![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. What is the overriding PMI philosophy of risk management? (4A)
|
The project manager
- is in control and proactively manages events, avoiding as many problems as possible - must understand how to anticipate and identify areas of risk - how to quantify and qualify them and - how to plan for them |
|
|
2. What are the the six risk management processes?
|
- Plan Risk Management
- Identify Risks - Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis - Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis - Plan Risk Responses - Monitor and Control Risks |
|
|
3. What is the output of "Plan Risk Management"?
|
Risk Management Plan
|
|
|
4. What is the output of "Identify Risks"?
|
Risk Register
|
|
|
5. What is the output of "Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis"?
|
Risk Register Updates
|
|
|
6. What is the output of "Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis"?
|
Risk Register Updates
|
|
|
7. What is the output of "Plan Risk Responses"? (2A)
|
Risk Register Updates
Contract Decisions |
|
|
8. What is the output of "Monitor and Control Risks"? (2A)
|
Risk Register Updates
Change Requests |
|
|
9. In which of the 5 process groups do the 6 risk management processes fall?
|
- Initiating: None
- Planning: => Plan Risk Management, Identify Risks Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis, Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis Plan Risk Responses - Executing: none - Monitoring & Controlling: => Monitor and Control Risks |
|
|
10. What are the two risk characteristics?
|
1. Risk is related to an uncertain event
2. A risk may affect the project for good or for bad. Although risk usually has negative connotations, it may well have an upside. |
|
|
11. The "Plan Risk Management" process is concerned with one thing ...
|
... with creating the risk management plan
|
|
|
12. What is planned in the "Plan Risk Management" process"?
|
... the remaining five risk management processes, which are:
- Identify Risks - Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis - Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis - Plan Risk Responses - Monitor and Control Risks |
|
|
13. When in the project is the "Plan Risk Management" process performed?
|
The "Plan Risk Management" process is general and high-level in nature.
It is performed early on the project, usually before many of the other planning processes are performed. |
|
|
14. Why is "Plan Risk Management" process performed early on the project?
|
Because the results of this (and other risk processes) can significantly influence decisions made about scope, time, cost, quality and procurement.
|
|
|
15. Sketch a diagram of the order of the Risk Management's processes and their outputs.
|
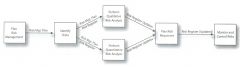
|
|
|
16. The risk management plan does what? (6A)
|
- is a roadmap to the other five risk management processes
- defines what level of risk is tolerable for the project - defines how risk will be managed - defines how risk will be categorized - defines who will be responsible for risk activities - defines the amounts of time and cost that will be allotted to risk activities - defines how risk findings will be communicated |
|
|
17. What is the single tool for the "Plan Risk Management" process?
|
The single tool for the "Plan Risk Management" process is
"Planning Meeting and Analysis" |
|
|
18. What is the single output of the "Plan Risk Management" process?
|
The single output of the "Plan Risk Management"
is the Risk Management Plan. |
|
|
19. What is one tool to categorize risk?
|
The RBS (risk breakdown structure) is a graphical, hierarchical decomposition used to facilitate understanding and organization.
|
|
|
20. What is the single output of "Identify Risks"?
|
The single output is the risk register, which is a list of all risks, their causes, and any possible responses to those risks that can be identified at this point in the project.
|
|
|
21. When is the "Identify Risks" process performed?
|
Although "Identify Risks" is typically performed early on the project, risks change over time, and new risks arise. Therefore it may be necessary to perform this process multiple times throughout the project.
|
|
|
22. What are "Information Gathering Techniques" used to create the risk register? (4A)
|
- Brainstorming
- Delphi technique - Expert interviews - Root cause identification |
|
|
23. What are "Diagramming Techniques" used to show how potential causes can lead to risk?
|
- Ishikawa diagrams or cause-and-effect diagrams or fishbone diagrams
- Influence diagrams - Flow charts (a graphical representation of complex process flows) |
|
|
24. SWOT Analysis is a tool used in the "Identify Risks" process. How does it work?
|
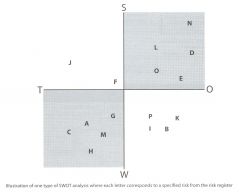
SWOT analysis is particularly useful since it is a tool used to measure each risk's strenghts (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), and threats (T). Each risk is plotted and the quadrant where the weakness and threats are highest, and the quadrant where strengths and opportunities are highest will represent the highest risks on the project.
|
|
|
25. What do you know about the Risk Register?
|
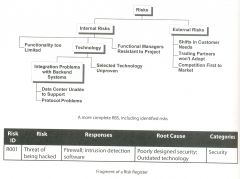
- It is an output of "Identify Risks"
- It provides a list of all identified risks on the project - It is an essential input into the remaining risk management processes and may be updated throughout the life of a project |
|
|
26. What do you know about "Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis"?
|
- It is usually done rapidly on the project in order to determine which risks are the highest priority on the project
- It takes each risk from the risk register and works to analyze its probability of occuring and impact to the project if it did occur - By using the probability and impact matrix (PIM), a prioritization and ranking can be created, which is updated on the risk register |
|
|
27. What are the tools used in "Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis"?
|
- Risk Probability and Impact Assessment
- Probability and Impact Matrix (PIM) - Risk Data Quality Assessment - Risk Categorization (RBS) - Risk Urgency Assessment - Expert Judgement |
|
|
28. What do you know about "Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis"?
|
- It seeks to assign a projected value to quantify the risks that have been ranked by Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
- This likely value is most often specified in terms of cost or time |
|
|
29. What are the tools used in "Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis"?
|
- Data Gathering and Representation Techniques
- Probability Distributions - Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Techniques - Expert Judgment |
|
|
30. What are the "Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Techniques"?
|
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Expected Monetary Value Analysis -> Decision Tree Analysis - Decision Tree Analysis - Tornado Diagrams - Modeling and Simulation -> Monte Carlo analysis - Expert Judgment |
|
|
31. What is the concept of "Decision Tree Analysis"?
|
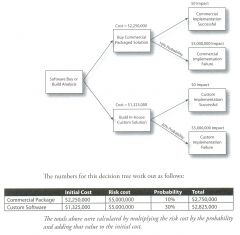
Decision trees are used to show probability and arrive
at a dollar amount associated with each risk. |
|
|
32. What are Tornado Diagrams used for?
|

Tornado diagrams are one way to analyze project sensitivity to cost or other factors.
A tornado diagram ranks the bars from greatest to least on the project so that the chart takes on a tornado shape. |
|
|
33. What is the Monte Carlo analysis used for?
|
- Monte Carlo analysis is one technique for simulating the schedule
- Performed by a computer, Monte Carlo analysis throws large numbers of scenarios at the schedule to see the impact of certain risk events - This technique will show you what is not always evident by simply looking at the schedule - It will often identify tasks that may not appear inherently high risk, but in the event they are delayed, the whole project may be adversely affected |
|
|
34. What are the strategies for negative risks or threats? (4A)
|
- Avoid
- Transfer - Mitigate - Accept |
|
|
35. What are common ways to transfer risks? (2A)
|
- Contractual agreements with another party
- Insurance agreements |
|
|
36. What are the strategies for positive risks or opportunities? (4A)
|
- Exploit
- Share - Enhance - Accept |
|
|
37. What does "Exploit" as a strategy for positive risks mean?
|
Exploiting means you are trying to remove any uncertainty.
For instance, if a positive risk of finishing the project early is identified, then adding additional people to ensure that the project is completed early would be an example of exploiting the risk. |
|
|
38. What does "Share" as a strategy for positive risks mean?
|
In order to share a positive risk, the project seeks to improve their chances of the risk occuring by working with another party.
|
|
|
39. What does "Enhance" as a strategy for positive risks mean?
|
By working to influence the underlying risk triggers, you can increase the likelihood of the risk occuring. For example, an airline might add flights to a popular route during holidays in order to enhance traffic and profitability during heavy travel times.
|

