![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does light travel and how fast? |
In straight lines at 300 000 000 m/s (in a vacuum) as long as what it is travelling through (the medium) remains constant |
|
|
Definition of transparent |
.See through them clearly .Light, when it travels through in parallel lines, will leave in parallel lines .Light passes through without being faded or dimmed .e.g. glass, windows |
|
|
Definition of translucent |
.Let some light through .Light, when it travels through, will be scattered on the other side .Cannot see through it clearly .e.g. tracing paper, tissue paper |
|
|
Definition of opaque |
.No light can travel through it .The light will be reflected scattered or absorbed .Cannot see through it .e.g. humans, a tree |
|
|
If light hits an object, what can it do? |
.Absorbed .Reflected or scattered at the boundary at the angle it came in but opposite .Let through but will change direction (transmitted) |
|
|
How does light reflect off a shiny surface and a matt surface? |
.Shiny: smooth so that the light reflects in straight lines .Matt: bumpy so the light is scattered |
|
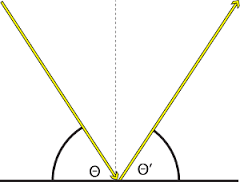
Label the diagram |
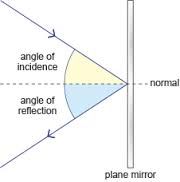
|
|
|
What are the 3 laws of reflection? |
.Angle of incidence=angle of reflection .Things reflected in a mirror will be reversed (words will be backwards) .Things reflected in the mirror appear the same distance away from the mirror line as the real object |
|
|
Definition of concave lens Definition of convex lens |
.Caving in, diverging the light, separating the rays .Bending out, converging the rays of light together so that they all meet |
|
|
Definition of refraction |
.When light changes speed crossing from one boundary to another. If it slows down it bends towards the normal and when it speeds up it bends away from the normal. |
|
|
What happens when you look at a fish that is beneath the surface of the water? |
.The actual fish will be deeper than we see it as the light is refracted and the light appears to travel in a straight line towards our eye when it actually changes direction at the surface. |
|
|
What is white light? |
All the colours of the spectrum in the same place at the same time, all these colours mixed together according to our brain makes a white light. |
|
|
How do we know about the colour spectrum in white light? |
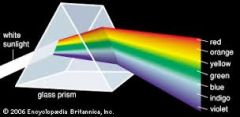
We can use a triangular glass block as each colour travels at different speeds, which makes them spread out. |
|
|
What are the seven colours in the colour spectrum in order? |
.Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet (Richard Of York Gave Battle In Vain) |
|
|
What are the three primary light colours and what colours do they make? |
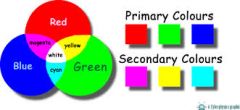
|
|
|
Which primary colour/colours will a magenta book absorb and which will it reflect and why? |
It will absorb green and reflect blue and red as they make magenta and magenta is the colour that we see. |
|
|
How is sound made? |
By the vibrations in the air caused by the sound molecules moving through the air molecules making them vibrate, this is a sound wave. |
|
|
How does the frequency of sound waves affect the sound? |
The more frequent the sound waves the higher the pitch will be |
|
|
Number of vibrations each second = |
Frequency |
|
|
What is sound measured in? |
Hertz |
|
|
What is the amplitude of a sound wave? |
It is the loudness and the greater the difference in pressure between the rarefactions and the compression and the greater the distance that the air molecules vibrate. |
|
|
What can and what can't sound travel through and what is the quality of the sound through different things? |
Sound cannot travel through a vacuum as there are no molecules to vibrate, space for example. Sound is faster the denser the molecules it has to travel through such as a solid is easier for it to travel through while it is slower through air and is medium in liquid. |
|
|
How fast does sound travel in air, liquid and solids? |
.Air: 330-340 m/s .Liquid:1500 m/s .Solid:6000 m/s |
|
|
How do you find the speed of sound? |
Speed=distance/time |
|
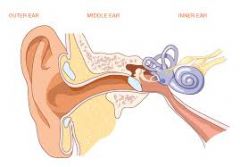
Label the diagram |
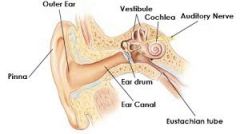
|
|
|
What is the human hearing range? |
20Hz to 20,000Hz |
|
|
With a string instrument, what makes it higher pitched? |
When you pluck the string the tighter it is the higher it will be. |

