![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 Divisions of the ear |
External, Middle and Internal ear |
|
|
Collects vibration; thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by skin |
Auricle / Pinna |
|
|
What supplies the auricle? |
Facial nerve (Extrinsic and intrinsic muscles) |
|
|
Curved tube from auricle and conducts sound waves |
External auditory meatus |
|
|
These are modified sweat gland that secrete yellowish brown wax |
Ceruminous glands |
|
|
Sensory innervatiob of ext. Auditory meatus |
Auricolotemporal n. Auricular branch of vagus n. |
|
|
Lymph drainage of external auditory meatus |
Supeficial parotid, mastoid, superficial lymph nodes |
|
|
What is the other name for middle ear? |
Tympanic Cavity |
|
|
Air-containing cavity in petrous part of temporal bone |
Tympanic cavity |
|
|
What are the 3 auditory ossicles? (Anterior to posterior) |
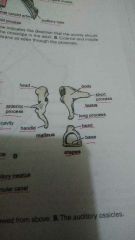
Hammer (Malleus) Anvil (Incus) Stirrup ( Stapes) |
|
|
Transmits vibrations of tyMoanic membrane towards the perilymph of internal ear |
Auditory ossicles |
|
|
Auditory ossicles communication with front |
Auditory tube via nasopharynx |
|
|
Auditory ossicle communication with back |
Mastoid antrum |
|
|
Roof of the ear; separates tyMoanic cavity from meninges and temp. lobe of brain in middle cranial fossa |
Tegmen tympani |
|
|
Separates tympanic cavity from internal carotid |
Floor of the tympanic cavity |
|
|
Rounded projection on greater part; underlying 1st turn of concha |
Promontory |
|
|
Thin, fibrous, pearly gray membrane |
Tympanic membrane or eardrum |
|
|
Innervation for tympanic membrane |
Auriculo temporal nerve+auricular branch of vagus |
|
|
Groove in bone where tympani membrane circumference is slotted |
Tympanic Sulcus |
|
|
Small triangular area bounded by folds found in the tymoanic membrane |
Pars flaccida |
|
|
Incus posses large body and 2 processes. Enumerate. |
Body of incus *rounded + articulates w/ the head of malleus
Long process *descends behind & parallel to malleus *lower end bends medially and articulates with the head of stapes Short process *projects backward & attached to posterior wall of tympanic cavity |
|
|
2 muscles of middle ear |
Tensor tympani Stapedius |
|
|
Dampens down vibration of tympanic membrane |
Tensor tympani |
|
|
Dampens down vibration of stapes |
Stapedius |
|
|
True or False. Motion is communicated to perilymph in scala vestibuli |
True |
|
|
What connects the ant wall of tympanic cavity and nasal pharynx? It equalizes air pressure in tympanic cavity |
Auditory tube |
|
|
When do mastoid air cells begin to develop |
2nd year of life |
|
|
Where does Tympanic nerve arise? |
From glossopharyngeal nerve below jugular foramen |
|
|
Forms from branches and supplies lining of middle ear |
Tympanic plexus |
|
|
This division of the ear can be found in the petrous temporal bone, medial to middle ear |
Internal ear/Labyrinth |
|
|
Cavities in dense bone; lined by endosteum and contains perilymph |
Bony labyrinth |
|
|
Central, posterior to cochlea and anterior to senicircular canalsl |
Vestibule |
|
|
Open into posterior vestibule |
Semicircular canals |
|
|
Swelling at the end of canal in semicircular canals. |
Ampulla |
|
|
Snail shell and open into anterior vestibule |
Cochlea |
|
|
At right angles to each other |
Semiciurcular ducts |
|
|
Triangular. Connected to saccule via ductus reunins |
Ducts of cochlea |
|
|
Recurrent dizziness |
Miniere's syndrome |
|
|
Usually caused by untreated actute otitis media (middle ear imfection) |
Mastoiditis |
|
|
A group of inflammatory diseases in the middle ear |
Otitis media |
|
|
Tube connected with the nasopharynx |
Eustachean tube |

