![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anion gap and Osmolar gap metabolic acidosis with rectangular, envelope-shaped crystals in urine. |
Ethylene glycol poisoning (anti-freeze)
(methanol and ethanol intox will cause anion, osmolar gap acidosis, too, but not the calcium oxalate crystals) |
|
|
Painful 3rd trimester bleeding with normal ultrasound
|
Placental abruption
|
|
|
Precocious puberty, Pigmentation (cafe au lait spots), and Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (multiple bone defects)
|
McCune-Albright syndrome
|
|
|
Occipital headaches, ataxia, facial weakness, gaze palsy (deviation of the eyes to left or right side)
|
Cerebellar hemorrhage
|
|
|
Older patient with back pain, hypercalcemia, anemia, and renal failure
|
Multiple Myeloma
|
|
|
Sudden onset of eye pain, photophobia, and a mid-dilated pupil:
|
Acute Glaucoma
|
|
|
a |
a
|
|
|
Exudative pleural effusion without evidence of infection
|
Malignancy
(breast cancer and lung cancer are the most common causes of malignant pleural effusions) |
|
|
Young patient with a recent viral illness who presents with heart failure, chest pain, or arrhythmias:
|
Myocarditis
(which can progress to dilated cardiomyopathy, but most patient will have a t least a partial recovery of myocardial function) |
|
|
Sickle cell patient with bacteremia/septic shock
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae
(encapsulated organism, and SC kids are predisposed to splenic auto-infarction!!!) |
|
|
Sickle cell patient with diffuse musculoskeletal pain
|
Microvascular occlusions
(vasoocclusive crisis) |
|
|
New mother will pain over lateral side of wrist
|
De Quervain tenosynovitis
|
|
|
HIV-patient with focal neurologic signs and multiple non-enhancing lesions in brain with no mass effect
|
Progrssive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
(caused by JC virus) (on MRI it would show as multiple demyelinating non-enhancing lesions, with no mass effect) |
|
|
Rapidly progressive skin lesions that develop into nontender nodules with central necrosis in an immunocompromised patients
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa bactermia--caused Ecthyma gangrenosum
|
|
|
Thready pulses over radial arteries that disappear with deep inspiration
|
Pulsus paradoxus
|
|
|
Chest pain, signs of decreased cardiac output, and pulsus paradoxus following a viral infection
|
Cardiac tamponade resulting from acute pericarditis
|
|
|
Dizziness, hearing loss, and tinnitus
|
Meniere's disease
|
|
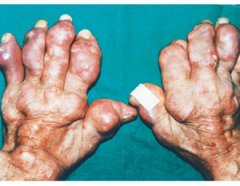
|
Chronic Tophaceous Gout )gouty arthritis)
Tophi can ulcerate a drain a chalky white material |
|
|
Triad of findings in Disseminated Gonococcal infection (Gonococcemia)
|
1-Polyarthralgias
2-Tenosynovitis 3-Vesiculopustular skin lesions (painless) (2 to 10) |
|
|
Lower abdominal pain that radiates to the thighs and back and begins a few hours prior to menses
|
Primary dysmenorrhea, caused by INCREASED PROSTAGLANDINS
(release of PGs during the breakdown of the endometrium ie before the actual bleeding starts) |
|
|
Cyanotic infant with left axis deviation
|
Tricuspid atresia
(90% assoc'd with VSDs, 30% w/ TGA) |
|
|
Pt from or ancestry of northern European ancestry with megaloblastic anemia, shiny tongue (atrophic glossitis), vitiligo, and thyroid disease, possibly with thrombocytopenia and/or leukopenia
|
Pernicious anemia = most common cause of B12 deficiency in whites of northern European ancestry, and they frequently have tiger autoimmune diseases like thyroid disease and vitiligo
(usu neuro sx there, too, but not always) |
|
|
Macrocytic anemia in a sickle cell patient
|
Folate deficiency
(b/c chronic hemolysis and bone marrow tries to make more RBC to compensate and uses up folate...so sickle cell patients should be on daily folate supplements) *Note: if on hydroxyurea, this can also cause macrocytosis |
|
|
Sudden onset of photopsia (flashes of light) and floaters, with description of "a curtain coming down over my eyes"
|
Retinal detachment
|
|
|
Teenage girl with primary amenorrhea, fully-deveoped breasts, absent pubic and axillary hair, short/blind-ended vagina, no uterus on ultrasound |
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome--karyotype would show 46 XY and labs would show elevated testosterone for a girl (but normal amount for a boy)
-Caused by defective androgen receptors resulting in androgen resistance in peripheral tissues -Mullerian Inhibiting Factor is still present as it was produced by the testes (which are likely in the abdomen or inguinal canal) and that is why no uterus cuz MIF inhibits the formation of uterus, fallopian tibes, and upper part of vagina. -No pubic or axillary hair because b/c ts production is dependent on testosterone, and its receptor are resistant/insensitive to testosterone. |
|
|
Female delivered baby 12 hours ago and now has temp of 100.4 and WBC 11,000, with shaking chills during and 10 min following delivery; uterus is found to be firm and nontender
|
Normal postpartum presentation
In the immediate postpartum period, a low-grade fever, leukocytosis, and vag discharge are normal findings. It would be worrisome if the lochia is foul-smelling or if the uterus is tender--then you'd be worried about endometritis. |
|
|
Smoker with whitish, localized plaques in oral mucosa with a granular texture and not removed by scraping
|
Leukoplakia--> has a risk of transformation into squamous cell carcinoma
-A biopsy should be done to exclude cancer, but at this point the most likely cause of this lesion is leukoplakia |
|
|
Fall on an outstretched hand with tenderness in anatomic snuffbox
(if + displacement, then open reduction and internal fixation is required) |
Scaphoid fracture--risk of nonunion so wrist should be immobilized for 6-10 weeks
|
|
|
HIV patient--pain with swallowing, has white plaques over pharynx, CD4 of 50, on TMP-SMX
|
Candida Esophagitis--tx with fluconazole
|
|
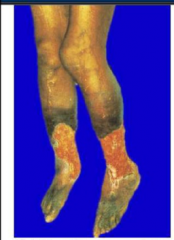
|
Venous stasis ulcers, form chronic venous valvular insufficiency
typically present on lower leg, above the ankle |
|
|
Middle age patient with weight loss & jaundice
|
Pancreatic cancer
--other signs and sx: palpable, nontender gallbladder (Courvoisier sign), -migratory thrombophlebitis (Trousseau syndrome), -epigastric pain, |
|
|
Fever, and an erythematous area on body which is swollen, painful, hyperesthetic to touch, and has a sharp demarcation separating the red area from te normal skin...with local lymphadenopathy |
ERYSIPELAS = a superficial thrombophlebitis caused by Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
Joint pain, splenomegaly, and neutropenia
|
Felty's syndrome
(anemia and leukopenia often present as well) (possible late consequence in rheumatoid arthritis) |
|
|
Painful oral and genital ulcers and erythema nodosum |
Behcet syndrome
also commonly uveitis/eye lesions, arthritis, or other skin lesions |
|
|
Alcoholic smoker with combination of elevated JVP, hepatomegaly, ascites, and lower extremity edema, without evidence of pulmonary congestion
|
Isolated Right Heart Failure secondary to Cor Pulmonale from COPD
Other findings that may be present: right-sided S3, right ventricular heave, ascites alcoholic part is there to throw off in thinking about liver issues from alcohol, but here there is hepatomegaly because of congestion whereas in alcohol cirrhosis there would be a small and firm fibrosed liver |
|
|
RUQ or epigastric pain in ICU patient with severe trauma/sepsis/etc
|
Acalculous cholecystitis
emergent tx is percutanoeous cholecystostomy (perc drain) followed by cholecystectomy once patient stabilizes |
|
|
6 year old with rash, joint pain, abdominal pain, and hematuria
|
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
typically purpuric rash, but apparently the question can say a maculopapular rash on lower extremities and btutocks usually |
|
|
Pt undergoes surgical repair of an AAA, then post-op he develops LLQ pain with bloody diarrhea. CT shows thickening of the rectosigmoid junction and colonoscopy shows ulecrations in that area but above and below it are normal |
Ischemic colitis
Bowel ischemia may complicate up to 7% of procedures on the aortoiliac vessels and most commonly affects the distal left colon Common causes: loss of collateral circa, manip of vessels with the surg instruments, prolonged aortic clamping, and impaired blood flow thru the inferior mesenteric artery. |
|
|
After blunt trauma to the chest, if an x-ray shows a deviated mediastinum with a mass in the left lower chest, one should suspect:
|
A diaphragmatic perforation with herniation of abdominal viscera
Dx with barium swallow or CT scan with oral contrast |
|
|
Elevated direct bilirubin and liver biopsy shows dark granular pigment in the hepatocytes
|
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
(DJ likes rainbows!) |
|
|
Pt complains of blurred vision, cough, and shortness of breath, along with mild fevers and malaise. CXR shows bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates & hilar adenopathy. |
SARCOIDOSIS
◆ Most common complaints: cough, dyspnea, fever, wt loss. ◆ Lungs most freq involved organ system--CXR will show B/L hilar LAD &/or B/L reticulonodular infiltrates/opacities (ground glass appearance) ◆ Eyes--Anterior uveitis (silt-lamp shows leukocytes in ant chamber) ◆ Skin--Erythema nodosum ◆Joints--Arthritis |
|
|
PainFUL genital ulcer(s)
|
"Holy Crap that hurts!"
Herpes & Chancroid The others are painLESS--Granuloma inguinale, Lymphogranuloma venerum, & Syphilis ("Gross Lesions without Stress"...ie no pain) |
|
|
PainLESS genital ulcer(s)
|
"Gross Lesions without Stress" (i.e. no stress=no pain)
Granuloma inguinale Lymphogranuloma venerum Syphilis Syphilis vs Granuloma inguinale = no LAD in granuloma inguinale and it has beefy red base |
|
|
Erythematous papules with a central scale and a "sandpaper-like" texture on palpation |
Actinic keratoses
|
|
|
2-hour old male LGA newborn, uncomplicated pregnancy, fine at birth but now 2 hours later--worsening cyanosis and respiratory distress, not relieved by oxygen. Has a normal S1 and a single & loud S2, with no murmur. |
Transposition of the Great Vessels
(the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus begin to close after birth, so decreased mixing of oxygenated with non-oxygenated blood Presents in first few hours of life Give PGE1 IV immediately and then surgical correction |
|
|
ICU patient with low T3, normal T4, and normal TSH
|
Sick euthyroid syndrome
any pt with acute severe illness can develop these abnormal labs which we call sick euthyroid syndrome (decreased peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 b/c under crazy stress, cytokines, etc) |
|
|
Newborn male with oliguria and a midline mass in lower abdomen
|
Posterior Urethral valves
= most common cause of congenital urethral obstruction the midline lower abdom mass likely represents a distended bladder next step = VCUG to confirm dx |
|
|
Ipsilateral headache and ipsilateral Horner's syndrome |
Carotid artery dissection (sympathetic nerves travel along the carotid, can still have sweating if partial horners as sweat fibers only on ext carotid) |

