![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you find magnification? |

Image size divided by real size |
|
|
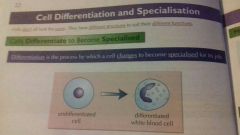
What is differentiation |
|
|
|
Why are sperm cells specialised for reproduction? |
●Long tail and streamlined head to help swim to the egg. ●lot of mitochondria to provide the cell with energy. |
|
|
Why are nerve cells specialised for rapid signalling? |
Long to cover more distance and have branched connections on the end to connect with other nerve cells to format a network around the body. |
|
|
Why are muscle cells specialised for contraction? |
Lots of mitochondria to generate energy and are long so they have space to contract. |
|
|
Why are root hair cells specialised for absorbing water and minerals? |
Hairs that stick out into the soil give it a large surface area for absorbing water and minerals. |
|
|
What happens in mitosis |

|
|
|
What is diffusion |

|
|
|
What is osmosis |

|
|
|
Equations for electricity |
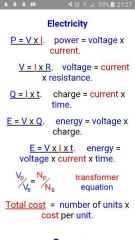
|
|
|
Equations for force and motion |

|
|
|
Equations for energy |

|
|
|
What does a group of cells make |
Tissues |
|
|
What does a group of tissues make |
Organs |
|
|
What does a group of organs make. |
Organ systems |
|
|
Starch is broken down to maltose by which enzyme? |
Amylase enzyme |
|
|
Proteins are broken down in to amino acids by which enzyme? |
Protease enzyme |
|
|
Lipids are broken down in to glycerol and fatty acids by which enzyme? |
Lipase enzyme |
|
|
What specialised cells produce amalayse |
Salivary glands |
|
|
What cells produce all 3 enzyme(amylase,lipase,protease) |
Small intestine and pancreas |
|
|
Which solution checks the presence of starch |
Iodine |
|
|
What solution is used to check the presence of lipids? |
Sudan III |
|
|
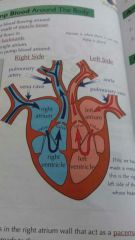
Label the 4 chambers of the heart |
|
|
|
What arteries used for? |
Take blood away from the heart |
|
|
What are capillaries is used for |
Exchange of material at the tissue |
|
|
What are veins used for |
Carry blood to the heart |
|
|
Why are arteries specialised to carry blood at high pressure? |
●Walls are strog and elastic ●thick walls contain thick layers of muscle to make them strong |
|
|
Why are capillaries specialised to exchange material at the tissue |
Permeable walls so substances can diffuse in and out |
|
|
Why are veins specialised to take blood to the the heart |
Valves to stop back flow and make the blood go in the correct direction |
|
|
What does phloem transport |
Food |
|
|
What does xylem transport |
Water |
|
|
Wieght |
Mass × gravitational field strength |
|
|
Force applied to spring |
Spring constant ×extension |
|
|
Accelration |
Change in velocity ÷time taken |
|
|
Momentum |
Mass × velocity |
|
|
Gravitational potential energy |
Height ×mass × gravitational field strength |
|
|
Power |
Work done ÷time |
|
|
Effeciency |
Useful power output×total power output |
|
|
Charge flow |
Current × time |
|
|
Power |
Potential difference ×current |
|
|
Energy transfered |
Power ×time |
|
|
Density |
Mass÷volume |
|
|
Work done |
Force ×distance |
|
|
Kinetic |
0.5×mass×speed squared |
|
|
Distance travelled |
Speed×time |
|
|
Resultant force |
Mass×acceleration |
|
|
Wavespeed |
Frequency × wavelength |
|
|
Power |
Energy transfered ÷time |
|
|
Potential difference |
Current×resistance |
|
|
Effeciency |
Useful output energy transfer÷useful input energy transfer |
|
|
Power |
Current squared×resistance |
|
|
Energy transfered |
Charge flow×potential difference |
|
|
Relative atomic mass |

|

