultrasound intensity decreases with distance and higher frequency |
|
|
How does Frequency relate to depth |
Frequency = cycles/second Frequency = velocity/wavelength The velocity of sound through tissue remains constant, so increasing frequency means decrease in wavelength. So less distance travelled > decrease in depth |
|
|
Rayleigh scattering |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
In an organized image, reflection and scattering is: |
Specular and Rayleigh |
|
|
If transmission speed is less than incident speed, then transmitted angle is |
Lower |
|
|
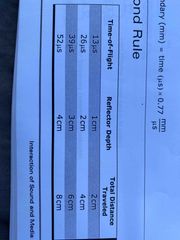
13 microsecond rule |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Axial Resolution -formula -relation to frequency and wavelength |

Improves with decreased wavelength and increased frequency |
|
|
Lateral resolution |

Best at beam focus. Usually not as good as axial resolution because pulses are wide but short in length |
|
|
Impedance within ultrasound structure |

Impedance = density x propagation speed
|
|
|
What is the difference between period and pulse duration |
Period is the time of 1 cycle. Period = 1/frequency Pulse duration is the time for all the cycles in 1 pulse Pulse duration + signal receiving time = pulse repetition period |
|
|
Difference between period and wavelength |
Period is TIME of 1 cycle Wavelength is DISTANCE travelled in 1 cycle |
|
|
Ways of increasing frame rate |
1) narrowing the imaging sector, which decreases the time it takes to scan one frame 2) decreasing the depth which decreases the PRP 3) decreasing the line density, which requires fewer lines to scan one frame (at the cost of spatial resolution) 4) turning off multifocus, which decreases the number of pulses needed per line. |
|
|
Frame rate formula |
1/time to scan one frame 1/(PRP x number of scan lines per frame) 1/(PRP x #pulses) |
|
|
Pulse Repetition Period |
Time for sending and receiving 1 pulse. Only related to depth PRP= Imaging depth x 13us/cm |
|
|
Backing / Damping material |
Absorbs sound and causes the emitted pulse to be short in duration and length Leads to: 1. decreased sensitivity - can not convert low level reflections in to electrical signals 2. Wide bandwidth - many diff frequencies of sound above and below main frequency 3. Low quality factor, QF = main frequency/ Bandwidth |
|
|
Frequency and thickness of PZT crystal |
Inversely related, thinner material produces higher frequency signal |
|
|
To increase the focal depth |
1. Increase transducer frequency 2. Increase diameter of PZT crystal |
|
|
To decrease beam divergence |
1. Increase beam frequency 2. Increases beam diameter |

