![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
124 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pt drops the hip |
what is a trendelinburg sign? |
|
|
is the lurch toward the side of weakness |
what is a trendelinburg gait? |
|
|
pelvis, femur, y ligament, triaxial jt |
what are the anatomical characteristics of the hip region? |
|
|
sway back , requires little muscle activity, iliofemoral ligament , anterior longitudinal ligament, posterior thoracic ligaments all on tension |
what is a pelvic shift? |
|
|
l/s sidebends toward the elevation, muscle causing hiking |
what is a lateral pelvic tilt? |
|
|
anterior and posterior- L/S moves opposite , hip IR/ER |
what is pelvic rotation ? |
|
|
pain from hip is felt primarily in the groin followed by the anterior thigh |
what is referred pain and nerve injury of the hip? |
|
|
sciatic , obturator, and femoral |
what are the nerves crossing the hip? |
|
|
indicative of a tumor, necrosis |
what is the sign of the buttocks ? |
|
|
OA, RA, AVN, dislocations, immobilization, slipped epiphyses |
what are the pathologies and symptoms of hiphypermobility? |
|
|
steroids from asthma causing no oxygen to tissue |
why would a hip pt have AVN? |
|
|
groin pain, stiffness following rest (OA), loss of IR and ext, later - 90 degrees flexion, antalgic gait, LBP due to limited hip ext, balance deficits, knee stress due to loss of hip ext. may have knee pain due to referred pain. |
what are the common hip hypo mobility impairments? |
|
|
Loss of IR> ext> ABD> Flex>ER
|
what is the capsular pattern of the hip?
|
|
|
oscillations,AD, shoe lifts, elevate chairs, ROM, muscle setting |
what must be done in the hip hypo mobility protection phase? |
|
|
mobs, stretching, PNF, thomas, obers, faber, strengthening, aerobic exercise |
what would be done in the hip hypo mobility controlled motion and return to function phase? |
|
|
capsule and illiofemoral ligament |
what is cut in a total hip arthroplasty? |
|
|
immediate WB |
what is the conditions of a cemented hip? |
|
|
6-8 weeks NWB |
what is the conditions of a cement less hip? |
|
|
surgical, DVT, infection, malpositioning, loosening, nerve damage, dislocation |
what are THA complications? |
|
|
90% of expected functional level @ 1 year, max out functional level progress at 2-3 years |
what is THA typical recovery percentage? |
|
|
education regarding precautions and reinforcement of them. ankle pumps to prevent DVT. train in bed mobility maintaining precautions ; hip ABD pillow to sleep, sit to stand transfers, car transfers without breaking precautions, knee ex, hip ABD depending on procedure in supine or side lying AA with ER. CKC bil based on WB status. |
what is the THA maximum protection phase? |
|
|
4-6 weeks post op. still under precautions due to tissue healing time, strength and mm endurance are important, especially progressing from hip ABD and ext. functional control within precautions. |
what is the THA mod protection phase? |
|
|
when femoral head is degenerated , but the acetabulum is in tact |
what is a hemiarthroplasty of the hip? |
|
|
yes they are the same |
Are THA and hemi arthroplasty precautions the same? |
|
|
70% occur in 70 y/o and >
84% woman
3% in 50 y/o or < and usually caused by high force trauma or stress fx
90% due to falls |
what are the risk factor %s of a hip fx? |
|
|
at the neck, intracapsular and extracapsular |
what is the most common site or type of hip fx? |
|
|
one year mortality rate 14-36%
50% fail to regain pre fx mobility
25% who previously lived independently , require long term nursing care. (1 in 3)
35-65% Hip fx pts are affected by delirium |
what are the comorbidities of a hip fx? |
|
|
tendonitis, bursitis, femoral acetabular impingement |
what are the painful hip syndromes/ overuse syndromes? |
|
|
pain - local site, hip, knee or back , gait deviations |
what are painful hip syndrome common impairments? |
|
|
decreased irritation and inflammation |
what is the painful hip sun. management protection phase? |
|
|
DFM, stretching, restore neuromuscular control, WB |
what is the painful hip sun. management: controlled motion phase? |
|
|
balance , eccentric control, plyometrics |
what is the painful hip syndrome management: return to function phase? |
|
|
pressup, thomas, k to c, piriformis ( not past 90), glute max |
what are techniques to stretch range limiting hip structures? |
|
|
thomas, prone, standing, hams-doorway |
what are techniques to stretch range limiting two joint muscles? |
|
|
pelvic protraction, hip flexion, ADD, ER, knee flexed ( or extended) , ankle and toes dorsiflexion and in version |
what is D1 LE flexion? |
|
|
pelvic retraction, hip ext,ABD,IR, knee extended or flexed, ankle and toes plantar flexed and everted |
what is D1 LE extension? |
|
|
pelvic elevation, hip flexion, ABD, IR ( fire hydrant) , knee flexed (or extended), ankle and toes dorsiflexed and ankle everted |
what is D2 LE flexion? |
|
|
pelvic depression, hip extension, ADD and ER, knee extended (or flexed), ankle and toes plantar flexed and ankle inverted |
what is D2 LE extension? |
|
|
ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL |
what are the ligaments of the knee? |
|
|
popliteus- unlocks flex. lateral/ext rotation |
what is the mechanism of screw home? |
|
|
hinge; bi axial |
what type of joint is the knee? |
|
|
wide pelvis, ante version, coxa vera, genu valgus, rotated tibia, IR of femur, pronation |
what are the causes of increased Q - angle? |
|
|
70-50/ flex to ext |
what is the peak torque of the quads? |
|
|
fixed resistance , greatest demand at 15 degrees |
what type of resistance will challenge the quads at end range rather than at mid range? |
|
|
help extend the knee via posterior pull on the tibia |
what do hamstrings do in a CKC? |
|
|
medial rotation- SGS ( sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus) |
what muscles attach to the Pes Anserine and how does it affect rotation? |
|
|
OA,RA, acute trauma, immobilization, effusion |
what are the common joint pathologies of the knee? |
|
|
distends the capsule and can cause reflex inhibition of the quads |
what does effusion do to the jt capsule? |
|
|
develops right away , is indicative of bleeding in the jt. swelling that takes more than 4 hours to develop is more often serous fluid |
what occurs with joint effusion? |
|
|
25 degrees of flexion |
what is the knee open packed position? |
|
|
pain with gait , WB -interfere with work, household and common activities |
what are the common functional limitations and disabilities of the knee? |
|
|
education, adaptations, soft tissue and joint mobs, quad setss |
what is the knee joint management protection phase? |
|
|
mobs , stretching, TherEx, WB, balance |
what is the knee jt management: controlled motion and return to function phases? |
|
|
from open packed position of 25 degrees, put the tibia in medial rot. and apply a posterior glide |
what is the knee flexion mob? |
|
|
from open packed position, put the tibia in external rotation, and apply anterior glide |
what is the knee ext. mob? |
|
|
mobilize patella - femoral and tibial jt |
what technique should be done prior to stretching the knee? |
|
|
repair of articular cartilage defects.used on smaller defects. protected WB 8-12 weeks (4 weeks for patella). prom , AArom, mm setting, ankle and hip OKC exercises |
what are knee microfxs used for? |
|
|
used for WB portions of bone , donor site, NWB. own tissue is used. adhere to WB precautions prescribed- longer than with microfx, may be in immobilizer for WB and night. |
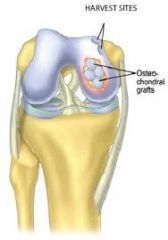
what is osteochondral autograft transplantation ? |
|
|
for defects 2-4cm full thickness defects two phases: harvest cells and grow them in lab. implant them via injection under periosteal patch.
may take 6-9 months for graft to become durable |
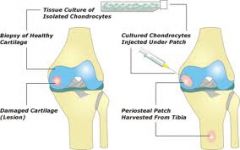
what is autologous chondrocyte implantation? |
|
|
for longer deficits > 4 cm2
cadaver -must be fresh, can not freeze or chondrocytes will die |
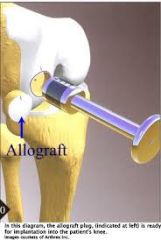
what is osteochondral allograft transplantation? |
|
|
seen mostly in RA. used to reduce pain. WBAT, immobilized 24-48 hours . full rom and independent ambulation in 10-14 days. full WB in 3-6 weeks- with AD |
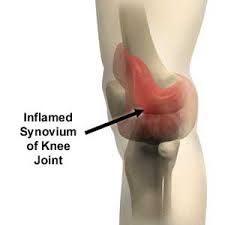
what are the management guidelines for synovectomy? |
|
|
cruciate ligaments retained and or excised. uni, bi, or tricompartmental replacement |
what is Total Knee Arthroplasty? |
|
|
-CPM: continous passive motion machine -WB -Ther EX -Quadriceps control is key- prevent deformity and DVT -ROM 1-4 weeks- flexion to 90 and ext to 0 -mobs : grades 1 and 2 initially , 3 and 4 to regain ROM, target tib- femoral and patella femoral -scar mobs -mm setting of quads, hamstrings, flute max, and ABD -mod protection weeks 4-8: goal ROM 0-110 degrees or higher, progress to ambulation with cane and then without device , progress quad and other LE functional control |
what is TKA post op management guidelines? |
|
|
when knee can be passively extended against gravity, but if released from assistance , pt cannot actively maintain terminal ext of the knee |
what is Quad lag or knee lag ext? |
|
|
do not allow AROM against gravity |
what should be prevented with quad lag present? |
|
|
1. girth measurements for swelling and atrophy 2. ROM and muscle recruitment / strength should be assessed 3.joint mobility and functional ability assessed 4.STM/MFR to decrease swelling , improve ROM, and normalize tissue 5. ROM and strenghtening exercises 6. Gait and balance training 7. General conditioning/ endurance exercises |
what are the steps taken by a therapist after a TKA? |
|
|
1.activities causing high impact stresses on the implant(high impact aerobics, high intensity jogging, skiing , powerlifting, rope jumping etc) 2. activities with potentially high risk of injury . 3. activities that may result in falling , which can result in a dislocation of the joint or fx of the bone surrounding the implant |
what are the do nots of TKA return to activity? |
|
|
restore functional ROM restore independent gait restore functional strength improve pt confidence educate in edema control instruct and educate in a HEP |
what are the goals of therapy? |
|
|
1. activities that produce lower stress levels on implant- walking , hiking, cross country skiing, horseback riding 2.driving-Rknee -typically 6 weeks , must have excellent control 3.if left-could drive once can sit comfortably behind the wheel and are off all medications that alter ability to operate machinery
|
what can a pt do with returning to activity after a TKA? |
|
|
30-60 degrees compression range |
what degree of motion should be avoided with patellofemoral dysfunction? |
|
|
-plica syndrome-overuse -fat pad syndrome- overuse -tendonitis- jumper knee -ITB syndrome- runners knee -housemaids knee; pre patellar bursitis -tight retinaculum - creates compression in groove -patella chondromalacia, PFS (patellafemoral syndrome) |
what are some related patellofemoral pathologies? |
|
|
most common cause of chronic knee pain. abnormal softening of the cartilage on the underside of the knee cap |
what is patella chrondromalacia? |
|
|
traction apophysitis of patellar ligament at attachment in tibial tuberosity. this happens in growing teens, causing excessive bone growth and acute repetitive trauma |
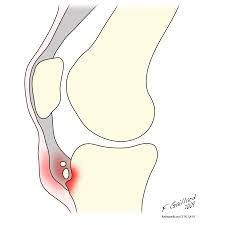
what is Osgood - schlatters disease? |
|
|
-lateral retinacular release -proximal realignment of the extensor mechanism - surgery above patellar log. -distal realignment of the extensor mechanism |
what are the patellofemoral and extensor mechanism postoperative guidelines? |
|
|
chronic pull of the knee cap laterally . this is a surgical procedure to re-align the patella |
what is lateral retinacular release? |
|
|
surgery on patellofemeoral jt, that is the articulation between the undersurface of the patella and front of the femur (trochlea groove), very common |
what is the distal realignment of the extensor mechanism? |
|
|
-ACL-most common(OKC 40-0, CKC 60-90) -PCL-posterior translation of patella on tibia -MCL- valgus translation -LCL- varus translation (least common)
unhappy triad- ACL, MCL, and meniscus |
what are the patella femoral mechanisms of injury ? |
|
|
grade 1: swelling, tenderness grade 2: swelling,pain on palpation, moderate tissue damage , lack of ROM grade 3: complete rupture , swelling, may not have pain |
what are the different sprain grades? |
|
|
patella tendon graft
semitendinosus graft |
what is the surgical approach to a knee ligamentous injury? |
|
|
twisting on a fixed tibia |
what are meniscal tear mechanisms of injury? |
|
|
locking into flexion, springy end feel, swelling |
what are the common meniscal tear impairments? |
|
|
pain with WB, knee buckling |
what are the common functional limitations and disabilities of meniscal tears? |
|
|
can manipulate to unlock the knee , reposition the meniscus . once reduces treat as acute jt lesion |
what is management of meniscal tears? |
|
|
for lesions in the outer third (vascular)
-PWB for 4-6 weeks with brace on until quad control is gained -full ROM by week 4 |
what are the meniscal repair guidelines ? |
|
|
for lesions in the inner third
-WBAT immediately, FWB by 4-7 days -full ext and flex to 90 by 10 days |
what are partial meniscectomy guidelines ? |
|
|
-SAQ. LAQ -quad sets -prone of table -ckc knee ext with band |
what exercises are needed to increase knee ext? |
|
|
-wall slides -scooting forward in chair -stool runs -ball rolls |
what exercises are needed to increase knee flex? |
|
|
talus , calcaneus |
what makes up the Hindfoot? |
|
|
navicular, cuboid, cuneiform |
what makes up the mid foot? |
|
|
metatarsal, phalanges |
what makes up the forefoot? |
|
|
sagital plane DF: 0-20 PF: 0-45 |
what are the DF/PF norms? |
|
|
frontal palne inv: 0-35 ever: 0-15 |
what are the INV/EVER norms? |
|
|
Pro: DF: EVER: ABD
Sup: PF: Inv: ADD |
what is Pro/ sup of the foot?
|
|
|
with supination, "lengthens " foot |
how is tibial ER achieved? |
|
|
with pronation " shortens leg" |
how is tibial IR achieved? |
|
|
high arch of foot |
what is Pes Cavis ? |
|
|
flat foot |
what is Pes Planus? |
|
|
10 degree PF |
what is ankle OPP? |
|
|
end range DF |
what is the ankle CPP? |
|
|
end range DF |
what is the CPP? |
|
|
loading response- DFs , foot moves into pronation
midstance- begin to supinate, eccentric PF
terminal stance- plantar flexors
swing- DFs |
what is the ankle / foot complex in gait? |
|
|
OA/DJD: 70 -80% of ankle OA is post traumatic
RA -forefoot early, hind foot later
gout, hallux valgus , post immobilization stiffness , claw toe, hammer toe |
what are the common jt pathologies and symptoms of the foot and ankle? |
|
|
microfxs of the periosteum from tibias post. overuse. caused by pronated/ flat feet with tight gastroc. |
what are shin splints? |
|
|
tight gastroc causing inflammation of the plantar fascia. may have a heel spur |
what is plantar fascia tis ? |
|
|
uric acid crystal build up during non WB. erosion of jt surfaces |
what is Gout ? |
|
|
DF: 5-10 PF: 20-25 |
what are the total ankle replacement arthroplasty expectations? |
|
|
DF: 0 degrees - where it is fused .all have bone grafts and internal fixation |
what is the ROM expectations of arthrodesis at the ankle and foot? |
|

|
what is a coxa valga? |
|

|
what is a coxa vara? |
|

|
what is a genu valgus? |
|

|
what is a genu varus? |
|

|
what is foot pronation and supination? |
|

|
what is foot inver/ ever? |
|
|
lurching gait |
what is a Glute max weakness? |
|
|
trendelinburg gait |
what is a flute med weakness? |
|
|
antalgic gait |
what is a pain at hip joint? |
|
|
foot slap gait |
what is weak DF? |
|
|
equinis gait |
what is a PF contracture or spasticity? |
|
|
genu recuvartum gait |
what is weak quads? |
|
|
hip hiking gait |
what is a hip flexor weakness |
|
|
hip flexor tightness test |
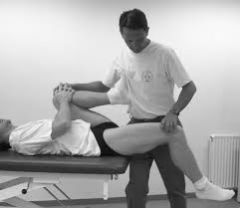
what is the Thomas test? |
|
|
ITB tightness |
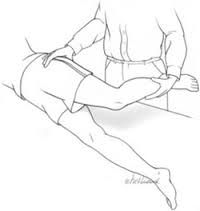
what is the obers test? |
|
|
rectus femoris tightness test |
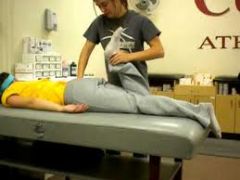
what is the elys test |
|
|
flexion,ABD, external rot tightness test |
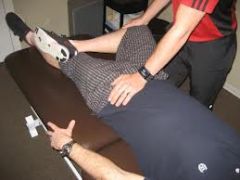
what is the Fabers Test? |

