![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
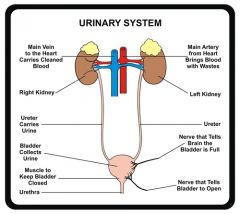
Function of Urinary system
|
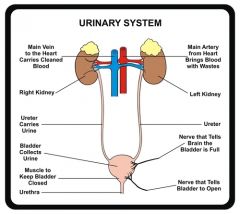
Produces and excretes urine.
|
|
|
Occurs when hydrostatic pressure forces water and small solutes across a membrane
|
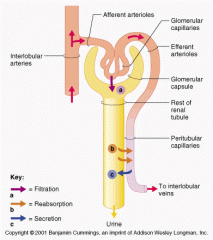
Filtration
|
|
|
The water and small solutes that are filtered (pushed through the membrane by hydrostatic pressure
|
Filtrate
|
|
|
The passage of substances across and epithelial layer into the blood or lymph
|
Absorption
|
|
|
Passage of a substance from a cell to extracellular fluid
|
Secretion
|
|
|
The condition in which the body's internal environment remains within normal physiological limits
|
Homeostasis
|
|
|
The elimination of wastes from the body
|
Excretion
|
|
|
The expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder
|
Micturition
|
|
|
Nitrogen-containing organic molecules other than proteins, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine |
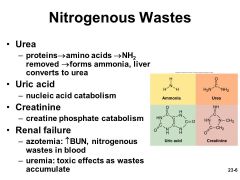
Nitrogenous Wastes |
|
|
Any substance not useful to the body
|
Waste
|
|
|
what is Hydronephrosis
|
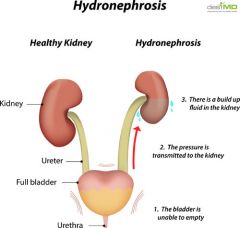
Urine backs up into kidney, increasing hydrostatic pressure, causing kidney damage
|
|
|
what is Renal Ptosis
|
Fallen kidney
|
|
|
Define: Afferent
|
Towards
|
|
|
Define: Efferent
|
Away from
|
|
|
Define: Peri
|
Around
|
|
|
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) |
|
|
what is the functional unit of the kidney
|
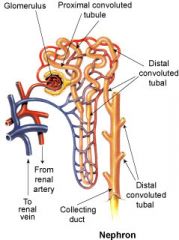
Nephron
|
|
|
Function of Nephron
|
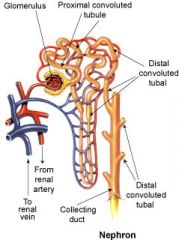
Filters blood and forms urine
|
|
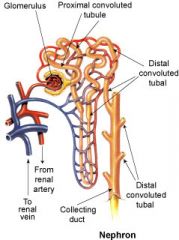
what are the main parts of a Nephron
|
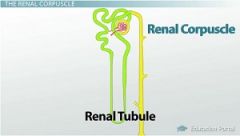
Renal Corpuscle, Renal Tubules
|
|
|
what makes up the Renal Corpuscle
|
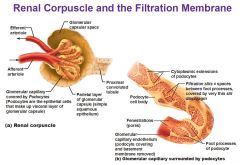
Glomerulus, Glomerular Capsule
|
|
|
what are the Renal Tubules |
Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Nephron Loop, Distal Convoluted Tubule |
|
|
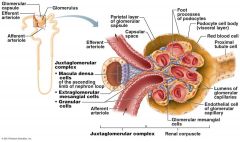
what does the Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC) consist of.
|
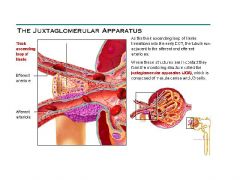
Granular Cells, Macula densa cells
|
|
|
What are Granular Cells
|
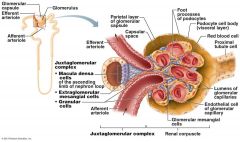
Modified smooth muscle cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole
|
|
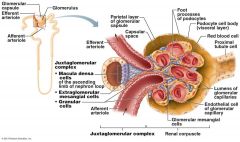
Function of Granular Cells |
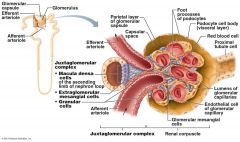
Monitor blood pressure, Secrete Renin |
|
|
What is Renin |
Enzyme involved in blood pressure homeostasis |
|
|
What are Macula densa cells |
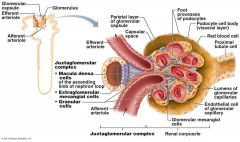
Modified epithelial cells lining the renal tubule that are columnar in shape and densely packed |
|
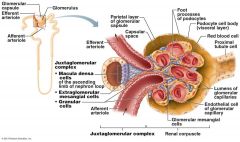
Function of Macula densa cells
|
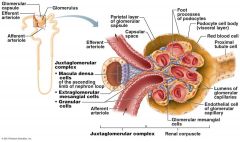
Monitor filtrate NaCi concentration,
Secrete Vasoconstrictor Chemicals |
|
|
Function of Vasoconstrictor Chemicals
|
Causes constriction of the afferent arteriole
|
|
|
What are the three layers of the Filtration Membrane |
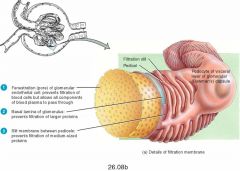
Capillary endothelium, Fused Basement Membrane, Slit diaphragm across filtration slits |
|
|
What are the three processes of urine formation |
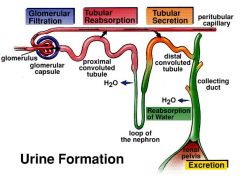
Glomerular, Tubular reabsorption, Tubular secretion |
|
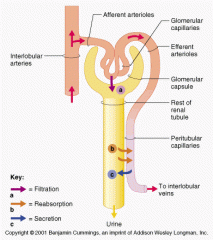
what are the four forces at work across the filtration membrane |
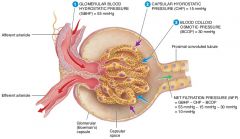
GBHP(glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure), GBOP(glomerular blood osmotic pressure), FHP(filtrate hydrostatic pressure), FOP(filtrate osmotic pressure) |
|
|
what is the average glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP)
|
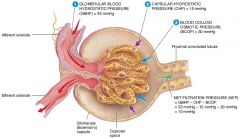
55mmHg
|
|
|
what is the average glomerular blood osmotic pressure (GBOP)
|
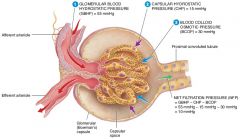
30mmHg
|
|
|
what is the average Filtrate Hydrostatic Pressure (FHP)
|
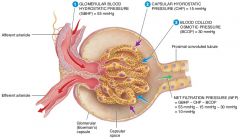
15mmHg
|
|
|
what is the average Filtrate Osmotic Pressure (FOP)
|
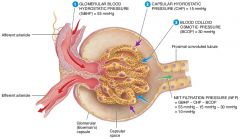
0mmHg
|
|
|
what are the forces that promote filtration |
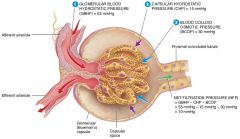
Glomerular Blood Hydrostatic Pressure(GBHP), Filtrate osmotic Pressure (FOP) |
|
|
what are the forces opposing filtration |
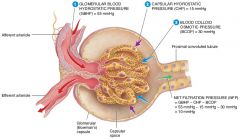
Glomerular Blood Osmotic Pressure(GBOP) , Filtrate Hydrostatic Pressure (FHP) |
|
|
what is Glomerular Filtration Rate
|
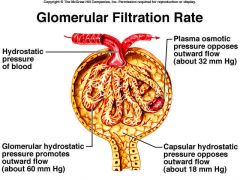
The amount of filtrate formed per minute by the kidneys
|
|
|
Define: Glomerulonephritis
|
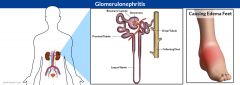
Autoimmune condition in which antibodies, produced in response to strep bacterial toxins, attack the filtration membrane
|
|
|
how is Glomerular filtration Rate(GFR) regulated |
Intrinsic Mechanisms, Extrinsic Mechanisms |
|
|
Function of Intrinsic Mechanisms |
Directly regulate Glomerular Filtration Rate(GFR) despite moderate changes in mean arterial blood pressure |
|
|
Function of Extrinsic Mechanisms |
Indirectly regulate glomerular filtration rate(GFR) by maintaining mean arterial pressure |
|
|
What is GFR |
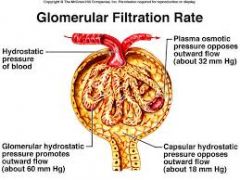
Glomerular Filtration Rate |
|
|
How much Glomerular Filtrate is produced each day
|
180 Liters
|
|
|
How much urine is excreted every day |
1-2 Liters |
|
|
How much Filtrate is reabsorbed each day
|
99%
|
|
|
Where does most reabsorption occur |
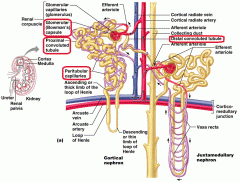
Proximal Convaluted Tubule (PCT) |
|
|
what is Glucosuria
|
Sugar in urine
|
|
|
function of Insolin
|
promotes movement of glucose out of blood and into tissue cells
|
|
|
Function of Tubular Secretion
|
Excretes unfiltered drugs, such as penicillin and phenobarbital
Excretes reabsorbed wastes, such as urea When blood pH is too low, tubular secretion maintains blood acid base balance by moving the excess H+ into the blood to the filtrate to be excreted in the urine |
|
|
what is the fluid exiting the nephrons called?
|
Urine
|
|
|
Trace a drop of urine from the Nephron to the external environment
|
Nephron, Collecting Ducts, Papillary ducts, Minor Calyx, Major Calyx, Renal Pelvis, Uriter, Urinary Bladder, Urethra
|
|
|
List histology of Urinary Bladder from deep to superficial
|
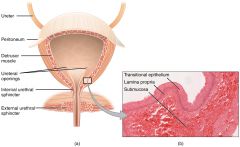
Mucosa, Detrusor Muscle, Adventitia
|
|
|
Microscopic folds in Urinary Bladder
|
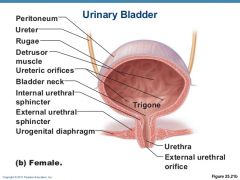
Rugae
|
|
|
what allows distention of the Urinary Bladder
|
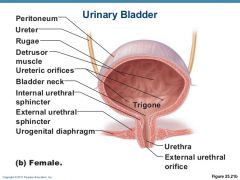
Rugae, Transitional Epithelium, Lamina Propria
|
|
|
what kind of muscle is the Detrusor Muscle
|
Smooth Muscle
|
|
|
What is the Urinary Bladder Adventitia
|
Connective Tissue Layer that connects with the connective tissues of surrounding structures to anchor the bladder
|
|
|
Why are females more prone to Bladder Infections than males
|
Because the female Urethra is shorter
|
|
|
what are the two hormones that regulate Urine production
|
Antidiuretic Hormone(ADH), Aldosterone
|
|
|
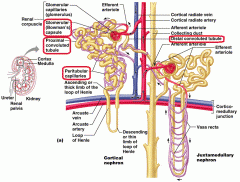
what vessel directly feeds into the Glomerulus
|
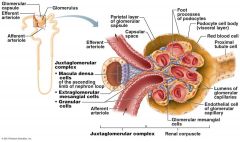
Afferent Arteriole
|
|
|
The fluid in the Glomerular Capsule is similar to plasma except that is does not contain a significant amount of ............?
|
Plasma Protein
|
|
|
what is the salt level monitoring part of the Nephron
|
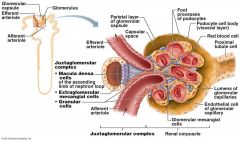
Macula Densa
|
|
|
True or False. Angiotensin 2 is the substance made by the body to lower blood pressure during stress
|
False
|
|
|
where is filtrate produced in the Nephron
|
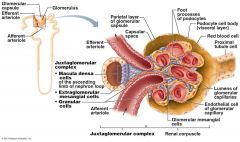
Glomerulus
|
|
|
what is the function and structural unit of the kidney
|
Nephron
|
|
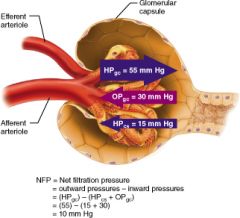
Calculate the net filtration pressure if blood pressure in the glomerulus is unusually high, around 68mmHG
|
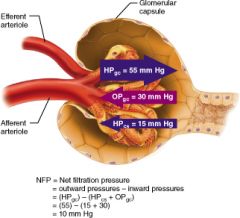
68-(15+30)=23mmHg
|
|
|
Function of Angiotensin2
|
Constrict arterioles and increase blood pressure
|
|
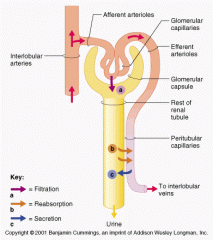
chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood across the filtration membrane
|
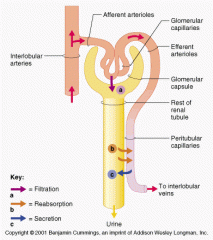
Glomerular Hydrostatic pressure(GHP)
|
|
Direct function of Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
|
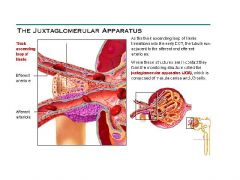
Help regulate blood pressure and the rate of blood filtration by kidneys
|
|
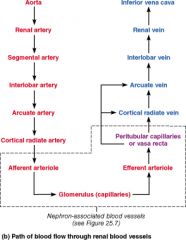
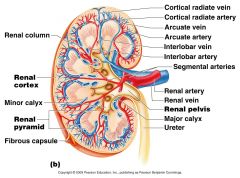
What arteries branch off the arcuate arteries?
|
Cortical Radiate (interlobular) Arteries
|
|
|
What type of capillaries make up the glomerulus?
|
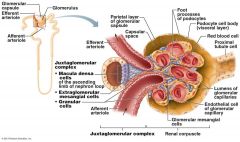
Fenestrated
|
|
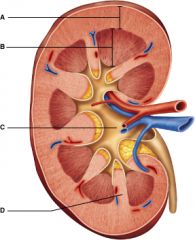
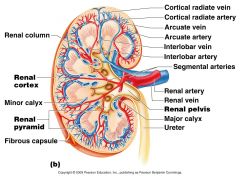
Which letter represents the most superficial region of the kidney?
|
A
|
|
|
True or False. The proximal convoluted tubule is the portion of the nephron that attaches to the collecting duct.
|
False
|
|
|
Which cells of the kidney are chemoreceptors that respond to changes in solute content of the filtrate?
|
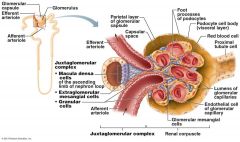
Macula densa cells
|
|
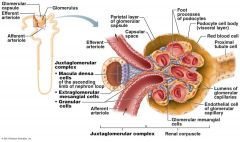
what makes the Glomerulus different from other Capillaries in the body
|
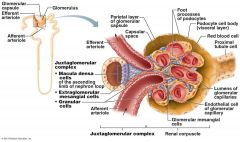
It is drained by an Efferent Arteriole
|
|
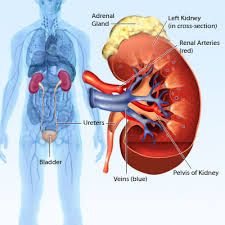
Why is the fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys importat
|
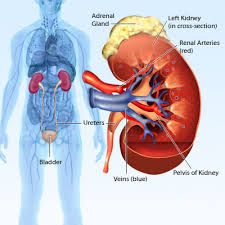
it stabilizes the position of the kidneys
|
|
|
What artery lies on the boundary of the Cortex and the medulla of the kidney
|
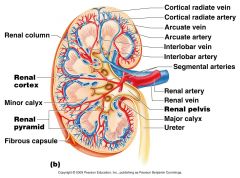
Arcuate Artery
|
|
|
True or False. Aldosterone is a hormone that causes the renal tubules to reclaim sodium ions from the filtrate.
|
True
|
|
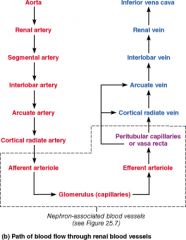
Which vessel is present in the arterial pathway as blood flows into the kidney but NOT present in the venous pathway exiting the kidney?
|
Segmental
|
|
|
True or False. The macula densa cells are chemoreceptors that respond to changes in the urea content of the filtrate.
|
False
|
|
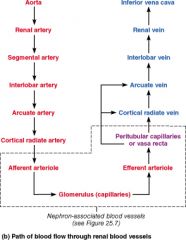
Which vessels supply the cortical tissue of the kidney with blood?
|
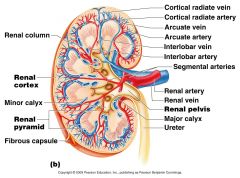
Cortical Radiate Arteries
|
|
|
Blood supply that directly receives substances from the tubular cells
|
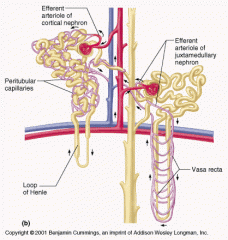
Peritubular Capillaries
|
|
|
True or False. Glomerular filtration is an ATP-driven process.
|
False
|

