![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Merocrine glands |
Secrete their products by exocytocis as they produce |
|
|
Holocrine glands |
Secretory cells accumulate their products within them until they rupture "dies for their cause" |
|
|
Apocrine glands |
Accumulate their products but in this case only just beneath the free surface |
|
|
Simple cuboidal function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
Stratified squamous |
Protect from wear and tear |
|
|
Simple squamous |
Filtration and diffusion |
|
|
Simple columnar |
Digestive tract lining absorption and secretion |
|
|
Unicellular glands |
Mucous cells and goblet cells |
|
|
Simple cuboidal |
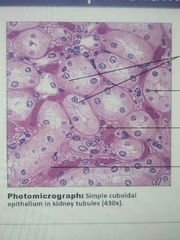
Secretion and absorption located in kidney tubules |
|
|
Simple squamous |

Diffusion&filtration location air sacs of lungs,lining of heart,blood vessels |
|
|
Simple columnar |
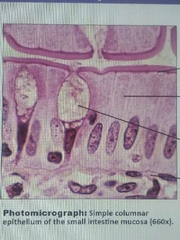
Absorption;secretion of mucus,enzymes location digestive tract,uterine tubes |
|

Secretes mucus;propulsion of mucus by ciliary action |
Simple pseudostratified columnar |
|
|
Stratified squamous |
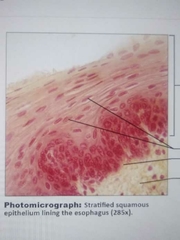
Protects underlying tissue 1.non keratinized (moist)linings esophagus mouth and vagina 2.keratinized epidermis of skin(dry) |
|
|
Stratified cuboidal |
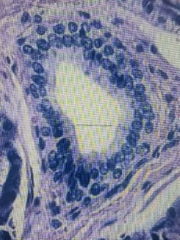
(RARE)Functions in secretion,protection,excretion |
|
|
Exocrine ducts |
Secrete products into ducts |
|
|
Endocrine glands |
Secrete products into tissue fluid or blood |
|
|
Unicellular exocrine gland |
Mucous & goblet cells..found in epithelial linings of intestinal and respiratory tracts |
|
|
Tissue repair steps |
Inflammation,blood clotting, organization,regeneration |
|
|
Mast cells roe (tissue repair) |
Release. Inflammatory chemicals |
|
|
Transitional epithelium |
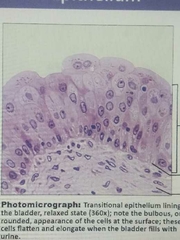
Stretch ready location lines the the ureters, bladder anf part of urethra |
|
|
Dermis is primarily composed of whatbtissue type |
Dense irregular ct |
|
|
Primary tissue type for papillary dermis |
Areolar CT |
|
|
Primary cell type of the epidermis |
Keratinocytes |
|
|
Cell types found in the dermis |
Fibroblasts.macrophages.mast cells.wbc |
|
|
A blister is a fluid fillled pocket that separates the |
Epidermis and the dermis |
|
|
Which region tends to accumulate carotene |
Stratum corneum and subcutaneous tissue |
|
|
Gland abundant on the palms soles and forehead |
Eccrine sweat glands |
|
|
Bone cells |
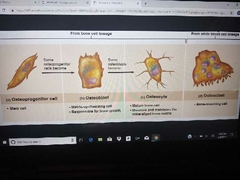
|
|
|
Major ECF cation |
Sodium |
|
|
Most abundant negative electrolyte in ecf |
Chloride |
|
|
Tissue repair |
1.inflammation-dilated vessels and clotting begins2.restores blood supply-blood clot replaced with granulation Tissue 3.regenration and fibrosis_the scab detaches |

