![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What vessel provides blood supply to the appendix? |
Appendiceal artery - branch of ileocolic artery |
|
|
Name the mesentery of the appendix? |
Mesoappendix (contains the appendiceal artery) |
|
|
How can the appendix be located if the cecum has been identified? |
Follow the taenia coli down to the appendix; the taenia converge on the appendix |
|
|
What is appendicitis? |
Inflammation of the appendix caused by obstruction of the appendieal lumen, producing a closed loop with resultant inflammation that can lead to necrosis and perforation |
|
|
What are the causes of appendicitis? |
- Lymphoid hyperplasia - Fecalith (aka appendicolith) - Rare: parasite, foreign body, tumor (eg, carcinoid) |
|
|
What ist he lifetime incidence of acute appendicitis in the US? |
~7% |
|
|
What is the most common cause of emergent abdominal surgery in the US? |
Acute appendicitis |
|
|
How does appendicitis classically present? |
Classic chronologic order: 1. Periumbilical pain (intermittent and crampy) 2. Nausea / vomiting 3. Anorexia 4. Pain migrates to RLQ (contant and intense pain), usually in <24 hours |
|
|
Why does periumbilical pain occur? |
Referred pain |
|
|
Why does RLQ pain occur with appendicitis? |
Peritoneal irritation |
|
|
What are the signs / symptoms of appendicitis? |
Signs of peritoneal irritation may be present: - Guarding - Muscle spasm - Rebound tenderness - Obturator and psoas signs - Low-grade fever (high-grade if perforation occurs) - RLQ hyperesthesia |
|
|
What is the Obturator sign? |
Pain upon internal rotation of the leg with the hip and knee flexed; seen in pts with pelvic appendicitis |
|
|
What is the Psoas sign? |
Pain elicited by extending the hip with the knee in full extension or by flexing the hip against resistance; seen classically with retrocecal appendicitis |
|
|
What is the Rovsing's sign? |
Palpation or rebound pressure of the LLQ results in pain in the RLQ; seen in appendicitis |
|
|
What is the Valentino's sign? |
RLQ pain / peritonitis from succus draining down to the RLQ from a perforated gastric or duodenal ulcer |
|
|
What is McBurney's point? |
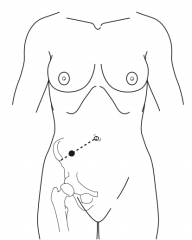
Point 1/3 from the ASIS to the umbilicus (often the point of maximal tenderness) |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis in general for patients suspected of having appendicitis? |
- Meckel's diverticulum - Crohn's disease - Perforated ulcer - Pancreatitis - Mesenteric lymphadenitis - Constipation - Gastroenteritis - Intussusception - Volvulus - Tumors - UTI (eg, cystitis) - Pyelonephritis - Torsed epiploicae - Cholecystitis - Cecal tumor - Diverticulitis (floppy sigmoid) |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for FEMALE patients suspected of having appendicitis? |
- Ovarian cyst - Ovarian torsion - Tuboovarian abscess - Mittelschmerz - Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) - Ectopic pregnancy - Ruptured pregnancy |
|
|
What lab tests should be performed on patients suspected of having appendicitis? |
- CBC: increased WBC (<10,000/mm3 in >90% of cases), most often with a "left shift" - U/A: to evaluate for pyelonephritis or renal calculus |
|
|
Can you have an abnormal urinalysis with appendicitis? |
Yes - mild hematuria and pyuria are common in appendicitis with pelvic inflammation resulting in inflammation of the ureter |
|
|
Does a positive urinalysis rule out appendicitis? |
No - ureteral inflammation resulting from the periappendiceal inflammation can cause abnormal urinalysis |
|
|
What additional tests can be performed if the diagnosis of appendicitis is not clear? |
- Spiral CT - U/S (may see a large, non-compressible appendix or fecalith) - AXR |
|
|
In acute appendicitis, what classically precedes vomiting? |
Pain (in gastroenteritis, the pain classically follows vomiting) |
|
|
What radiographic studies are performed in patients suspected of having appendicitis? |
- CXR: to rule out RML or RLL pneumonia, free air - AXR: abdominal films are usually non-specific, but calcified fecalith present in about 5% of cases |
|
|
What are the radiographic signs of appendicitis on AXR? |
- Fecalith - Sentinel loops - Scoliosis away from the right because of pain - Mass effect (abscess) - Loss of psoas shower - Loss of preperitoneal fat stripe - Ver rarely a small amount of free air is perforated |
|
|
With acute appendicitis, in what percentage of cases will a radiopaque fecalith be on AXR? |
Only ~5% |
|
|
What are the CT findings with acute appendicitis? |
Periappendiceal fat stranding, appendiceal diameter >6 mm, periappendiceal flat, fecalith |
|
|
What are the preoperative medications / preparation for a patient with appendicitis? |
1. Rehydration with IV fluids (LR) 2. Pre-operative antibiotics with anaerobic coverage (appendix is considered part of the colon) |
|
|
What is a lap appy? When is it indicated? |
Laparoscopic appendectomy; used in most cases in women (can see adnexa) or if patient has a need to quickly return to physical activity, or is obese |
|
|
What is the treatment for non-perforated acute appendicitis? |
Non-perforated: - Prompt appendectomy (prevents perforation) - 24 hours of antibiotics - Discharge home usually on POD #1 |
|
|
What is the treatment for perforated acute appendicitis? |
Perforated: - IV fluid resuscitation and prompt appendectomy - All pus is drained with post-op antibiotics continued for 3-7 days - Wound is left open in most cases of perforation after closing the fascia (heals by secondary intention or delayed primary closure |
|
|
How is an appendiceal abscess that is diagnosed preoperatively treated? |
Usually by percutaneous drainage of the abscess, antibiotic administration, and elective appendectomy ~6 weeks later (aka interval appendectomy) |
|
|
If a normal appendix is found upon exploration, should you take out the normal appendix? |
Yes |
|
|
How long after removal of a non-ruptured appendix should antibiotics continue post-operatively? |
For 24 hours |
|
|
Which antibiotic is used for non-perforated appendicitis? |
Anaerobic coverage: - Cefoxitin - Cefotetan - Unasyn - Cipro - Flagyl |
|
|
Which antibiotic is used for a perforated appendix? |
Broad-spectrum antibiotics: - Ampicillin / Ciprofloxacin / Clindamycin OR - Zosyn |
|
|
How long do you give antibiotics for perforated appendicitis? |
Until the patient has a normal WBC count and is afebrile, ambulating, and eating a regular diet (usually 3-7 days) |
|
|
What is the risk of perforation with acute appendicitis? |
~25% by 24 hours from onset of symptoms ~50% by 36 hours ~75% by 48 hours |
|
|
What is the most common general surgical abdominal emergency in pregnancy? |
Appendicitis (about 1/1750; appendix may be in the RUQ because of enlarged uterus) |
|
|
What are the possible complications of appendicitis? |
- Pelvic abscess - Liver abscess - Free perforation - Portal pylethrombophlebitis (very rare) |
|
|
What percentage of the population has a retrocecal, retroperitoneal appendix? |
~15% |
|
|
What percentage of negative appendectomies is acceptable? |
Up to 20%; taking out some normal appendixes is better than missing a case of acute appendicitis that eventually ruptures |
|
|
Who is at risk of dying from acute appendicitis? |
Very old and very young patients |
|
|
What bacteria are associated with "mesenteric adenitis" that can closely mimic acute appendicitis? |
Yersinia enterolytica |
|
|
What is an "incidental appendectomy"? |
Removal of normal appendix during abdominal operation for different procedure |
|
|
What are complications of an appendectomy? |
- SBO - Enterocutaneous fistula - Wound infection - Infertility with perforation in women - Increased incidence of right inguinal hernia - Stump abscess |
|
|
What is the most common post-op complication of appendectomy? |
Wound infection |
|
|
What is the difference between a McBurney's incision and a Rocky-Davis incision? |
- McBurney's is angled down (follows ext oblique fibers) - Rocky-Davis is straight across (transverse) |
|
|
What are the layers of the abdominal wall during a McBurney incision? |
1. Skin 2. Subcutaneous fat 3. Scarpa's fascia 4. External oblique 5. Internal oblique 6. Transversus abdominis muscle 7. Transversalis fascia 8. Pre-peritoneal fat 9. Peritoneum |
|
|
What are the steps in a lap appy? |
1. Identify the appendix 2. Staple the mesoappendix (or coagulate) 3. Staple and transect the appendix at the base (or use Endoloop and cut between) 4. Remove appendix from the abdomen 5. Irrigate and aspirate until clear |
|
|
Do you routinely get peritoneal cultures for acute appendicitis (non-perforated)? |
No |
|
|
How can you find the appendix after identifying the cecum? |
Follow the taenia down to where they converge on the appendix |
|
|
Which way should your finger sweep trying to find the appendix? |
Lateral to medial along the lateral peritoneum - this way you will not tear the mesoappendix that lies medially |
|
|
How do you get to a retrocecal and retroperitoneal appendix? |
Divide the lateral peritoneal attachments of the cecum |
|
|
Why use electrocautery on the exposed mucosa on the appendiceal stump? |
To kill the mucosal cells so they do not form a mucocele |
|
|
If you find Crohn's disease in the terminal ileum, will you remove the appendix? |
Yes, if the cecal / appendiceal base is not involved |
|
|
If the appendix is normal, what do you inspect intraoperatively? |
- Terminal ileum: Meckel's diverticulum, Crohn's disease, intussusception - Gynecologic: cysts, torsion, etc - Groin: hernia, rectus sheath hematoma, adenopathy (adenitis) |
|
|
Who first described the classic history and treatment for acute appendicitis? |
Reginal Fitz |
|
|
Who performed the first appendectomy? |
Harry Hancock in 1848 (McBurney popularized the procedure in 1880s) |
|
|
Who performed the first lap appy? |
Dr. Semm (GYN) in 1983 |
|
|
What is the most common appendiceal tumor? |
Carcinoid tumor |
|
|
What is the treatment of appendiceal carcinoid less than 1.5 cm? |
Appendectomy (if not through the bowel wall) |
|
|
What is the treatment of appendiceal carcinoid greater than 1.5 cm? |
Right hemicolectomy |
|
|
What percentage of appendiceal carcinoids are malignant? |
<5% |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of appendiceal tumor? |
- Carcinoid - Adenocarcinoma - Malignant mucoid adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What type of appendiceal tumor can cause the dreaded pseudomyxoma peritonei if the appendix ruptures? |
Malignant mucoid adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What is a "mittelschmerz"? |
Pelvic pain caused by ovulation |
|
|
Should one remove the normal appendix with Crohn's disease found intra-operatively? |
Yes, unless the base of the appendix is involved with Crohn's disease, the normal appendix should be removed to avoid diagnostic confusion with appendicitis in the future |

