![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae |
- Multicellular - Autotrophic - Eukaryotic - Cell Wall made from cellulose - Reproduce sexually + asexually |
|
|
Plants are made up of 2 parts: |
- Root System (below ground) - Shoot System (above ground) |
|

External Structure of a Flowering Plant |

|
|
|
Types of Roots |

- Main (tap) root with side (lateral) roots e.g. Dandelions - Fibrous roots (grow from stem) e.g. Grass - Adventitious roots (don't develop from radicle) [main root] e.g. Onion |
|

|
Tap root |
|

|
Fibrous root |
|
|
What protects tip of root? |
Root cap + root hairs |
|
|
Function of Root Hairs |
Absorb water + minerals. More root hairs = greater surface area for absorption. |
|
|
Function of Roots |
- Anchor plant into ground - Absorb water + minerals from soil - Storage of food (in certain plants) e.g. Carrot + turnip - Vegetation reproduction e.g. Strawberries |
|
|
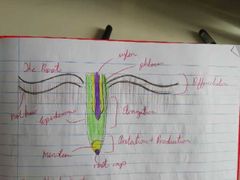
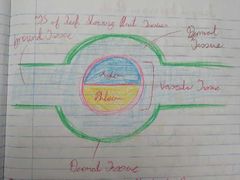
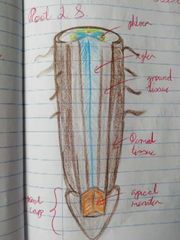
Zones of Roots |
1. Zone of Protection 2. Zone of Production 3. Zone of Elongation 4. Zone of Differentiation |
|
|
Zone of Protection |
Root cap protects growing tip which contains root cells |
|
|
Zone of Production (Meristem) |
- Contains meristematic tissue which is capable of mitosis - Apical meristem are found in the root + shoot tip - Some meristematic tissue is located around the edge of the plant |
|
|
Zone of Elongation |
Plant growth regulators stimulate growth in plants |
|
|
Zone of Differentiation |
Elongated cells develop into other types of plant tissue 1. Ground 2. Dermal 3. Vascular |
|

|
|
|
|
Shoot System |
Consists of the stem, leaves, flowers + buds |
|
|
Functions of the Stem |
- Transport of water + minerals from the roots to leaves + flowers - Transports food made in the leaves around the plant - Supports the leaves, flowers + fruits so they are in position for photosynthesis - Food storage e.g. Stem tuber of potato - Vegetative reproduction e.g. Stem tubers of potato - Stems can be herbaceous (don't have wood or lignin) or woody (do have wood or lignin) |
|
|
What attaches leaf to stem? |
At node by petiole |
|
|
Sessile |
If leaves are directly attached to stem |
|
|
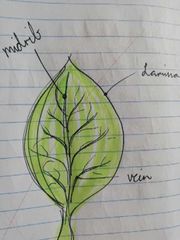
Function of veins of leaf blade (lamina) |
Give leaf support + transports nutrients |
|
|
Types of Veins on a Leaf |
Parallel: veins run in parallel lines (usually monocots) e.g. Grass Net/Reticulate: veins branch out from midrib (usually dicots) e.g. Rose |
|

|
Parallel Veins |
|
|
Net/ Reticulate Veins |
|
|
Functions of Leaves |
- To make food through photosynthesis - Gaseous exchange - Oxygen + Carbon Dioxide pass in + out through stomata - Transpiration - water evaporates through the leaf which allows roots to take in water - Storage of food in some plants e.g. Lettuce |
|
|
Function of Flowers |
Sexual reproduction |
|
|
Function of Buds |
- Food storage e.g. Onion - Growth of the stem to form new leaves + flowers - Forms branches by lateral buds - Vegetative reproduction e.g. Onion |
|
|
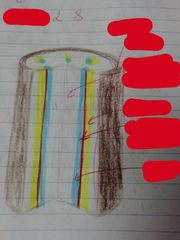
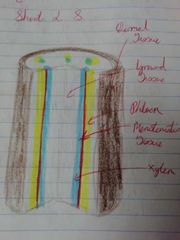
Plant Tissues |
1. Meristematic 2. Dermal 3. Ground 4. Vascular |
|
|
Meristematic Tissue |
- Meristem contains meristematic cells which reproduce by mitosis - Meristematic cells develop into other types of plant cells e.g. Flower, root - Only area in plant responsible for growth |
|
|
Meristem |
Region of active cell division (mitosis) in plant |
|
|
Dermal Tissue |
- Forms epidermis or outer covering of stem, root + leaves - Protects the plant from water loss (cuticle) + entry of pathogens - Epidermal cells of the leaves + stem secrete a waxy cuticle which prevents water loss |
|
|
Ground Tissue |
- Fill space between dermal + vascular tissue to form bulk of plant - Contains chloroplasts which allows photosynthesis to make food - Stores food + waste - Gives strength + support to plant |
|
|
Vascular Tissue |
Specialised for transport 1. Xylem 2. Phloem |
|
|
Function of Xylem |
- Transport water + dissolved salts - Gives support to the leaves |
|
|
Location of Xylem |
Roots, stem, leaves, flowers (vascular bundle) |
|
|
Function of Phloem |
- Transport food (sugar) made by photosynthesis |
|
|
Location of Phloem |
Roots, stem, leaves, flowers (vascular bundle) |
|
|
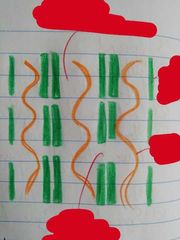
Types of Xylem Cells |
Xylem Tracheids + Xylem Vessels |
|

|
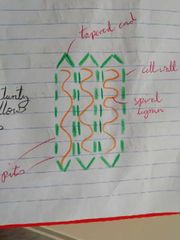
Xylem Tracheids - Long tapered cell - Inside hollow at maturity - Overlap of cell walls allows passage at pits e.g. Coniferous trees |
|
|
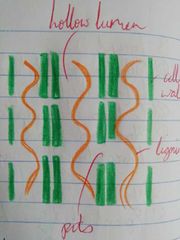
Xylem Vessels - Tubular vessels that join end to end - Pits in the walls alow water + salts to travel between vessels - More efficient e.g. |
|
|
Lignin |
- Hard chemical which gives plant wall strength - Arranged in a spiral in xylem - Forms wood in trees |
|
|
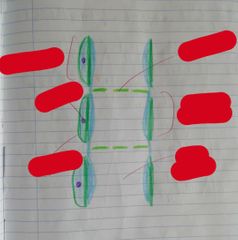
Types of Cells in Phloem |
Sieve tube elements + companion cells |
|
|
Sieve Tube Element |
- Long stacked cells form sieve tube - Walls have pores (sieve) which allows movement of materials - Walls contain cellulose + a cytoplasm - Lack a nucleus - End wall is a cell plate |
|
|
Companion Cells |
- Cell that lies along each sieve tube element - Contains cytoplasm + a nucleus - Controls itself + attached sieve tube cell - Considered living part of phloem |
|
|
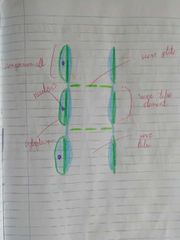
Phloem diagram |
|
|
What is formed as meristematic cells undergo mitosis? |
Dermal, ground or vascular tissue |
|
|
Groups flowering plants are divided into |
Monocots + dicots |
|
|
Cotyledon |
Embryonic seed leaf used for storage |
|
|
Monocotyledon |
A plant with one seed leaf |
|
|
Dicotyledon |
A plant with 2 seed leaves |
|
|
Characteristics of Monocots |
- One seed leaf for storing food - Parallel venation in the leaves - Scattered vascular bundles in stem - Flowers have 3 petals - Mostly herbaceous e.g. Grass, cereals, tulip, daffodils |
|
|
Characteristics of Dicots |
- 2 seed leaves for storing food - Net/Reticulate venation - Arranged vascular bundles - Flowers have 4/5 petals - Herbaceous or woody e.g. Beans, peas, sunflower, trees |
|
|
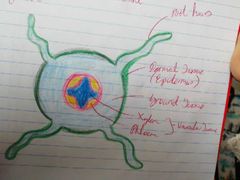
TS of Root |
|

|
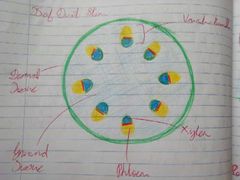
|
|
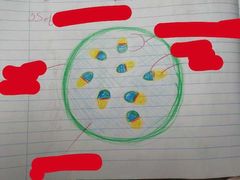
|
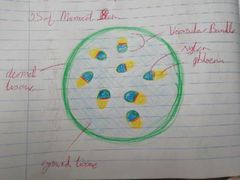
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

