![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
180 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most common "tumor" of the oral cavity; most likely representing a reactive hyperplasia |
fibroma |
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of a fibroma? Treatment? |
|
|
|
________ is a generic term for any tumor of the gingiva or alveolar mucosa |
Epulis |
|
|
Hyperplastic fibrous connective tissue associated with the flange of an ill-fitting denture |
Epulis Fissuratum |
|
|
Clinical presentation of epulis fissuratum |
|
|
|
Histological features of epulis fissuratum |
|
|
|
Reactive tissue growth that usually develops beneath a denture |
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia |
|
|
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia is related to: |
may also occur in dentate patients who are mouth breathers or who have highly arched palate |
|
|
Where does inflammatory papillary hyperplasia usually present? |
Hard palate |
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of inflammatory papillary hyperplasia? |
|
|
|
An exuberant tissue response to local irritation or trauma; smooth or lobulated mass that bleeds easily. May arise in pregnant women. |
pyogenic granuloma |
|
|
What 3 soft-tissue tumors exhibit psuedoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH)? |
|
|
|
List two histopathologic ft of inflammatory papillary hyperplasia? |
- PEH -may be associated with candida |
|
|
List two histopathologic ft of epulis fissuratum? |
- hyperplastic fibrous connective tissue - PEH |
|
|
Histology of fibroma |
nodular mass of fibrous CT (collagen) |
|
|
What are the "three P's"? |
|
|
|
clinical presentation of pyogenic granuloma |
-75% of lesions arise on the gingiva -most on the anterior facial maxillary gingiva -children and young adults (F) |
|
|
Histology of pyogenic granuloma |
-Highly vascularized granulation tissue -Surface ulceration |
|
|
What is the treatment for all 'three P's' ? |
excise and SRP adjacent teeth |
|
|
The soft-tissue counterpart of the central giant cell granuloma |
peripheral giant cell granuloma |
|
|
Clinical ft of peripheral giant cell granuloma |
- occurs only on the gingiva or edentulous alveolar ridge - more often in the mandible - mosty occurs in older women |
|
|
Radiographic findings assocaited with peripheral giant cell granuloma |
"cupping" resorption of the underlying alveolar bone
- radiolucency |
|
|
histological ft of peripheral giant cell granuloma |
-proliferation of multinucleated giant cells in a fibrous CT stroma -hemorrhage and hemosiderin -surface ulceration |
|
|
Which of the two 'three p's' occur on the maxillary gingiva of young women? |
pyogenic granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma
(pyogenic granuloma on gingiva 75% of time whereas POF is ALWAYS ONLY on gingiva) |
|
|
histologic ft of POF |
fibrous proliferation with mineralized cementum, bone, or dystrophic calcification |
|
|
benign tumor of fat; 50% occur in the buccal mucosa or buccal vestibule |
lipoma |
|
|
histology of lipoma |
mass of mature adipose tissue |
|
|
clinical ft. of lipoma |
- M = F - usually buccal mucosa/vestibule - lesions float in formalin - pt. usually over 40yo |
|
|
reactive proliferation of neural tissue after transection of a nerve |
traumatic neuroma |
|
|
traumatic neuromas are commonly found in the area of the ____, ____, and ____. A ___ to a ___ are painful. |
-area of the mental foramen -tongue -lip
a quarter to a third are painful |
|
|
occur as a radiolucency in posterior mandible |
1. traumatic neuroma 2. neuroliemoma 3. neurofibroma |
|
|
benign neural tumor of schwann cell origin (an encapsulated tumor) |
neuroliemoma |
|
|
Are neurofibromas encapsulated? |
No |
|
|
clinical ft. of neuroliemoma |
-asymptomatic -young adults -commonly found on tongue: macroglossia |
|
|
The two microscopic patterns of neuroliemoma include |
1. antoni A
2. antoni B |
|
|
most common peripheral nerve sheath neoplasm; composed of a mixture of schwann cells and perineural fibroblasts |
neurofibroma |
|
|
clinical ft. of neurofibroma |
-may be solitary or associated with neurofibromatosis -young adults -most common on tongue and buccal mucosa: macroglossia |
|
|
histology of the most common peripheral nerve sheath neoplasm |
(neurofibroma)
-interlacing bundles of spindle-shaped cells with wavy nuclei -delicate collagen fibers -axons are often present |
|
|
autosomal dominant; associated with chromosome 17 |
neurofibromatosis |
|
|
What are the 4 clinical ft of neurofibromatosis (Von Recklinghausen's disease of the skin) |
1. Crowe's sign : axillary freckling 2. Lisch nodules: brown spots on the iris 3. Cafe au lait pigmentation 4. Multiple neurofibromas |
|
|
Which soft-tissue tumor may transform into a neurofibrosarcoma/neurogenic sarcoma/malignant schawnnoma ? |
neurofibromatosis |
|
|
tumors or hyperplasias of neuroendocrine tissues; autosomal dominant (mutation of the RET protooncogene on chromosome 10) |
multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b |
|
|
clinical ft. of MEN2B |
-marfanoid body build -neuromas on the conjunctiva and oral mucosa -pheochromocytomas (50% of patients; secrete catecholamines leading to hypertension) -medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (90% of patients; increased calcitonin production) |
|
|
histology of MEN2B |
haphazard proliferation of nerve bundles within a fibrous CT stroma |
|
|
Lab findings of MEN2B |
-elevated serum or urinary calcitonin and urinary vanillymandelic (VMA) -increased epi and norepi ratios |
|
|
derived from schwann cells or neuroendocrine cells, common in the oral cavity (dorsal tongue) and on skin and presents with histologic PEH (pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplastia |
granular cell tumor |
|
|
What three soft-tissue tumors are associated with schwann cells? |
1. neuroliemoma* AKA schwannoma 2. neurofibroma 3. granular cell tumor |
|
|
histology of granular cell tumor |
-large polygonal cells with abundant granular, eosinophilic cytoplasm -cells are positive with an s-100 protein stain -pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH) in 50% of cases |
|
|
Which soft-tissue tumor might indicate prophylactic removal of the thyroid gland |
MEN2B |
|
|
Occurs exclusively on the maxillary (usually) alveolar ridge of newborn girls (90%) |
congenital epulis |
|
|
histology of congenital epulis |
-large, round cells with abundant, granular, eosinophilic cytoplasm -no PEH -cells DO NOT stain with s-100 protein |
|
|
most common tumor of infancy |
hemangioma |
|
|
What four soft tissue tumors is macroglossia a clinical ft of? |
1. neuroleimoma 2. neurofibroma 3. hemangioma 4. lymphangioma |
|
|
benign, hamartomoatous tumors of lymphatic vessels; most likely representing developmental malformations |
lymphangioma |
|
|
What is a hamartoma? |
proliferation of normal tissues in normal location |
|
|
Classic presentation of lyphangioma |
-baby (0-2yo) -anterior tongue; MACROGLOSSIA -pebbly surface/cluster of translucent vesicles
|
|
|
Histology of lymphangioma |
-lymphatic vessels containing proteinaceous fluid (bluish) and lymphocytes
-vessels located just beneath epithelial surface (thin overlying epithelium) |
|
|
recurrence is common for this soft-tissue tumor found on the anterior tongue of babies: |
lymphangioma |
|
|
soft tissue malignancy arising from endothelial cells associated with human herpesvirus 8 |
Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
What are the four clinical presentations of Kaposi's sarcoma? |
1. classic (chronic) 2. endemic 3. iatrogenic immunosuppresion-associated 4. AIDS-related |
|
|
Classic (chronic) presentation of Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
|
Endemic (african) presentation of Kaposi's sarcoma: |
|
|
|
Iatrogenic immunosuppresion-associated presentation of Kaposi's sarcoma: |
|
|
|
AIDS-related features of Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
|
Histology of Kaposi's sarcoma: |
3 stages: patch, plaque and nodular
-malignant spindle cell proliferation -slitlike vascular spaces (does not form true vesicles) from ENDOTHELIAL cells -extravasated erythrocytes -hemosiderin |
|
|
In what two soft-tissue tumors is hemosiderin a histological feature? |
1. peripheral giant cell granuloma 2. Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of metastases to oral soft tissue? Which oral metastasis are most common in men and women? |
Men: Lung > Kidney > melanoma
Women: Breast> Genital > lung > bone > kidney |
|
|
histology of metastases to oral soft tissue |
-resembles tumor of origin (well-differentiated) -most cases are carcinomas (epithelium-derived) -sarcomas are rare (mesenchyme-derived) -pleomorphism, atypical mitosis |
|
|
Benign proliferaiton of stratified squamous epithelium induced by HPV 6 & 11 (50% of cases) |
squamous papilloma |
|
|
Most common location for squamous papilloma |
tongue, lips, and soft palate |
|
|
Squamous papillomas may be difficult to distinguish from what? |
verruca vulgaris and condyloma acuminatum |
|
|
Clinical ft. of squamous papilloma |
if solitary: papilloma if multiple: verruca or condyloma
white, papillary projections (due to keratin acculumation) |
|
|
Histology of squamous papilloma |
-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium arranged in finger-like projections
-each projection had a fibrous CT core & blood supply |
|
|
Focal hyperplasia of stratified squamous epithelium associated with HPV 2,4,6, and 40 |
Verruca vulgaris |
|
|
Classic case of verruca vulgaris |
child
-skin of the hands, vermillion border, labial mucosa, anterior tongue |
|
|
Clinical presentation of verruca vulgaris |
contagious; often multiple papillary projections |
|
|
Histology of verruca vulgaris |
-numerous papillary projections covered by hyperkeratotic stratified squamous eptihelium (SSE)
-Rete ridges at ledge of lesion converge toward cetner
-Koliocytes (epi cell altered by HPV, perinuclear halo/clearing) |
|
|
Veneral wart associated with HPV types 2,6,11,53, 54
May also be associated with HPV 16 and 18 (high risk types) |
Condyloma acuminatum |
|
|
Clinical ft. of condyloma acuminatum |
-develops at a site of sexual contact or trauma (incubation time 1-3 months)
-autoinoculation common
-multiple, mucosal colored lesions (little or no keratin), not distinctly papillary
-clinically indistinguishable from Heck disease |
|
|
Histology of condyloma acuminatum |
-acanthotic (thickened spinous layer) of stratified squamous epithelium
-koilocytes |
|
|
Localized proliferation of SE associated with HPV types 13 and 32; first described in native americans and inuits |
Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia (Heck disease)
|
|
|
Focal epithelial hyperplasia most often presents in/on |
in children (or adults)
on labial, buccal and lingual mucosa |
|
|
Histology of Heck disease |
(focal epithelial hyperplasia)
-acanthosis -koilocytes -mistosoid cells |
|
|
Flat, brown, mucosal discoloration of unknown etiology |
Oral melatonic macule (oral freckle) |
|
|
Classical presentation of oral melatonic macule is in/on
|
in: 42 year old pt
on: vermillion of lower lip
|
|
|
Most common intraoral location of melatonic macule |
buccal mucosa |
|
|
Histology of oral melatonic macule |
-increase in melanin in basal and parabasal layers -melanin incontinence (leaches into CT) |
|
|
General term for congenital or developmental malformation of skin and mucosa |
Nevus |
|
|
Benign proliferation of nevus cells (neural crest in origin) |
acquired melanocytic nevus |
|
|
Acquired melanocytic nevus is more common on ____ than in _____. |
skin > oral mucosa |
|
|
Clinical ft of acquired melanocytic nevus both in skin and mouth |
skin: whites > asians & blacks
oral: 35 YO female on palate/gingiva typically arise on bone-supported mucosa
three stages in both 1) junctional: epi and rete pegs 2) compound: epi and CT components and 3) intradermal
|
|
|
Histology of acquired melanocytic nevi ? |
-unencapsulated -proliferation of nevus cells (melanocytes) -superficial nervus cells arranged in ruond aggregates (theques) in junctional stage -classified in accordance to stage of development |
|
|
Clinical term describing white plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease, color due to thickened surface keratin |
leukoplakia |
|
|
Leukoplakia is considered a ____- _________ lesion |
pre-malignant |
|
|
Causes of leukoplakia: |
- tobacco - alcohol - sanguinaria (herbal extract in toothpastes) - UV radiation - microorganisms |
|
|
in/on for leukoplakia ready, go: |
in: adult (40+) male
on: lip vermillion, buccal mucosa, and gingiva
lesions on the lateral, ventral tongue, lip vermillion, floor of the mouth and soft palate account for 90% of cases that show dysplasia or carcinoma!
|
|
|
Lesions on the ........&...........& .... & ..blah blah account for 90% of cases of leukoplakia that show dysplasia or carcinoma |
- lateral & ventral tongue - lip vermillion - floor of the mouth - soft palate |
|
|
The type of leukoplakia that occurs more commonly in WOMEN and is characterized by thin, thick (?) granular or nodular leukoplakia |
PVL : proliferative verrucous leukoplakia |
|
|
PVL is characterized by |
(proliferative verrucous leukoplakia)
-multiple keratotic plaques with roughened surface projections -spreads slowly and involves multiple oral sites -eventually develops into dysplasia, verrucous carcinoma and SCC |
|
|
histology of leukoplakia |
- hyperkeratosis or acanthosis - epithelial dysplasia - enlarged nuclei and nucleoli - increased nuclear cytoplasmic ratio - bulbous or teardrop-shaped rete pegs - loss of cellular polarity - blibbidy blah blah blah ...
|
|
|
which 5 epithelial pathologies exhibit histological acanthosis? |
-condyloma acuminatum -focal epithelial hyperplasia (heck disease)
-leukoplakia
-smokeless tobacco keratosis -nicotine stomatitis
|
|
|
which three epithelial pathologies include koilocytes as a histologic ft ? |
-verruca vulgaris -condyloma acuminatum -focal epithelial hyperplasia |
|
|
Red patch that cannot be diagnosed clinically as any other condition; less common that leukoplakia |
erythroplakia (erythroplasia) |
|
|
in/on for erythroplakia: |
in: elderly men (65-74 YO)
on: floor of mouth, tongue, soft palate |
|
|
histology of erythroplakia |
90-100% cases exhibit dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or SCC |
|
|
clinical presentation of smokeless tobacco keratosis |
- loss of gingival and periodontal tissues with gingival recession - keratosis (white, wrinkled appearance) - teeth staining - halitosis - caries |
|
|
histology of smokeless tobacco keratosis |
-hyperkeratosis and acanthosis -CHEVRONS (keratin layer forms peak) -amorphous eosinophilic (pink) material in CT -dysplasia is uncommon |
|
|
etiology of nicotine stomatitis |
uncommon mucosal change of hard palate as a result of cigar and pipe smoking (in response to heat generated from smoking) |
|
|
is nicotine stomatitis premalignant? |
no |
|
|
in/on for nicotine stomatitis |
in: middle aged men
on: hard palate |
|
|
classic presentation for nicotine stomatitis |
-dilated minor salivary glands (red dots) surrounded by keratosis (gray halo) |
|
|
premalignant alteration of lower lip vermillion as a result of long term sun exposure |
actinic chelitis |
|
|
in/on actinic cheilitis |
in: light complected middle-aged men
on: lower lip vermillion |
|
|
histology of actinic cheilitis |
-atrophic, thin SSE -varying degrees of epithelial dysplasia -basophilic degeneration of collagen |
|
|
what percent of actinic cheilitis develops into carcinoma? |
6-10%; tx with vermillionectomy |
|
|
94% of all oral malignancies are ____________ |
squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Oral cancer: if lesion is above labial commissures it's _____ _____ ___________, if below it's ________ ______ ____________. |
above: basal cell carcinoma
below: squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
in/on for squamous cell carcinoma ready, go: |
in: elderly male
on: pretty much errywhere
|
|
|
classic precursor lesions for SCC |
- leukoplakia - erythroplakia - erythroleukoplakia |
|
|
SCC on the lower lip is precursed by |
actinic cheilosis |
|
|
most common intraoral site for SCC? |
tongue (posterior lateral border); common site in young patients due to HPV |
|
|
second most common site for SCC? |
floor of mouth (occurs a decade earlier in females compared to males) due to leukoplakia or erythroplakia |
|
|
SCC on the gingiva is common in ... |
female non-smokers; often destroys underlying bone leading to tooth mobility |
|
|
represents a low-grade variant of SCC (1-10% oral carcinomas) |
verrucous carcinoma |
|
|
What's plummer-vinson disease? |
related to iron-deficiency; poses an increased risk of SCC of the esophagus, oropharynx and posterior mouth |
|
|
Syphilis is often implicated in SCC on the ______ _______ |
dorsal tongue |
|
|
Oncogenes involved in SCC include |
- ras - myc - cerbB |
|
|
Verrucous carcinoma in/on |
in: elderly men (smokeless tobacco users)
on: mandibular vestibule or buccal mucosa at site of tobacco placement |
|
|
Histology of verrucous carcinoma |
-rete pegs that push into underlying CT (BASEMENT MEMBRANE IS IN TACT)
-papillary or verriciform surface with hyperparakeratosis
-parakeratin plugging |
|
|
Most common skin cancer |
basal cell carcinoma |
|
|
Begin as a papule then ulcerate and undergo elevation and curling of the borders as lesion progresses |
basal cell carcinoma |
|
|
histology of basal cell carcinoma |
-islands and strands of basaloid cells located in CT
-palisading of cells at periphery of islands
-retraction artifact |
|
|
malignant neoplasm of melanocyte origin; acute sun exposure |
melanoma |
|
|
what are the four clinicopathologic types of melanoma? |
1. superficial spreading 2. nodular 3. lentigo maligna 4. acral lentiginous (most common oral form) |
|
|
the most common form of melanoma |
superficial spreading
|
|
|
the most common oral form of melanoma |
acral lentiginous |
|
|
oral melanoma most common in elderly men and presents on the .... |
hard palate or maxillary alveolus (fixed mucosa overlying bone which may be "moth-eaten") |
|
|
histology of melanoma |
- radial growth phase versus vertical growth phase
-atypical melanocytes in basal cell layer
-invasion of atypical melanocytes into underlying CT
-melanin may be seen in atypical melanocytes |
|
|
Not a cyst; rupture of salivary duct- mucin spillage |
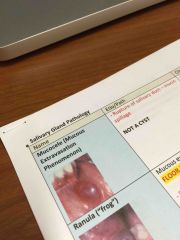
Mucocele |
|
|
Do Mucoceles have epithelial lining? |
No; they are not true cysts |
|
|
Histology of mucoceles |
|
|
|
Mucous extravasation reaction in the floor of the mouth |
Ranula |
|
|
Mucous extravasation reaction in the floor of the mouth |
Ranula |
|
|
Most common location of ranula |
Floor of mouth |
|
|
Characterized by blue, fluctuating swelling, elevation of the tongue |
Ranula |
|
|
Histology of ranula |
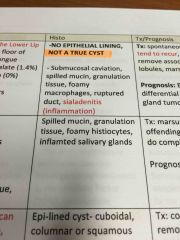
Back (Definition) -spilled mucin -granulation tissue -foamy histiocytes -inflamed salivary gland |
|
|
True epithelial lined cyst related to ductal dilation |
Salivary duct cyst |
|
|
True epithelial lined cyst related to ducal dilation |
Salivary duct cyst |
|
|
Histology of salivary duct cyst |
|
|
|
Calcification within salivary duct system; calcium salt deposition unrelated to calcium/phosphorus metabolism |
Sialolithiasis |
|
|
Calcification within salivary duct system; calcium salt deposition unrelated to calcium/phosphorus metabolism |
Sialolithiasis |
|
|
Salivary duct cysts most commonly occur |
In parotid gland(but can also occur in minor glands as well) |
|
|
Most common gland involved in Sialolithiasis |
Submandibular gland |
|
|
Histology of Sialolithiasis |

|
|
|
Autoimmune disease affecting salivary and lacrimal glands; associated with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus |
Sjogren's Syndrome |
|
|
Oncocytic epithelial cells -PINK CYTOPLASM due to mitochondria
Is a histo characteristic of what? |
Oncocytoma |
|
|
Parotid gland, rare, bilateral (pink cytoplasm in oncocytic epi cells) |
Oncocytoma |
|
|
Keratoconjunctivitis is associated with ... And characterized by... |

Sjögren's syndrome
|
|
|
Benign salivary gland neoplasm usually on upper lip; histo= epithelial cells look like they're in canals |
Canalicular adenoma |
|
|
Monomorphic adenoma (BCA) |
|
|
Malignant epithelial salivary gland tumor; second most common salivary gland tumor |
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|
|
Salivary gland tumor most common location, sex predilection and most frequent site of malignancy |

Parotid (most common) Females (6-7 decade) Malignant in sublingual gland |
|
|
Histology of mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|
|
|
Intraosseous; found in mandibular 3rd molar region |
Central mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|

Oncocytic epithelial cells -PINK CYTOPLASM due to mitochondria
Is a histo characteristic of what? |
Oncocytoma |
|
|
Most affected by Sjögren's syndrome |
Middle-aged women |
|
|
Encapsulated cystic lesion Papillary projections Oncocytic columnar cells Lymphoid stroma
Histo ft of... |
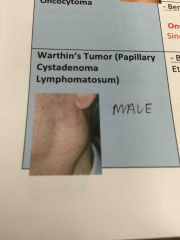
Warthin's tumor |
|
|
Acinic cell adenocarcinoma most frequently arise in --- gland. |
Parotid gland |
|
|
Zymogen granules and serous acinar differentiation |
Acinic cell adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Histology of adenoid cystic carcinoma |
|
|
|
List the 4 malignant salivary pathologies |
|
|
|
List the benign salivary pathologies |
|
|

Front (Term)
|
Central mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|
|
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is associated with ... And characterized by... |
Sjögren's syndrome
|
|
|
Causes of necrotizing sialometaplasia |
1.Ischemia (gland becomes necrotic due to ischemia and duct becomes metaplastic) 2.Trauma |
|
|
Necrotizing sialometaplasia occurs where 75% of the time? |
Palatal salivary glands |
|
|
Salivary pathology with histology that includes PEH |
Necrotizing sialometaplasia |
|
|
Histology of adenoid cystic carcinoma |

|
|
|
Benign glandular neoplasm occurring most commonly in the parotid gland or on palate and involving myoepithelial cell histology |
Pleomorphic adenoma |
|
|
Oncocytic adenocarcinoma |
Sinusoidal tract
(Variant of oncocytoma) |

