![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
229 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Difference in length b/w geodetic and plane survey |
10 cm in 18.2 km |
|
|
|
As per American surveyors geodetic survey require if |
Area more than 100sq mile (260km2) |
|
|
|
Principle of surveying |
Work whole to part Fix new station |
|
|
|
RF |
Representative factor = ( drawing length /actual length) |
|
|
|
Plane scale |
Only two dimensions |
|
|
|
Diagonal scale |
3 dimensions |
|
|
|
Comparative scale |
Common representive factor |
Measurements can be directly taken from map |
|
|
Shrinkage factor |
The ratio of shrunk length to true length SF < 1 |
|
|
|
Scale of chords |
Used to measure angles |
|
|
|
1 engineers chain |
100ft |
|
|
|
Metric chain length & links |
20m -100 links , 30m -150 links |
|
|
|
Length of one link in chain |
20c.m |
|
|
|
Permissible error in 20m chain &30m chain |
5mm &8mm |
Metric chains |
|
|
EDMs in survey? |
Electronic Distance Measuring equipment |
|
|
|
Trailetaration |
Process of measuring sides of a triangle with the help of EDMs |
|
|
|
Instruments which measure Vertical distance and angle? |
Theodolite , sextant , total station, Tacheometer |
|
|
|
Shrunk scale = |
Original scale x SF |
|
|
|
Corrected distance , area using SF |
CD=MD / SF CA=MA / SF^2 |
|
|
|
Error due to wrong scale |
CD=MD x (RF of WS / RF CS) CA=MA x (RF of WS / RF CS)^2 |
|
|
|
Baseline? |
Longest line laid through middle of the field in chain survey |
|
|
|
Offsets |
Lateral distance measured from base line |
|
|
|
Standard temperature and allowable pull in chain |
20deg , 8 kg |
|
|
|
Type of chains and length(4 types) |
Metric chain 20m &30m Gunters chain 66ft , 100 links ( surveyors chain) Revenue chain 33 ft ,16 links Engineers chain 100ft 100 links |
|
|
|
Invar tapes are made from |
Nickel 36% Steel 64% |
|
|
|
Cross staff type (3 types) |
Open type 90° French type 45° & 90° Adjustable 15° intervals |
|
|
|
Error due to incorrect chaining corrected length , A & V |
L' =L(1+e), A' =A(1+2e) V' =V(1+3e) |
|
|
|
Hypotenuse allowawance in chain survey |
chain length x Sec theta-1 |
|
|
|
Correction for slope (Tape correction) |
Ca =(L -squrt(L^2 -h^2)=h^2 /2L Always negative |
|
|
|
Correction for miss alignment |
Cma =( d^2 /2 L 1 )+ ( d^2 /2 L 2 ) Always negative |
|
|
|
Correction for temperature |
Ct = Lx alpha x (Tm-To) Ct is +ve if Tm > To Ct is -ve if Tm < To |
|
|
|
Correction for pull |

|
|
|
|
Sag correction formula. |
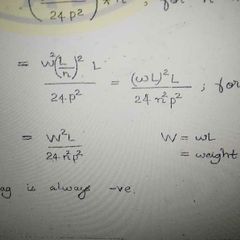
|

|
|
|
Correction for sag if supports at different level |
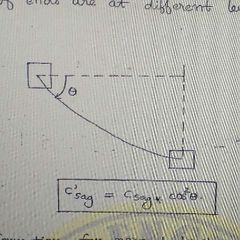
|
|
|
|
Correction for normal tension |

|
|
|
|
Correction for MSL |
Cmsl =Lh/R R=6370km C -ve if obj above MSL C +ve if obj below MSL |
|
|
|
Obstacle to chaining but not ranging |
Pond , river |
|
|
|
True meridian? |
Point of a grade circle passing through the geographical north and south pole of earth surface |
|
|
|
Magnetic meridian? |
It is the direction shown by a magnetic north when it is freely suspended |
|
|
|
Systems of bearing. |
Whole circle bearing(Azimuthal system) Quadrantal (or) Reduced Bearing system |
|
|
|
Back bearing and Fore bearing relation |
BB = FB (+ or -)180 |
|
|
|
Prismatic compass & surveyors compass difference. |
P.C - Whole circle bearing system SC- QB system followed |
|
|
|
Temporary adjustment of compass suvey includes |
Centering , levelling & focusing the prism |
|
|
|
Magnetic declination |
Horizontal angle between True meridian and magnetic meridian |
|
|
|
Isogonic lines |
Line joining point of same declination. |
|
|
|
Agonic lines |
Line joining point of zero declination |
|
|
|
Dip? |
Vertical inclination of magnetic needle with horizontal plane . Zero at the equator 90 at S& N magnetic poles |
|
|
|
Plane table survey is suitable for |
1, Traverse surveying ( plotting and measurements can be done simultaneously) 2. Can be used for areas which are affected by local attraction. |
|
|
|
Temporary adjustment of plane table |
Fixing , Levelling , centering & orientation. |
|
|
|
Method of plane Tabling |
Radiation method Intersection method Traversing Resection |
|
|
|
Temporary adjustment in compass survey |
Centering, levelling & focusing the prism |
|
|
|
Station ? |
Location of levelling staff |
|
|
|
Height of instrument? |
Reduced level of line of sight. |
|
|
|
Line of sight |
It is imaginary line passing through the centre of objective and intersection of cross hairs |
|
|
|
Check for HI method |
Sum of (BS )- sum of (FS) = Last RL - First RL |
|
|
|
Rise and fall method check |
Sum of (BS) - sum of (FS) = Sum of ( Rise ) - sum of (Fall) Superior method because it varifies IS |
|
|
|
Error due to line of collimation |
y = D x tan (alpha) |
|
|
|
Correction for curvature ( - ve) |
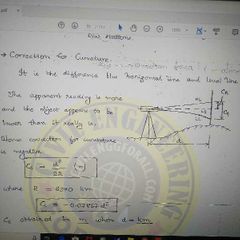
|
|
|
|
Correction for refration (+ve) |
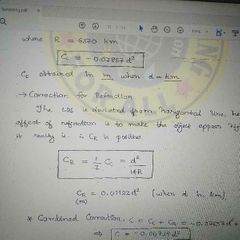
|
|
|
|
Combined correction |
C= Cc + CR = - .06735d^2 |
|
|
|
Distance to visible Horizon |

|
|
|
|
Profile levelling. |
Profile levelling is used to locate the centre line of path. |
|
|
|
Reciprocal Levelling.Diifference in level between two points. |
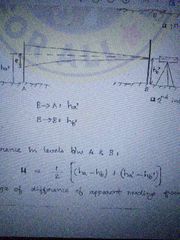
|
|
|
|
Total error in reciprocal levelling |

|
|
|
|
Sensitivity of bubble tube |

|
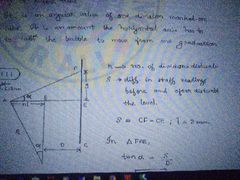
|
|
|
Contour lines |
Imaginary line passing through points of same elevation. |
|
|
|
Contour interval |
RL difference between two adjacent contours .it is constant for a map |
|
|
|
Contour interval and scale relation. |
Inversely proportional |
|
|
|
Horizontal equivalent in contour. |
Horizontal distance between any two points on two consecutive contour. |
|
|
|
Contour Gradient (CG) |
It is a line laying on ground surface and maintain a constant inclination to horizontal surface. CG =( contour interval/ Horizontal equivalent ) |
|
|
|
Grade contours. |
Lines having equal Gradient along slope |
|
|
|
1 hectare |
10, 000 m^2 |
|
|
|
1 Acre = |
4046.7 m^2 |
|
|
|
Mid ordinate method. |

|
|
|
|
Average ordinate method |

|
|
|
|
Trapezoidal Rule |

|
|
|
|
Simpson's Rule |
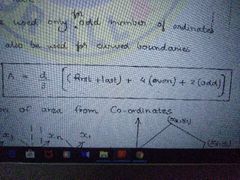
|
|
|
|
Latitude of a line |
L x cos theta |
|
|
|
Departure |
L x sin theta |
|
|
|
Abney level usage? |
It is used for measurement of difference in level and tracing contour. |
|
|
|
Abney clinometer |
It is used for measurement of slopes and setting grades. |
|
|
|
Tangential clinometer |
To find RL difference by measuring through inclined line of sight. |
|
|
|
Ceylon Ghat tracer |
It is used for measuring slopes and especially setting grades. |
|
|
|
Pantagraph |
It is used for reproducing , enlarging & reducing the maps |
|
|
|
Sextant |
Used for measurement of horizontal and vertical angles. |
|
|
|
Mining Dial |
It is the combination of theodolite and prismatic compass and used for mining survey. |
|
|
|
Planimeter |
Used for measurement of area on the plan. |
|
|
|
Stream gauge |
Used to measure discharge of stream |
|
|
|
Telleurometer |
It is a microwave EDM used for linear measurement. |
|
|
|
Heliograph |
It is used as a sun signal in triangulation survey. |
|
|
|
Fathometer |
Used to measure the depth of ocean. |
|
|
|
Altimeter |
Height measuring equipment. |
|
|
|
Tide gauge |
To determine water level and it's variation. |
|
|
|
Distomat |
EDM used for accurate linear measurement |
|
|
|
Britons compass |
Combination of prismatic compass and clinometer used for measurement of bearing and vertical angle. |
|
|
|
Eideo graph |
Improved version of pantagraph |
|
|
|
Theodolite usage |
Used for measurement of horizontal and vertical angle directly |
|
|
|
Transiting / plunging / Reversing |
It is the process of rotating the telescope in a vertical plane about horizontal axis. |
|
|
|
Size of a theodolite. |
Size of theodolite is the dia. of main horizontal graduated circle.Generally 80 mm to 120 mm |
|
|
|
Temporary adjustment of theodolite. |
Setting Centering Levelling Elimination of parallax |
|
|
|
Sign convention of Latitude and departure. |
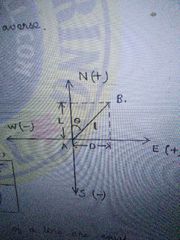
|
|
|
|
For a closed travers L & D condition |
Sum of L = 0 Sum of D =0 |
|
|
|
permanaent adjust ment of theodolite |
Plate level test- To make the plate bubble centre to their run. Cross hair ring test -To make the vertical cross hair lie in a plane perpendicular to horizontal axis Azimuth test- To make LOS per to horizontal axis. Spire test - To make horizontal axis per Vertical axis |
|
|
|
Closing error |

|
|
|
|
Angle of mis closure |

|
|
|
|
Fixed stadia method k value and beta value. |
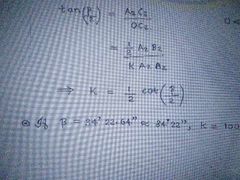
|
|
|
|
Tacheometer distance formula with LOS horizontal |
D=ks + c K- multiplicative const.=f/i S- staff intercept C- additive const= f+d f - focal length d-distace b/w optical centre and centre of instrument. |

|
|
|
Distance and elevation formula - LOS inclined and staff vertical |
D= KS cos^2 @+ C cos @ V= (KS/2) sin 2 @ + C sin@ |

|
|
|
D & V when staff held normal to LOS |
D= (KS + C) cos @ + r sin @ V= (KS + C) sin @ |
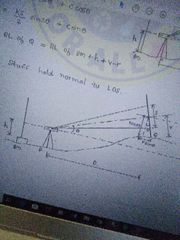
|
|
|
Movable hair method |
D= (k/m ) S + C i = mp P- pitch of micrometre screw m - no of rotations |
|
|
|
Omni meter |
It is a special Tacheometer invented by Eckhold and used for tangential method of tacheometry. |
|
|
|
For 30m arc , Radius equals. |

|
|
|
|
Setting out a curve offset from long chord |

|
|
|
|
Setting out a curve perpendicular offset from tangent |
O1 =( x^2 / 2R) |
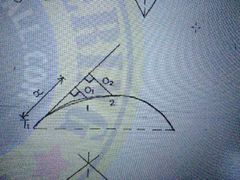
|
|
|
Setting out a curve - off sets from chords produced |
On = (Cn / 2R) x (Cn-1 + Cn) |

|
|
|
Setting out a curve- Rankin's method of deflection angles or method of tangential angles |

|
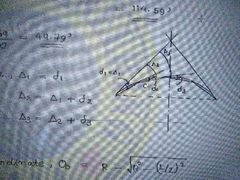
|
|
|
Best suited vertical curves. |
Parabola or circular arc |
|
|
|
Length of vertical curve |
L=( g1-g2)/r r-Rate of change of grade |
|
|
|
Heights are found by temp diff. |
Hypsometry |
|
|
|
Yard to cm |
1 yard =91.44cm |
|
|
|
Inch to foot |
12 inch = 1 foot |
|
|
|
Feet to yard |
3 feet = 1 yard |
|
|
|
Pole to gunters chain Gunters chain to furlong Furlong to mile |
4 pole - 1 Gunters chain 10 Gunters chain- 1 furlong 8 furlong- 1 mile |
|
|
|
Cent to m2 Are to m2 |
1 cent -40.42 m2 1 are -100m2 |
|
|
|
1 pacing approx .? Allowable error? |
1 pacing -80cm Allowable error - (1/100) |
|
|
|
Passometer and pedometer |
Passometer- it will count the number of steps and we have to calculate the distance. Pedometer- Directly gives the distance ( No of steps x pace length) |
|
|
|
Odometer |
It is fitted on the wheel of a slow moving vehicle and gives the number of cycles the wheel rotates |
|
|
|
Perambulator |
Improved version of odometer , it will directly show the distance |
|
|
|
Ranging? |
It is the operation of establishing instrument points between two terminal stations. |
|
|
|
For direct and indirect ranging minimum ranging rods required? |
Direct -3 nos Indirect -4nos |
|
|
|
Accuracy of chainings 4 conditions |

|
|
|
|
Chaining on a slopping ground 2 methods
|
1, Direct method or stepping method (crude method) 2,Indirect method |
|
|
|
Slope correction using height diff |
Slope correction=- h2 /2L |
|
|
|
Relation of cumulative error and compensatary error with chain length |

|
|
|
|
Use of tie line |
To avoid long offsets Also serves as a check line |
|
|
|
Long offsets |
Length greater than 15m |
|
|
|
Error due to miss alignment |
D2/2L |
|
|
|
Field book size |
20 x 12 cm |
|
|
|
Open cross staff |
Height 1.2 to 1.5 Used to set 90deg |
|
|
|
French cross staff |
Octagonal prism Used to set 45 & 90 deg |
|
|
|
Optical square |
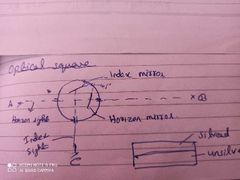
Used to measure 90deg. Angle b/w hor. Sight and hor. mirror-120deg.. Angle b/w index sight and mirror-105 |
|
|
|
For area measurement error in angles |
1'' for 195.5km2 |
|
|
|
Error due to incorrect ranging |

|
|
|
|
Principle of optical square |
Reflection or double refraction |
|
|
|
Least count for microptic theodolite and vernier theodolite |
Micro-1" and vernier -20" |
|
|
|
Transit theodolite.Trunion axis & azimuth |
With telescope that can rotate in a vertical plane about horizontal axis Horizontal axis -Trunion axis Vertical axis- azimuth |
|
|
|
Size of theodolite means |
Diameter of lower plate |
|
|
|
Lower and upperclampong screws attached to? |
Lower clamp screw or lower plate -outer axis Upper clamp screw or vernier or upper plate -inner axis |
|
|
|
Face right and face left observationa |
Vernier scale is right of the observor. |
|
|
|
Transiting ? Swinging |
Swinging- Rotating telescope in horizontal plane about vertical axis. Transiting-Rotating telescope in a vertical plane about horizontal axis. |
|
|
|
Telescope normal condition and telescope direct condition |
Telescope normal-Face left and bubble up condition Telescope direct-Face right and bubble down condition. |
|
|
|
External focusing telescope |
Object lens moves and focus the object |
|
|
|
Internal focusing telescope |
An additional double concave lens provided for focussing |
|
|
|
Stadia diaphram |
Diaphram with 3 horizontal cross hairs |
|
|
|
Line of collimation and axis of telescope |
Line of collimation - Line joining centre of cross hairs and optical centre and it's prolongation. Axis of telescope - Line joining eyepiece centre and optic centre |
|
|
|
Collimation error. |
When bubble is centre but pine of collimation is not parallel to bubble axis |
|
|
|
Spherical abration |
Due to excess sphericity Image formed in multiple points Not a serious defect |
|
|
|
Chromatic abration |
Dispersion of white light It is a serious issue Chromatic lenses ( compound lens - covex+ concave ) used to avoid this |
|
|
|
Objective lens properties |

|
|
|
|
Eyepiece properties |

|
|
|
|
Parallex |
Apparant movement of image w.r.t cross hairs to eliminate this focusing of objective and eyepiece are required. |
|
|
|
Types of eyepiece (2 types) and it's characteristics |
1)+ve /Non erecting/Rampson/inverting - Free from spherical abration but not free from chromatic abration. -two plano convex lenses - it will give inverted image ( same as seen on diaphram) 2, Erecting type -4 plano convex lens. -Length is more -Invert the diaphram images
|
|
|
|
Aplatism , Achromatism, Definition Illumination, size field ,Magnification |
1,Aplatism - absence of spherical abration. 2,Achromatism- Absence of chromatic abration 3,Definition-Ability to produce sharp image 4, Illumination- Ability to produce bright image 5,Size field - Circular area which can be seen 6,Magnification - (f obj/ f eye piece) |
|
|
|
Deflection angle |
-Angle made by prolongation of previous line to the following line. -Range 0 to 180 deg - used in pen traverse. |
|
|
|
Sum of deflection angle of a closed traverse |
360 d g |
|
|
|
Method of repetition |

|
|
|
|
Reiteration method/method of series |

|
|
|
|
Balancing of traverse methods |
1,Bowditch rule 2, Transit rule 3, 3rd rule |
|
|
|
Bowditch /compass rule |

|
|
|
|
Transit rule |

|
|
|
|
3rd rule |

|
|
|
|
Balancing in and linning in |
Balancing in- Indirect ranging using a theodolite Linning in- Direct ranging using a theodolite. |
|
|
|
Calculation of area of a traverse using coordinates |

|
|
|
|
Meridian distance |
Distance of centre of a line to meridian |
|
|
|
Double meridial distance |
Sum of distance of end point of a line from meridian |
|
|
|
Trapezoid rule for area calculation |
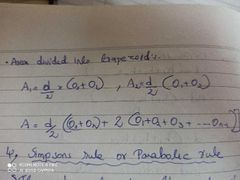
|
|
|
|
Simpson rule area calculation |

|
|
|
|
Prismoidal correction |
Difference in area calculated using Simpsons rule and Trapezoidal rule It will be always negative |
|
|
|
Fixed hair method |
Stadia intercept is kept constant |
|
|
|
Multiplying and additive constants |
Multiplying const, k= ( f/i ) Additive constant,C= f+d f- focus of objective lens i- Stadia intercept d-distance from optical centre to centre of instrument |
|
|
|
Analytic lens ? |
To make k as 100 and C as zero external focussing telescope one external convex lens is used which is called analytic lens. |
|
|
|
LOC is inclined and staff held verical |
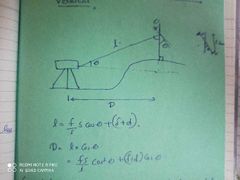
|
|
|
|
LOC is inclined and staff held normal to LOC |
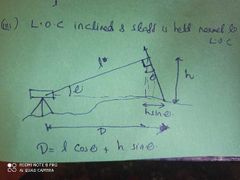
|
|
|
|
Tangential method or moving hair method |
Measuring distance using theodolite |
|
|
|
Tangential method - Both angles are on elevation |

|
|
|
|
Tangential method - Both angles are angles of depression |
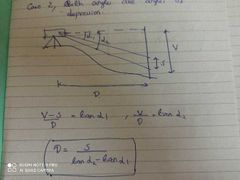
|
|
|
|
Tangential method - one angle is angle of elevation a d other angle of depression. |

|
|
|
|
Evolute |
Locus of centres of transition curve |
|
|
|
Transition curves used in railways |
Cubic parabola. Clothoid/Spiral |
|
|
|
Transition curve used in highways |
Laminascale |
|
|
|
Alidade is mad of |
Brass |
|
|
|
Methods of plane table |
1,Radiation 2,Intersection or Graphical triangulation method 3,Traversing 4, Resection |
|
|
|
Traversing methods |
1, chain angle method 2,Free or loose needle method-compass survey 3,Fast needle method- using theodolite 4, Direct measurment of angle |
|
|
|
Prismatic compass |

|
|
|
|
Surveyors compass |

|
|
|
|
Level surface |
Surface parallel to earth curvature eg: Still water surface |
|
|
|
Vertical line or plumb line |
Line perpendicular to level surface |
|
|
|
Reversible and non reversible levelling instruments |

|
|
|
|
Capston headed nuts |
To adjust level of bubble tube in dumpy level |
|
|
|
Least count in levellimg staff |
5mm |
|
|
|
GTS |
Great trignetruc survey -For establish BM with high precision |
|
|
|
Curvature correction value , nature of error |

Cc (in m)= 0.0785 D^2, D in km |
|
|
|
Refraction correction |
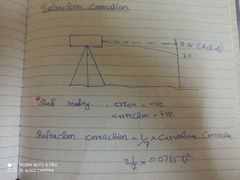
Cr= 0.0112 D^2 |
|
|
|
Combined correction |
Ccomb = 0.0673 D^2 |
|
|
|
Allowable error for levelling |

|
|
|
|
Classification of levelling |

5,profile levelling/Longitudinal levelling 6,Cross sectioning 7,Barometric levelling - Level difference base on atmospheric pressure 8,Hypsometry -Level diff based on boiling point of water 9,Trignometric levelling |
|
|
|
Generally used contour intervals |

|
|
|
|
Boning in ? |
Method to set bed slope for canal and drains |
|
|
|
Box sextant |

|
|
|
|
Cyclon ghat tracer |
To establish contour gradient |
|
|
|
Edigraph |
Instrument used to enlarge a plan |
|
|
|
Centre of celestial sphere |
Observor |
|
|
|
Zenith and Nadir |
Zenith - A point on celestial sphere directly above observer Nadir -A point on a celestial sphere below observer |
|
|
|
Celestial horizon /True horizon / Rational horizon /Geometric horizon |
A great circle passing perpendicular to Zenith and nadir |
|
|
|
Celestial pole , Terestrial pole |

|
|
|
|
Sensible horizon |
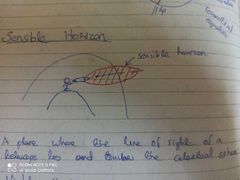
|
|
|
|
Visible horizon |
A plane where line of sight and object lies |
|
|
|
Vertical circle |

|
|
|
|
Observers meridian |
A circle passing through Zenith ,Nadir and celestial poles |
|
|
|
Prime vertical |
A circle perpendicular to observors meridian |
|
|
|
Latitude ( advanced survey) |
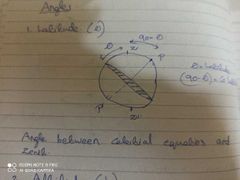
|
|
|
|
Altitude |
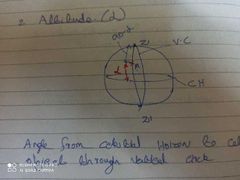
Zenith distance - Co altitude |
|
|
|
Declination(celestial) |

|
|
|
|
Hour circle |
Same as declination circle but without a celestial body |
|
|
|
Azimuth in advanced aurvey |
Angle between observors meridian and vertical circle |
|
|
|
Hour angle |
Angle between observors meridian and declination circle |
|
|
|
Points based on sun position |

|
|
|
|
Size off plane table |
600* 750mm |
|
|
|
Three point problem methods |
1,Mechanical or Tracing sheet method 2,Graphical Method ( Besseles method) 3,Trial and error method-Most accurate method (using leemans method) |
|
|
|
Spherical excesa |
Difference between sum of internal angle of astronomical triangle and normal triangle |
|

