![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. You are managing the construction of a data center, but the location is in an area highly prone to earthquakes. In order to deal with this risk, you have chosen a type of building and foundation that is particularly earthquake resistant. This is an example of:
A. Risk transfer B. Risk avoidance C. Risk mitigation D. Risk acceptance |
Answer C
The best answer here is risk mitigation since you are taking steps to lessen the risk. 'A' is incorrect because you are not transferring the risk to anyone else. 'B' is incorrect because you would need to relocate in order to cornpletely avoid the risk of earthquake. 'D' is incorrect because you are not merely accepting the risk - you are taking steps to make it less severe. |
|
|
2. You are evaluating the risk by trying to produce a risk score for each risk. This is an example of which tool?
A. Monte Carlo analysis B. Probability impact matrix C. RACI Chart D. Cause and effect diagrams |
Answer B
The probability impact matrix (PIM) derives a risk score by multiplying the probability of the risk by its impact (both of these numbers are estimated). This resulting risk score may be used to help prioritize the risk register. |
|
|
3. As part of your project, you have identified a significant risk of cost
overrun on a software component that is integral to the product. Which represents the BEST strategy in dealing with this risk? A. Outsource the software development B. Insure the cost C. Double the estimate D. Eliminate the need for this component |
Answer A
Outsourcing the software development could allow you to cap the cost. 'B' is not a good choice because costs for development such as this cannot be insured in a cost-effective manner. 'C' is not correct because doubling the estimate does not deal with the root of the problem. It only arbitrarily changes the estimate. 'D' is incorrect because you cannot simply eliminate every high risk component in the real world. |
|
|
4. Planning meetings and analysis are used in which process?
A. As part of Manage Stakeholder Expectations B. As part of Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis C. As part of Plan Risk Responses D. As part of Plan Risk Management |
Answer D
Planning meetings and analysis are a tool of the process of Plan Risk Management. Choice 'A' was from a communications process. |
|
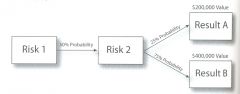
5. Refer to the diagram below. What is the expected value of Result A?
A. $200,000 B. $100,000 C. $50,000 D. $25,000 |
Answer D
The way this problem is solved is by multiplying out the probabilities times the value. In this case, it is the 50% probability of Risk 1 X the 25% probability of Risk 2 X the $200,000 value of result A. 0.5 X 0.25 * 200,000 = $25,000. |
|
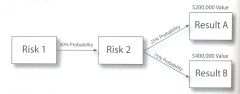
6. Refer to the diagram from the previous question.
What risk management tool is employed in this diagram? A. Earned value management B. Sensitivity analysis C. Decision tree analysis D. Flowcharting |
Answer C
This is an example of decision tree analysis. |
|
|
7. Marie is meeting with her project team to evaluate each identified risk and try to assign an estimated dollar amount or time impact estimate to it. Which process is her team performing?
A. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis B. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis C. Plan Risk Responses D. Monitor and Control Risks |
Answer A
You should have seen the fact that Marie's team was quantifying the risks by seeking to assign a dollar or time estimate to them, and Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis is the process that does this. |
|
|
8. If a project manager is recommending that immediate corrective action be taken, which process is he involved in?
A. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis B. Plan Risk Management C. Identify Risks D. Monitor and Control Risks |
Answer D
Recommended corrective action is the result of monitoring and controlling processes, and the only monitoring and controlling process in the choices was Monitor and Control Risks. |
|
|
9. What is the BEST source of information about potential risk on your project?
A. Computer risk analysis B. Interviews with team members from other projects C. Historical records from similar projects D. Your own experience in this industry |
Answer C
Historical records from similar projects would provide you with the best source of information on potential risks. 'A', 'B', and 'D' are all good sources, but they would not be as pertinent or helpful as the records from other similar projects. Historical information gets brought into your planning processes as an organizational process asset. |
|
|
10. You have just finished a thorough Monte Carlo analysis for your project. Which of the following would the analysis MOST likely identify?
A. Divergent paths causing risk B. Points of schedule risk C. Points of schedule conflict that lead to risk D. Gaps in the project path that could create risk |
Answer B
One of the things Monte Carlo analysis would show you is where schedule risk exists on the project. 'A' is incorrect, because it is typically convergent and not divergent tasks that create schedule risk. 'C' is incorrect because it is not looking for schedule conflicts - those would be corrected in Develop Schedule. 'D' is incorrect because gaps in the project path do not, by themselves, cause risk. |
|
|
11. Your company is beginning a new building project and has assigned you the role of project manager. During the first few meetings with stakeholders you become aware of several risks that are of concern to the project sponsor. The topic of risk management, however, has yet to be addressed. What is the first thing you should do to address the project risks?
A. Develop a risk management plan B. Identify project risks C. Plan responses to project risks D. Determine how risks will be controlled |
Answer A
You should develop the risk management plan. A risk management plan will outline how all risk planning activities and decisions will be approached. Methods of identification, qualilication, quantification, response planning, and control will all follow the development of the risk management plan. |
|
|
12. Plan Risk Management is:
A. A process of identifying potential risks for a project B. Deciding how risk management activities will be structured and performed C. Assessing the impact and likelihood of project risks D. Numerical analysis of the probability of project risks |
Answer B
Plan Risk Management is not planning for actual risks (which include choices 'A'', 'C', and 'D'); it is the PROCESS of deciding how all risk planning activities and decisions will be approached. It is the plan for how to plan. |
|
|
13. Which of the following is an output of Identify Risks?
A. Risk register B. Probabilistic analysis C. Risk-related contractual agreements D. Recommended cash reserves |
Answer A
The risk register is the only output of Identify Risks, and it is updated in Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis, Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis, Plan Risk Responses, and Monitor and Control Risks. |
|
|
14. Which of the following would NOT be a strategy
for dealing with negative risk? A. Avoid B. Transfer C. Share D. Mitigate |
Answer C
There are three identified strategies for dealing with negative risks. They are: mitigate, transfer, and avoid. The reason that 'C' was incorrect is that share is a strategy for managing a positive risk or opportunity. |
|
|
15. A risk probability and impact assessment is used in:
A. Identify Risks B. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis C. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis D. Plan Risk Responses |
Answer B
The hardest part about risk is keeping the various processes straight. Since the outputs are similar (for the most part), focus more of your study on the processes themselves and their tools. In this question, the tool of risk probability and impact assessment is a tool of Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis. |
|
|
16. The BEST definition of risk management is:
A. The process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk B. The process of reducing risk to the minimum level possible for the project C. The process of proactively ensuring that all project risk is documented and controlled D. Creation of the risk response plan |
Answer A
The process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk is the definition of risk management. |
|
|
17. Which of the following is NOT a tool or technique for gaining expert
opinion as it relates to risk? A. Brainstorming B. Delphi technique C. Monte Carlo analysis D. Expert interviews |
Answer C
Monte Carlo analysis, which is a computer-based analysis, might be useful for revealing schedule risk, but it would not be useful for gaining expert opinion. Choices 'A', 'B', and 'D' are all tools used as part of project risk management. |
|
|
18. Which of the following would NOT be contained in the risk
management plan? A. A risk breakdown structure B. A description of the overall approach to risk on the project C. Risk roles and responsibilities D. A list of identified risks |
Answer D
The risk management plan does not contain the identified risks. It is more general and high-level than that. The identified risks will be listed in the risk register, produced after the risk management plan. |
|
|
19. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding risk?
A. All risk events must have a planned workaround B. All risk events are uncertain C. All risk events are negative D. All risk events should be covered by a contingency budget amount |
Answer B
Risk events are, by definition, uncertainties. These could either be positive or negative. 'A' is incorrect because some risks are simply accepted and have no workaround. 'C' is incorrect because a risk may be positive or negative. 'D' is incorrect because not all risks are budgeted. Some are transferred to other parties or are too small or unlikely to consider. |
|
|
20. Which of the following is NOT a valid way to reduce risk?
A. Select a contract type that reduces risk B. Insure against the risk C. Create a workaround for the risk D. Plan to mitigate the risk |
Answer C
Read these questions carefully! The workaround is what you do if the risk occurs, but it does not reduce the risk as the question specified. 'A', 'B',and 'D' all focus on reducing risk by transferring or mitigating it. |

